Top 9 Mobile IoT Apps and What You Need to Know About It
Updated: June 4, 2025
Venture into 2025, where life is intertwined with smart technology – your coffee maker starts as you wake, your car syncs with your schedule, and your home adjusts to your preferences as you enter. This new reality will be particularly evident for you if you look at the IoT Apps list we created in our article below.
Why is IoT mobile app development so crucial, you ask? Because most of the smart devices we rely on daily are commanded and monitored through these apps. Simply put – IoT applications let us control all our connected things.

We provide companies with senior tech talent and product development expertise to build world-class software. Let's talk about how we can help you.
Contact usBased on data from Statista, the number of IoT (Internet of Things) devices is expected to increase significantly, from $15.14 billion in 2023 to $29.42 billion by 2030. Consequently, the demand for IoT apps will rise progressively.
But let’s not jump the gun. Instead, we’ll methodically cover each key aspect from the ground up. Our main goal here is to deepen your understanding of the Internet of Things (IoT) and the crucial role of mobile applications within it. Besides, we’ll take a closer look at several trending IoT apps that could positively affect our future.
Table of Contents
What Is IoT Exactly?
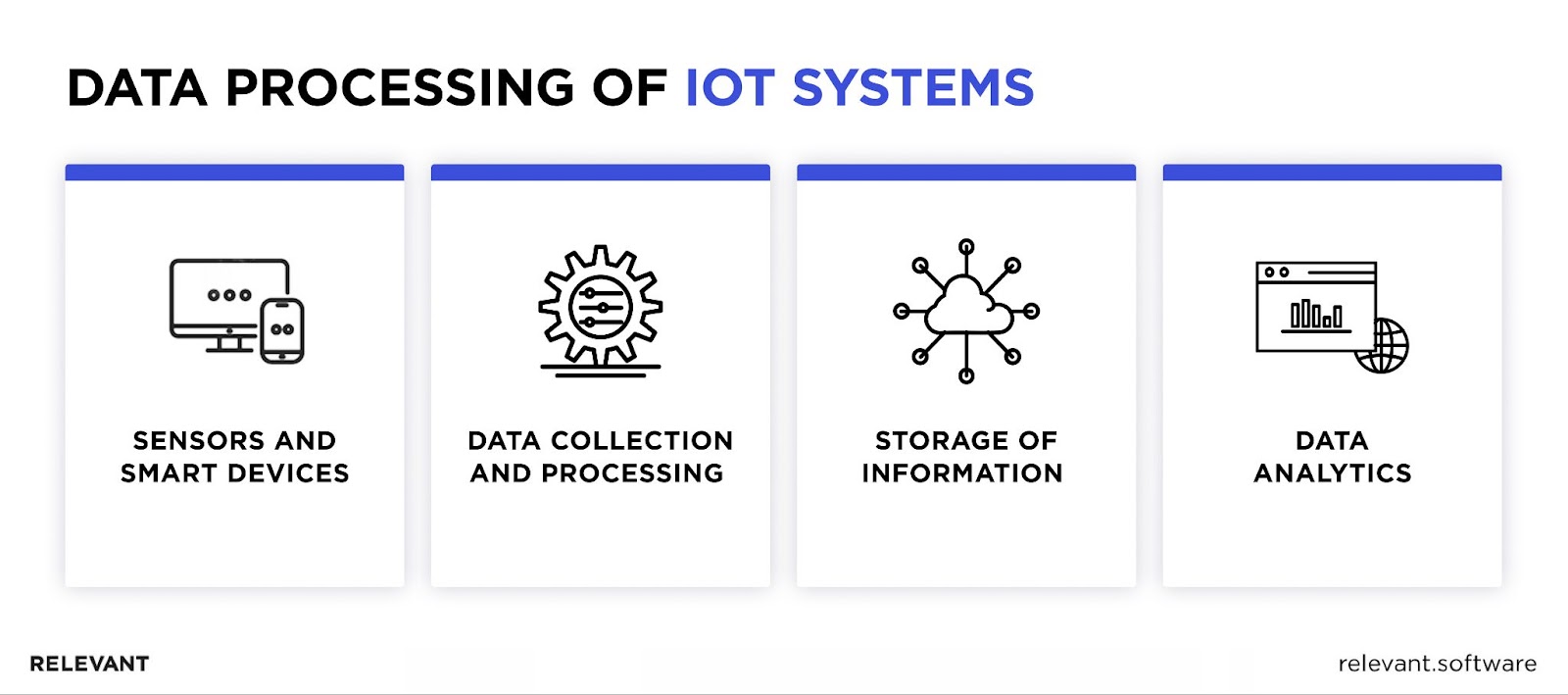
The Internet of Things (IoT) relates to a network of cross-connected, wireless devices with direct access to the Internet that continuously gather information from their surroundings. Equipped with embedded sensors, processors, and communication hardware, they can process and respond to the data they collect or exchange.
