Remote Patient Monitoring Software Development: An Expert's Guide

One of the most transformative opportunities IoT has brought to healthcare is the rise of remote patient monitoring software. This solution extends far beyond simple tools that track vital signs remotely. They help automate routine tasks, reduce costs, and elevate the overall quality of care through more intelligent analytics and faster insights across an organization.
That alone makes a strong case for adopting remote patient monitoring software systems. In this guide, we share our experience, highlight the real benefits of RPM, and explain how our healthcare software development services, with a strong emphasis on user-centered design, help providers build reliable, secure, and compliant solutions.
from 25 countries outsourced software development to Relevant
We provide companies with senior tech talent and product development expertise to build world-class software.
What is remote patient monitoring? The basics
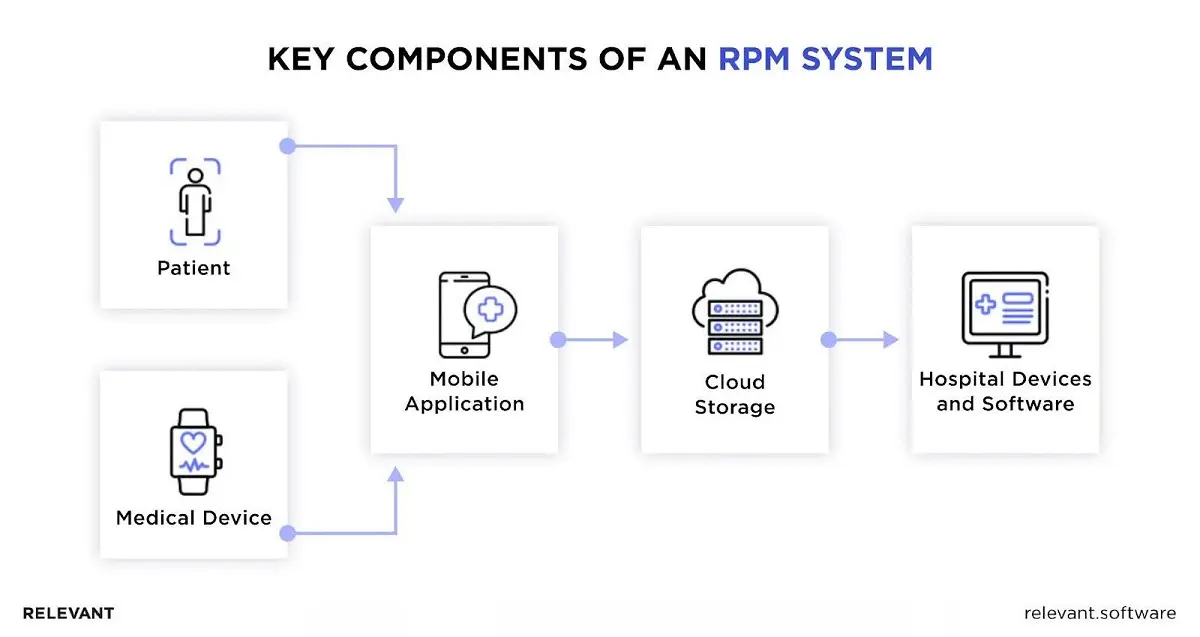
Remote patient monitoring (RPM) involves extending care beyond traditional clinical settings. Think of it as a bridge: patients sit at home with familiar devices, and their doctors are still connected, seeing what’s happening in near real time. An IoT network system ties it all together, connecting blood pressure cuffs, glucose sensors, and wearables to the hospital’s secure software.
A healthcare remote patient monitoring system is rarely a single gadget. It typically combines medical devices, such as pulse oximeters, heart rate sensors, or digital thermometers, with consumer wearables that track steps, sleep, and activity. Each by itself offers a fragment. Together, they create a timeline that provides doctors with more than a single snapshot from an office visit.
The data doesn’t sit idle. Through Bluetooth, Wi-Fi, or cellular networks, it flows into clinical dashboards. Providers can set safe ranges, watch for gradual trends, and receive alerts when something drifts. In real life, that means catching an abnormal rhythm on Monday morning instead of waiting three weeks for the next appointment.