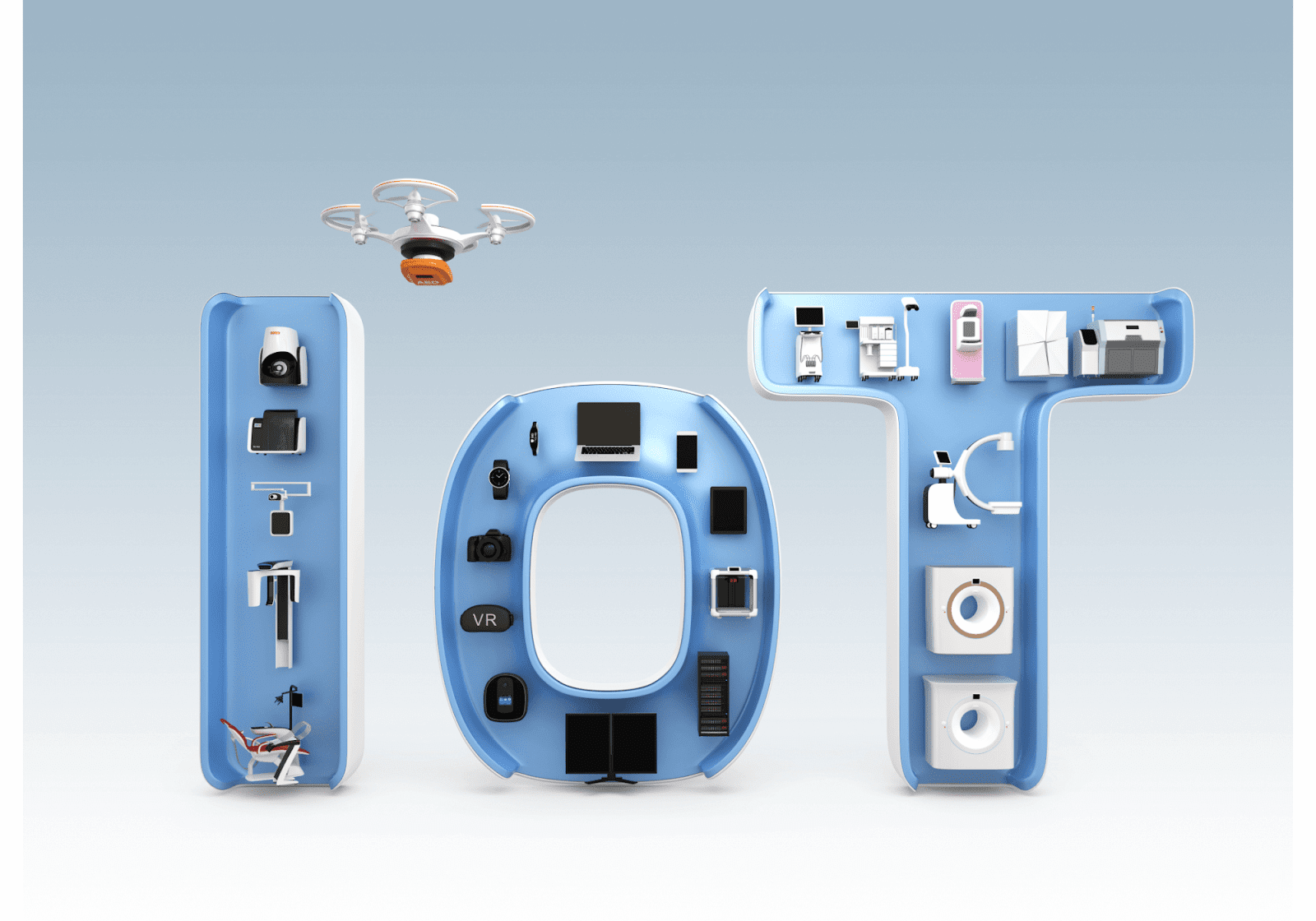
To enable smart things to communicate effectively, special software is being developed. An IoT mobile app acts as one of these solutions, integrating data and providing a user-friendly platform to control and monitor smart devices.
The concept of IoT is not new. In 1989, John Romkey and Simon Hackett connected a toaster to the Internet. Initially, the toaster could only turn the power on and off, thereby controlling the toast’s darkness by varying the cooking time. In 1991, the setup was enhanced: a small robot, also controlled via the Internet, was added to automate the process of placing a slice of bread into the toaster.
Fast forward to today, and the range of IoT devices we have imagined and created is astonishingly vast, stretching far beyond that early toaster.
Why Is Mobile IoT the Hottest Trend?
With global spending on IoT reaching $805.7 billion in 2023, marking a 10.6% increase from 2022, it has become a present-day reality. Businesses and manufacturers are not merely exploring but are also heavily investing in the mobile IoT ecosystem, with projections suggesting it will surpass $1 trillion by 2026. The lion’s share of the IoT market is dominated by software, including mobile apps, and this year, considerable growth is anticipated in the mobile IoT app market.
Why is this so? Because billions of people worldwide use smartphones, this number is increasing every day. With the app development process becoming more streamlined and mobile app integration with IoT increasing, it’s no surprise that smartphones have emerged as the primary means of interacting with smart devices. You can effortlessly access and control IoT systems using just a single app on your phone.