For patients living with chronic conditions or for older adults who struggle to attend repeated visits, the effect is noticeable. Care moves closer to daily life. Doctors intervene sooner. And the system builds confidence on both sides: patients know they’re still being watched over, and clinicians gain sharper tools to act before problems escalate. And outcomes back this up: UMass Memorial Health study found a 50% reduction in 30-day readmissions for heart failure with their RPM program.
Devices and technologies used in RPM
RPM technology covers a wide range of tools, from portable medical devices to online portals that give patients direct access to their health records and care plans. In many cases, this involves patient portal software development, which creates secure platforms for data entry, communication with providers, and real-time tracking of health information. Here are some noteworthy remote patient monitoring examples:
| Device/Technology | Application | Potential advantages |
| Wearable sensors | Measure heart rate, blood pressure, and body temperature | Enable continuous, real-time data collection. Promote early detection and intervention |
| Implantable medical devices | Deliver medication; assess or support organ function; capture rhythm or pressure data. | Work quietly 24/7 inside the body. Patients spend less time in the hospital, while physicians get steady, high-quality data for dose and device adjustments. |
| Mobile Health (mHealth) apps | Collect readings; store logs; send medication and visit reminders; support self-care | Keep patients involved day to day. Clear trends on screen improve adherence and make clinician–patient decisions faster and more precise |
| Telemedicine software | Run secure video or chat visits; share images and notes; coordinate care | Cuts travel and wait time. Brings specialists to rural patients and allows quicker follow-ups after a change in therapy |
| Wireless communication technologies (e.g., Bluetooth, Wi-Fi) | Transmit health data from wearable remote patient monitoring devices to care providers | Seconds, not days. Current values are transmitted to the care team without manual steps, allowing immediate action if anything appears to be off. |
| Medical alert systems | Trigger help in an emergency; detect falls; route alerts to responders or caregivers | Fast escalation when seconds matter. Help arrives within minutes; patients feel safer at home, and families gain assurance. |
By 2025, remote patient monitoring won’t be a niche market. More than 71 million Americans — about one in four — will rely on it in some form.
The global market echoes the story. In 2024, RPM was already worth $27.7 billion. Forecasts point to almost $57 billion by 2030, a steady 12.7% annual growth rate. The growth is not limited to software. The device segment, valued at $14.3 billion in 2025, is on track to pass $40 billion by 2032. That kind of scale only happens when both providers and patients trust the technology.
Competition in the remote patient monitoring market is intense, but that pressure drives innovation. New FDA-approved devices, smarter data platforms, and more intuitive tools appear every year. For patients with chronic diseases, this is not a market trend. It’s fewer trips to the hospital, earlier interventions, and a daily routine that feels more secure.
| Device | Description |
| Blood pressure monitors | Measure blood pressure levels and provide essential data for managing cardiovascular conditions. |
| Glucose level monitors | Provide continuous blood sugar monitoring, which is essential for effectively managing diabetes. |
| Maternity care monitors | Monitor the health of both expectant mothers and fetuses, improving prenatal and postnatal care. |
| Heart rate monitors | Record heart rhythm and rate, valuable for fitness tracking and managing cardiac conditions. |
| Asthma management devices | Often integrated with telehealth software, these tools assess lung function and support asthma treatment through reminders and monitoring. |
| EEG devices | Capture and record brain activity, primarily for neurological assessments. |
| Mood tracking devices | Help patients track their emotional states over time, supporting mental health evaluations and therapy. |
| Spirometers | Measure lung function and capacity, useful in respiratory disease management. |
| Smart scales | Provide insights into weight and body composition to support nutrition and lifestyle programs. |
| Pedometers | Count steps and promote physical activity, often part of broader fitness or chronic disease programs. |
| GI tract monitors | FDA-approved devices that assess gastrointestinal function and assist in diagnosing digestive disorders. |
| ECG devices | Monitor the heart’s electrical activity to support the diagnosis and treatment of heart conditions. |
| Pulse oximeters | Measure blood oxygen saturation, a widely used tool in respiratory illness management and sleep disorder treatment. |
| Temperature sensors | Track body temperature and provide early warnings for fever or infection. |
The wide variety of connected medical devices explains why remote patient monitoring software development has become one of the most active areas in healthcare technology today.
The benefits of healthcare remote patient monitoring
Digital tools such as RPM deliver clear advantages for clinicians and patients. They improve care quality, maintain a real-time view of health status, and ground decisions in data from home and the clinic. Teams act sooner, coordinate better, and personalize treatment without extra burden on staff or families. Below are the core benefits to highlight next.
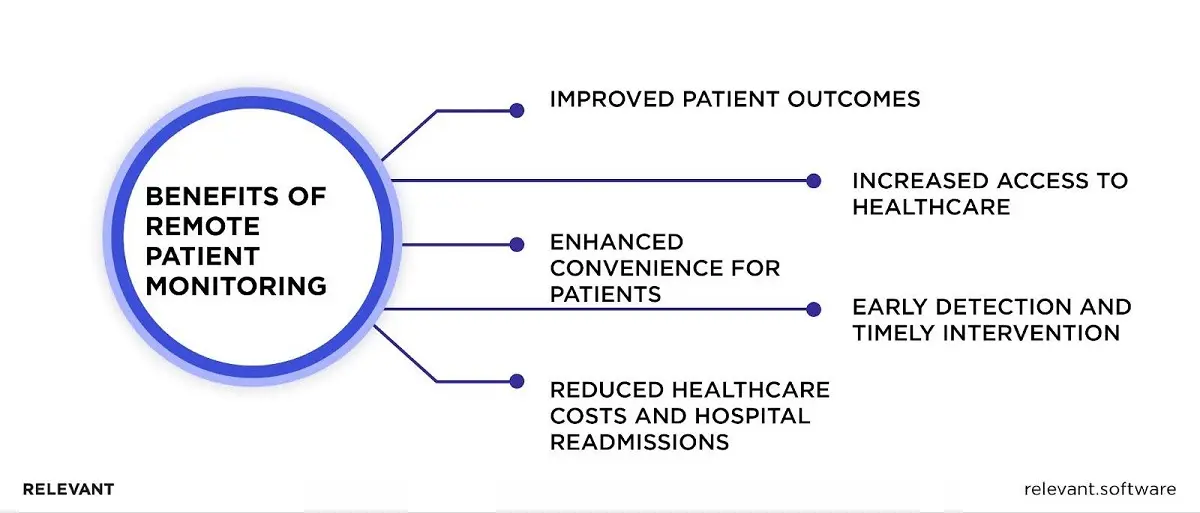
Improved patient outcomes
A strong remote patient monitoring system changes how patient care is delivered. Instead of relying on occasional visits, providers receive live patient vitals, from heart rate to oxygen saturation. That information flows through secure RPM software and reaches clinical staff in time to guide early adjustments. For patients in chronic care, this visibility allows providers to adjust treatment immediately, avoiding unnecessary complications.
The link between early intervention and stronger clinical outcomes is clear. Hospitals see financial benefits from remote patient monitoring, including reduced readmissions, while patients experience steadier health outcomes supported by proactive decision-making and timely care delivery.
Increased access to healthcare
Remote monitoring extends remote care into areas where traditional services are challenging to reach. A mobile application, paired with blood glucose meters or wearable sensors, sends RPM data directly to providers. Integration with the electronic health record ensures patient health information supports accurate care management without long travel.
Patients in chronic care management benefit most, as they receive virtual care and patient education that keep them engaged. For providers, smoother clinical workflows improve efficiency, while patients gain control and confidence.
Reduced healthcare costs and hospital readmissions
The financial benefits of remote patient monitoring are clear. Continuous health tracking lets providers catch problems early and reduce the need for costly hospitalizations. Consistent glucose readings, routine weight checks, and shared patient vitals help prevent complications that would otherwise require acute care.
Through CPT codes, reimbursement for RPM services has become more predictable, making adoption practical. Hospitals highlight remote therapeutic monitoring as a tool that limits costs without reducing quality. For patients, the outcome is less disruption.
Enhanced convenience for patients
Convenience is one of the most apparent benefits of remote patient monitoring solutions. Instead of sitting in waiting rooms, patients use a mobile application that automatically shares RPM data with clinical staff. These systems also provide patient education, send medication reminders, and support stronger patient adherence. Integration with existing EHR platforms means data appears directly in clinical workflows, reducing strain on providers.