The IoT mobile trend changes our lives for the better. The concept of interconnected devices accessible from anywhere is too appealing to ignore.
How Are IoT Devices and Mobile Apps Related?
A mobile app is a bridge between an IoT device and a mobile phone, acting as the primary interface through which we can manage our smart things. Whether you want to adjust the lighting in your home or monitor the temperature of a manufacturing unit, mobile IoT apps provide the control panel, making the management of IoT technologies intuitive and effortless.
IoT apps do more than just supplement the use of IoT; they enhance it, making it work more efficiently and responsively. Imagine an intelligent irrigation system that uses weather forecasts and soil moisture data to automatically adjust watering schedules for your garden, all controlled through a mobile app. This strong synchronization turns generic devices into intelligent assistants.
While you can use desktops to control IoT devices, smartphones are simply more convenient tools for this purpose. Why? First, they come with various sensors and can connect through Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, and other means. Secondly, in a world where smartphones are almost extensions of ourselves, always within reach, they naturally become the most suitable gateway for remote access to IoT-enabled devices, wherever you are. Additionally, your phone’s ability to share geolocation information is beneficial. For example, this feature can be used to instruct your smart car to warm up in cold weather based on your location.
Mobile IoT solutions are more like a strategic asset offering insights, agility, and competitive advantage for businesses. They turn day-to-day data into smart decisions, ordinary devices into a network of intelligence, and shape firms to respond quickly and deeply to customers’ wants.