Behavioral health programs benefit as well, with virtual care making regular sessions easier to maintain. The outcome is improved patient health, streamlined care delivery, and increased satisfaction.
Early detection and timely intervention
Remote patient monitoring services accelerate medical response. Patient vitals flow continuously into the electronic health record, giving clinicians a complete picture rather than isolated reports. If a blood glucose meter shows unusual patterns or body weight rises too quickly, clinical staff can act immediately. For chronic disease management, this often prevents deterioration before it begins.
Population health initiatives also benefit, as remote care reduces unnecessary hospital visits and lowers overall costs. With strong data security in place, leading remote patient platforms maintain trust. Ultimately, this constant visibility protects patient health and strengthens clinical outcomes.
The reasons for building a patient monitoring solution today
Long before the pandemic, remote patient monitoring (RPM) was being tested in hospitals and clinics. COVID-19 turned it from an experiment into a necessity. Overnight, it became the safest way to keep doctors connected to patients who still needed constant care. That moment changed expectations and showed that monitoring someone from home could be as reliable as a clinic visit.
How does remote patient monitoring work?
The structure of a remote patient monitoring (RPM) system is complex, yet, at its core, it’s composed of building blocks designed to serve three primary user groups: patients, healthcare institutions, and administrators.
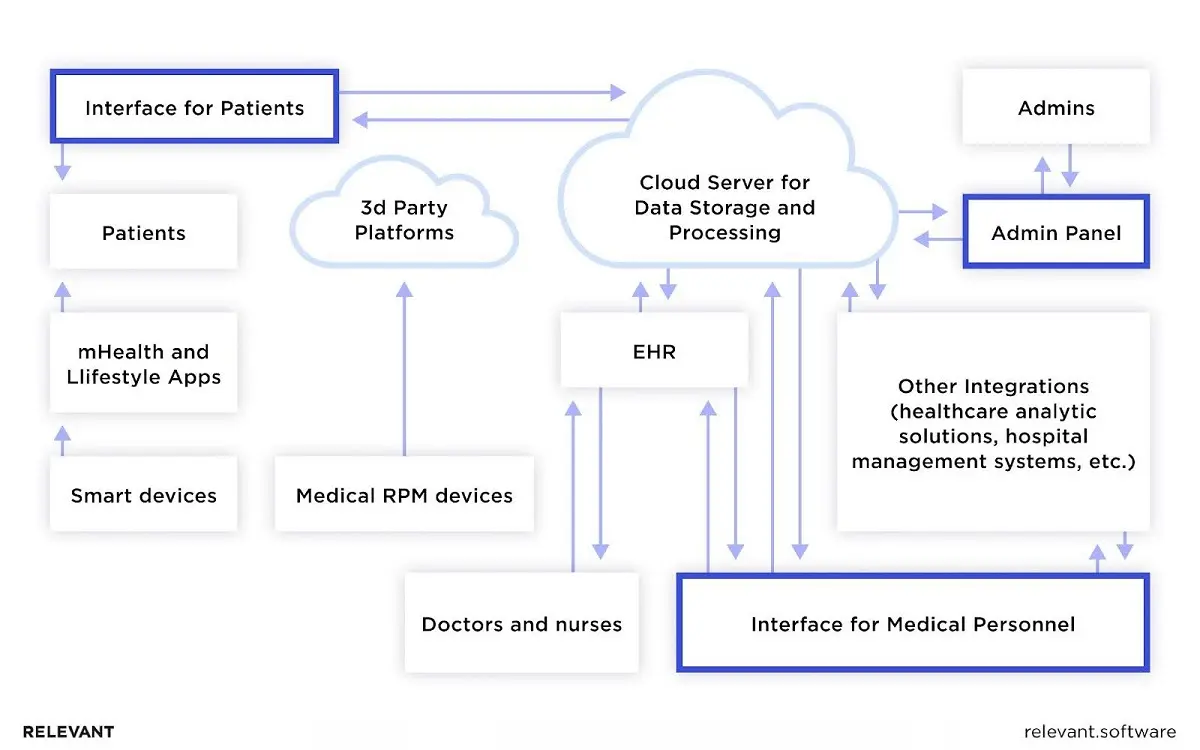
Step 1. Health data collection: Working with a remote patient monitoring system requires activating the patient’s health gadget. These devices, ranging from implanted sensors to wearable tech like Fitbits and Apple Watches, collect vast amounts of information, including heart rate, oxygen levels, and blood pressure. These devices log and transmit health data to healthcare professionals through Bluetooth connection with a mobile app.
Step 2. Health data transmission: The information must reach the relevant healthcare provider after the data is recorded and sent to a dedicated mobile app. Cutting-edge advancements have honed the accuracy and efficiency of data collection and transmission. Modern monitors scrutinize real-time data for anomalies before transmitting health data to the healthcare institution, using high-tech methods such as the Internet, text, or phone. The institution should have a HIPAA-compliant web application to receive and “view” the patient’s health data.
Step 3. Data evaluation and alert notifications: Data from the patient’s RPM device is stored either in the cloud or in the healthcare institution’s data repository. Comparisons are made against physician-set threshold values, and any breaches trigger a system notification that alerts the physician to abnormal conditions via SMS, in-app messages, or email. Many RPM systems use data visualization tools and machine learning/BI technologies to provide real-time readings, allowing healthcare providers to spot trends, predict risks, and make informed treatment decisions.
Step 4. Actionable steps: When a patient requires urgent medical attention, the relevant authorities are promptly notified, and immediate assistance is provided. When data suggests a treatment change is needed, physicians update the plan and advise patients on how to avoid future health issues. In both RPM and remote therapeutic monitoring, this rapid response loop improves safety and gives patients confidence that their care team remains engaged.
How to develop patient monitoring software: Step by step
To understand what IoT development looks like, we present the steps from the client and developer perspectives.
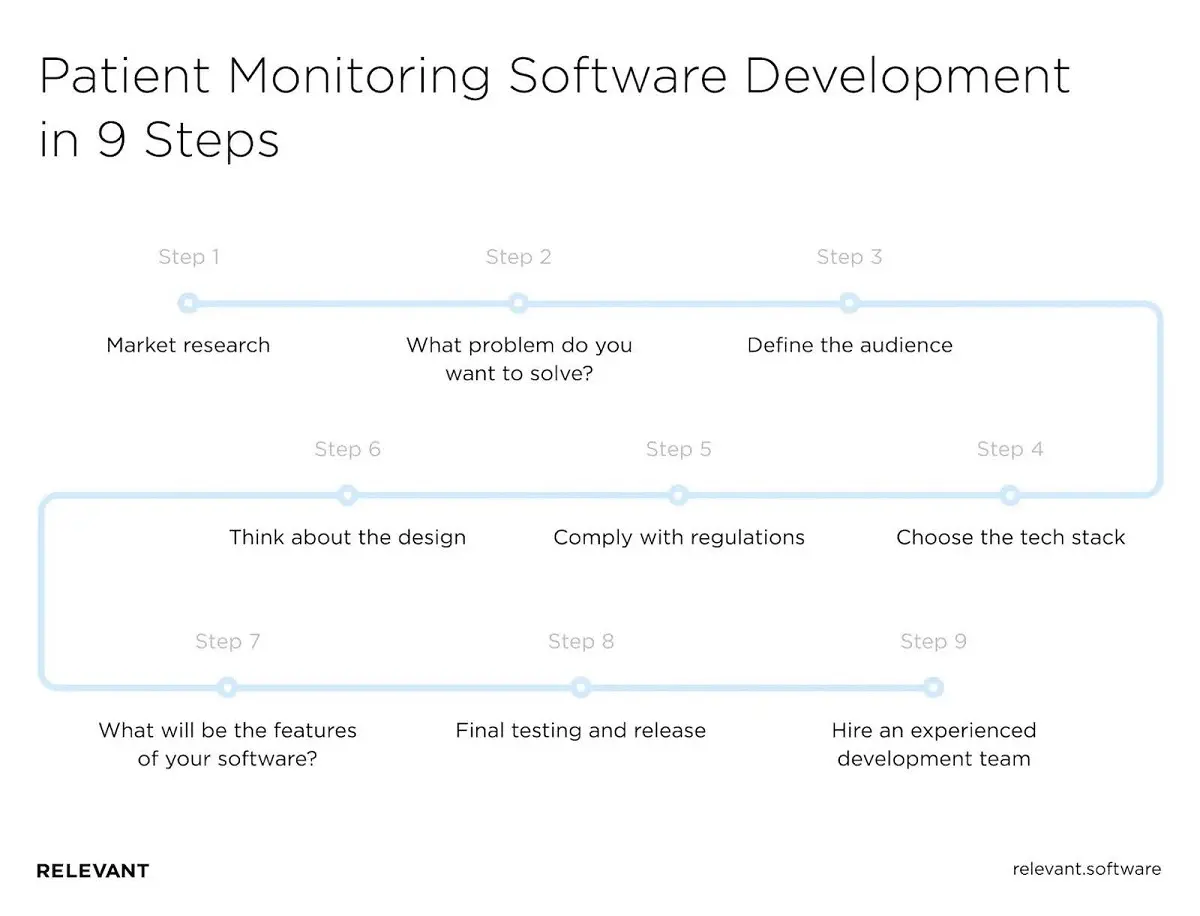
Step 1. Market research
First, you must familiarize yourself with the latest market trends, including new features, existing applications, and, most importantly, the pros and cons of each solution. To do this, conduct a competitor analysis and study user reviews. Understanding common mistakes can help you see what your app needs to succeed and attract users.
Based on the insights you gain from market research, you will build a key RPM value, outline a set of features that deliver that value, and set measurable goals for developers.
Step 2. What problem do you want to solve?
The second step is to decide what purpose your application will serve. Every successful patient monitoring solution starts with solving a specific problem to achieve a clear goal. As you ponder various ideas for a healthcare app, ask yourself these targeted questions:
- How will my app improve users’ lives?
- What problem should it solve?
- Will it fill the existing gap in today’s services?
- How will it stand out from the competition?
There are plenty of mobile RPMs in the market, and you need to understand that your application will compete with many others. That is why you and your development team will need to plan a clear and unique value proposition with key, or even unusual, values.