Top 9 IoT Applications
The advancements in IoT app technology and its fusion with emerging technologies like artificial intelligence (AI) allow the creation of innovative solutions that solve real-world challenges we face and enhance everyday experiences. Here are 9 major IoT applications that are already affecting the reality we live in.

1. IoT Applications in Smart City
The Internet of Things app ecosystem can make cities more efficient and better to live, reshaping the way they function and evolve. Urban centers can control traffic, modernize government services, reduce waste, and improve the efficiency of utilized resources through the automation of services, possible due to the IoT technology. It can also contribute to improved economic growth and help become an environmentally sustainable city.

For example, in Barcelona, the implementation of smart streetlights equipped with sensors helped save energy. These lights adjust their brightness based on traffic, saving energy and providing optimal illumination. Similarly, Singapore’s Smart Nation initiative uses a network of sensors and cameras to monitor the cleanliness of the streets and crowd density, to manage city services more proactively.
Smart cities can grow thanks to a scalable IoT app architecture that can adapt to a city’s growing needs and complexities. Due to this architecture, it’s possible to create a cohesive network of various vital systems that can respond to dynamic urban challenges and adapt to the needs of their inhabitants.
Real-life IoT Apps for Smart City:
- Intelligent Transportation Systems (ITS)
- Environmental Monitoring and Resource Management
- Public Safety and Security
- Enhanced Citizen Engagement and Services
- Energy Efficiency and Renewable Energy Integration
2. Mobile IoT Usage in Logistics and Transportation
A lot of IoT apps and devices for logistics exist today that offer unprecedented visibility and automation. They are highly popular, as they allow real-time tracking of shipments and vehicles, predictive maintenance, reducing costs, and choosing optimal routes.
We can see a vivid example of IoT app innovation and design in DHL’s solution. They have implemented sensors and machine learning algorithms to monitor and analyze the location and temperature of their shipments. In such a way, the company ensures the best condition for sensitive goods.

Emerging IoT app development is also focusing on fleet management. Companies like UPS are embedding sensors into vehicles to monitor their condition, driver behavior, and fuel efficiency. The data received from those sensors help take proactive maintenance, foster safer driving practices, and achieve better overall operational efficiency.
Regardless of whether you’re a small courier company or a multinational corporation, innovative IoT app deployment strategies are what you need to enjoy all these innovations and improve your bottom line.
Real-life Internet of Things Applications in Logistics and Transportation:
- Precision Tracking and Real-Time Visibility
- Optimized Fleet Management and Route Planning
- Improved Cold Chain Management and Spoilage Reduction
- Frictionless Border Crossings and Paperless Customs
- Hyperlocal Delivery and On-Demand Services
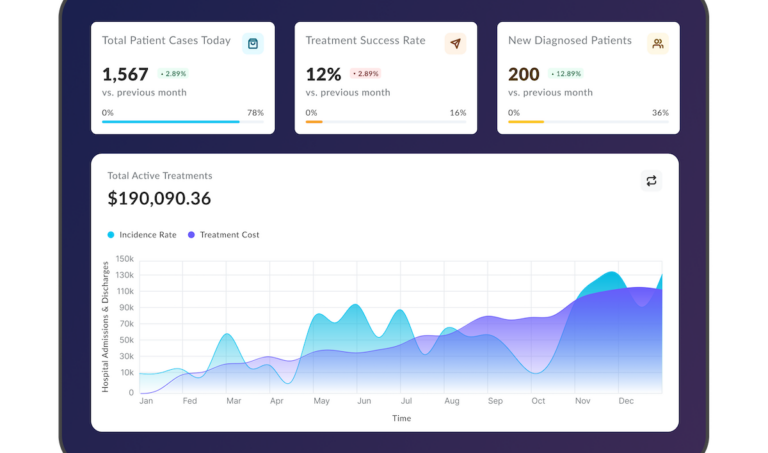
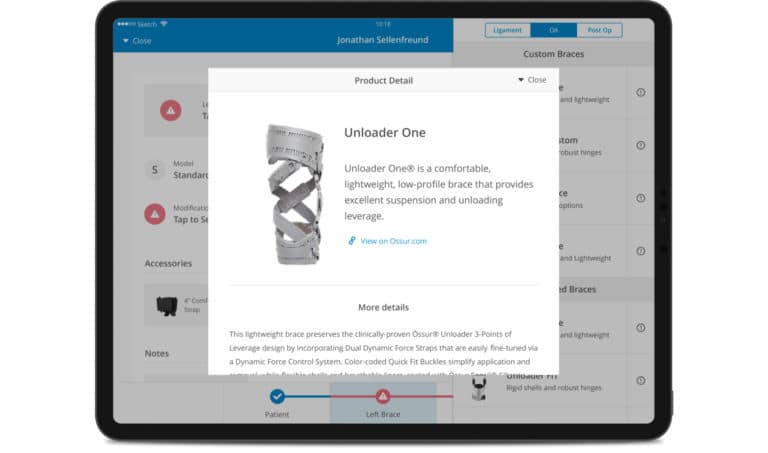
3. IoT Apps Affecting Healthcare