Step 3. Define the audience
The third step is to define the stakeholders’ goals (investors, doctors, and medical personnel). Since elderly patients, children, and people with chronic illnesses have different needs, developers can group them by health condition or by the length of care required.
Step 4. Choose the tech stack
Now, focus on studying the requirements and defining the product specifications. You must clearly understand the technology stack, budget, and time estimates. A trusted IT provider and the team can help you meet this challenge.
Step 5. Comply with privacy and compliance regulations
The safety and security of medical data, as protected health information, remain essential. Data collected by wearable and connected medical devices is subject to the same strict rules. To protect patients and avoid legal risks, providers must ensure that every solution complies with industry standards. Partnering with experts in HIPAA compliance services helps guarantee that your remote patient monitoring software meets all regulatory requirements from day one.
Your IoT software solutions must also comply with all safety guidelines for remote patient monitoring, such as SOC 2 Type 2 and ISO 27001. When developing medical monitoring apps, it’s important to follow best practices such as:
- Two-factor authentication for personal identification.
- Encryption of health data both at rest and in motion.
- Secure network connections (for example, HTTPS).
Step 6. Design a healthcare remote patient monitoring system
At this stage, the development team creates the UI / UX design:
- sitemap and interface elements for desktop, mobile, and web applications;
- types of monitoring devices;
- database (local server or cloud solution);
- methods of synchronization between the RPM application and your database.
Step 7. Choose the features of your remote patient monitoring software
If you want a custom health monitoring system, it makes sense to start with a minimum viable product (MVP) with basic functionality to test further. You can gradually add features to the final product (perhaps even after release). Below, we list the primary functions that the best patient monitoring systems should have.
- Platform customization. The application must sync with existing and future systems, whether it comes out-of-the-box with leading built-in integration frameworks or provides APIs for custom integrations.
- Device integration. The platform should collect and log data from wearable or other devices your patients can use to track progress.
- Workflow management. The platform should automate and optimize your team’s processes. Ideally, the data should be addressed to the patient’s profile so that doctors can guide them every step of the way to treatment.
- Communication capabilities. A sound system supports the channels you need, such as text messaging, video conferencing, or chat applications.
- Tracking. You may need to track activities on your platform and the corresponding RPM billing codes.
- Scalability. The program should grow with the organization, allowing the healthcare team to serve more patients with the same resources.
- User-friendliness. The software should be intuitive for users and require minimal training.
Advanced features such as integrated billing, geolocation, or voice commands make the application even more attractive.
Step 8. Finally test and release
System development is only part of the work required; you must thoroughly test devices to ensure the accuracy of the data they receive and transmit. In addition, after you and your team release your application, it will need to be regularly updated and all processes tested to ensure it runs smoothly.
Step 9. Hire an experienced development team
This step appears last, but in reality, it should come first. The success of a patient monitoring solution depends heavily on the people who design and build it. You need specialists who understand both healthcare regulations and IoMT technologies, and who can balance clinical requirements with user-friendly design. Finding such a team at a reasonable cost is not always easy.
Many healthcare providers now look to Ukraine for this expertise. The country has a strong talent pool, competitive rates, and a proven record in healthcare software. For organizations seeking value without sacrificing quality, outsourcing IoMT development to Ukraine often provides the best balance between cost efficiency and technical depth.
Wrapping up
The growth of remote patient monitoring makes sense. Lower costs, fewer hospital visits, and constant access to patient data create clear benefits for both patients and providers. Care takes place at home without loss of quality, while doctors gain timely insights without adding pressure on staff. The real challenge lies in building remote patient monitoring software that remains accurate, compliant, and secure. That is where specialized expertise matters.
Relevant Software experts have supported healthcare providers worldwide and delivered successful remote patient monitoring solutions. Our team combines regulatory knowledge with technical precision to create platforms that improve outcomes and meet strict standards.
- Healthcare IT сonsulting: We review healthcare IT systems, define the right RPM strategy, estimate costs, and ensure compliance throughout the process.
- Software development: Our engineers design software that integrates with monitoring devices, hospital platforms, and third-party applications while maintaining strong security.
- Software migration: We transfer data across RPM devices, IoT systems, and healthcare platforms with safeguards that prevent loss or corruption.
- Modernization and support: We upgrade existing remote patient monitoring platforms, extend functionality, and provide round-the-clock system monitoring and optimization.
With our expertise, healthcare organizations gain more than a development service. Relevant Software clients gain a partner who understands both healthcare and technology and turns remote patient monitoring benefits into measurable results.
FAQs
What is remote patient monitoring software?
At its core, remote patient monitoring software is a system that combines connected devices, secure apps, and healthcare platforms. A blood pressure cuff at home, a smartwatch, or a glucose sensor can all feed data into it. Doctors then receive that information in real time, often through platforms built by remote patient monitoring companies in the USA. Many of these solutions rely on FDA-approved devices to ensure accuracy. In some cases, the setup also supports remote therapeutic monitoring, allowing a physical therapist or physician to see not only health data but also how closely a patient follows a treatment or exercise plan.What are examples of remote patient monitoring applications?
Healthcare remote patient monitoring comes in many forms. Some systems are as simple as software for remote patient monitoring that connects to a heart rate device. Others involve full programs that track multiple conditions. Common examples include medical alert systems, electrocardiography tools, medication reminders, glucose monitors, and sleep trackers. For doctors, the benefits of remote patient monitoring include earlier detection of problems, reduced readmissions, and better visibility into patient behavior between visits.How long does it take to develop a patient monitoring app?
Timelines vary widely. A lean MVP can be ready in three months, while a complex solution may take close to a year. The deciding factors are project scope, the chosen tech stack, and team size. Some remote patient monitoring companies now work in phases: launch a small core version first, then expand. That way, remote patient monitoring for healthcare providers becomes possible sooner, without waiting for every advanced feature to be finished.How much does it cost to create a remote patient monitoring app?
Budgets range from $50,000 for a simple platform to several hundred thousand dollars for a system with multiple integrations and strict compliance needs. Costs depend on features, scale, and whether you need support for FDA-approved devices or additional modules. In practice, healthcare providers often compare remote patient monitoring companies in the USA with offshore vendors to balance cost and expertise. The right partner delivers secure, reliable technology while keeping development aligned with business goals.

Hand-selected developers to fit your needs at scale! Let’s build a first-class custom product together.