IoT, or IoMT (Internet of Medical Things) in healthcare, greatly impacts the industry today. Mobile app IoT solutions help healthcare providers offer personalized care. They can monitor vital signs, chronic conditions, and patient well-being, allowing for timely interventions in critical patient health changes and easier ongoing management of chronic conditions.

Remote patient monitoring systems are the most popular IoT applications in healthcare. Companies like Medtronic offer devices that continuously monitor heart conditions and automatically transmit data to healthcare professionals, who can immediately react to changes in a patient’s health status and adjust treatment plans accordingly.
Medication management is another promising area that actively adopts smart device applications. For instance, there are pill dispensers that remind patients of the correct dosages and even notify caregivers if a dose is missed. Such solutions enhance adherence to medication regimens and improve overall patient health.
Hospitals can also benefit from utilizing IoT apps to monitor medical equipment, track assets, and even monitor hygiene compliance. With these insights, clinics can repair or replace equipment in time, streamline operations, and reduce costs while contributing to a safer healthcare environment.
Real-life IoT App Examples in Healthcare:
- Remote patient monitoring
- Medication adherence and smart dispensers
- Mental health and emotional wellbeing with wearable devices
- Fall detection and emergency response
- Connected medical devices and Telehealth
4. IoT Applications in Insurance
By leveraging real-time data transmitted by IoT-enabled mobile applications, insurers can personalize policies, manage risks proactively, and enhance user experiences. In fact, these applications help you understand, predict, and respond to individual needs.
Let’s see how IoT apps can reshape the automotive insurance sector. Progressive Insurance’s Snapshot program uses a plug-in device to track driving behavior, including speed, braking, and driving time. Insurers can offer personalized premiums using IoT data on individual driving habits and reward safe drivers with better rates.
Health and life insurance sectors are also embracing IoT mobile app trends. John Hancock, for instance, offers a program for tracking fitness activities. Policyholders who meet certain fitness goals can earn discounts and rewards that motivate them to maintain a healthy lifestyle.
IoT mobile apps in home insurance are making a significant impact as well. Smart home devices that detect leaks, smoke, or unauthorized entry into the house can be integrated with insurance policies to offer additional protection. Thus, insurers can mitigate risks, reduce claims, and enhance customer satisfaction.
Real-life IoT Apps Examples in Insurance:
- Telematics for auto insurance
- Smart homes for property insurance
- Wearables for health and life insurance
- Connected agriculture for crop insurance
- Supply chain monitoring for cargo insurance
5. IoT Applications in Retail
IoT technology helps retailers unlock unprecedented savings, efficiencies, and innovation. You can accomplish a lot with connected devices, including improving inventory control, optimizing supply chain management, reducing waste, and enhancing sustainability. Walmart, for example, can monitor the freshness of perishable goods with the help of sensors, reducing spoilage and ensuring product quality.

What’s more, the Internet of Things applications are turning traditional shopping experiences into personalized, interactive journeys. For instance, Rebecca Minkoff’s stores offer tablets to allow customers to browse products, request fitting rooms, and even change the lighting in the fitting rooms to simulate different times of the day.
Meanwhile, Amazon Go’s cashier-less stores eliminate the need for traditional checkout lines. You simply walk in, pick up the necessary items, and walk out, with the total amount automatically charged to your Amazon account. The blend of IoT sensors, computer vision, and deep learning algorithms is making it possible.
Moreover, thanks to the IoT application, retailers can monitor such customer shopping patterns as purchase history, preferences, and location information, to personalize experiences that resonate with individual needs.
Real-life IoT Applications Examples in Retail:
- Smart shelves and inventory management
- Interactive fitting rooms and virtual try-ons
- Frictionless checkouts and personalized payment
- Immersive shopping experiences and AR/VR integration
- Enhanced security and loss prevention with cameras and sensors
6. IoT in Agriculture
Farmers can use IoT mobile apps to optimize various time-consuming operations and make informed decisions about harvesting, fertilization, and irrigation. For example, John Deere’s precision farming solution gives farmers data-driven insights on soil health, moisture levels, and equipment performance. This data is invaluable in preventing resource wasting, increasing yields, and improving efficiency.

Talking about indoor planting, IoT allows monitoring and managing micro-climate conditions, resulting in increased production and quality control. For outdoor planting, IoT application helps create smart irrigation and fertilizer systems. For example, there are sprinkler systems that dispense water only when needed, promoting responsible resource management.
Smart farming extends to livestock management as well. Companies like Cowlar offer intelligent collars for cows that monitor health, activity, and reproductive cycles. It helps farmers detect illnesses early, manage feeding efficiently, and predict the best time for breeding. It’s a level of control that was previously unimaginable.
Real-life Examples of IoT applications in Agriculture:
- Precision farming with smart sensors and drone-based monitoring
- Livestock management with GPS collars and automated feeding systems
- Climate-Smart agriculture with smart irrigation systems and carbon sequestration
7. IoT-Connected Factories
The industrial landscape is undergoing a seismic shift with the advent of the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT). Factories are embracing connected device applications primarily to harness the power of data. By connecting machine equipment and factory items to sensors, they create a network that enables real-time analytics, forming the basis for strategic planning and operational efficiencies. As a result, factories benefit from decreased energy consumption, enhanced asset tracking, and early detection of equipment issues.

At Siemens’ Amberg Electronics Plant in Germany, the future of manufacturing is already here, and it’s nearly 75% automated thanks to IoT mobile app solutions. Sensors attached to factory equipment continuously monitor the production line, identifying bottlenecks and reducing waste. They not only keep things running smoothly but also track machine performance, predicting maintenance needs and preventing those costly breakdowns.
And it doesn’t stop at the factory floor. RFID tags and GPS technology provide a bird’s-eye view of the entire supply chain from the product’s birth to its delivery, ensuring transparency and accountability.
Real-life Examples of IoT applications in Manufacturing:
- Predictive maintenance with AI algorithms
- Smart inventory management with RFID tags
- Collaborative robots (Cobots) for assembly, welding, and packaging
- Digital Twins to production processes and data flows
8. Smart Grid
A smart grid is like a high-tech version of the electrical system that brings power to homes and businesses. It’s a holistic solution that uses digital technology to control and keep track of the electricity that flows from power plants to buildings. The Internet of Things app ecosystem is behind the smart grid’s improved electricity distribution and reliability, reduced energy waste and cost.
For instance, Chattanooga, Tennessee, has implemented a smart grid that has significantly reduced power outages by allowing the city’s Electric Power Board to monitor the entire electricity infrastructure in real time. It resulted in quicker response times to outages and millions of dollars in savings.
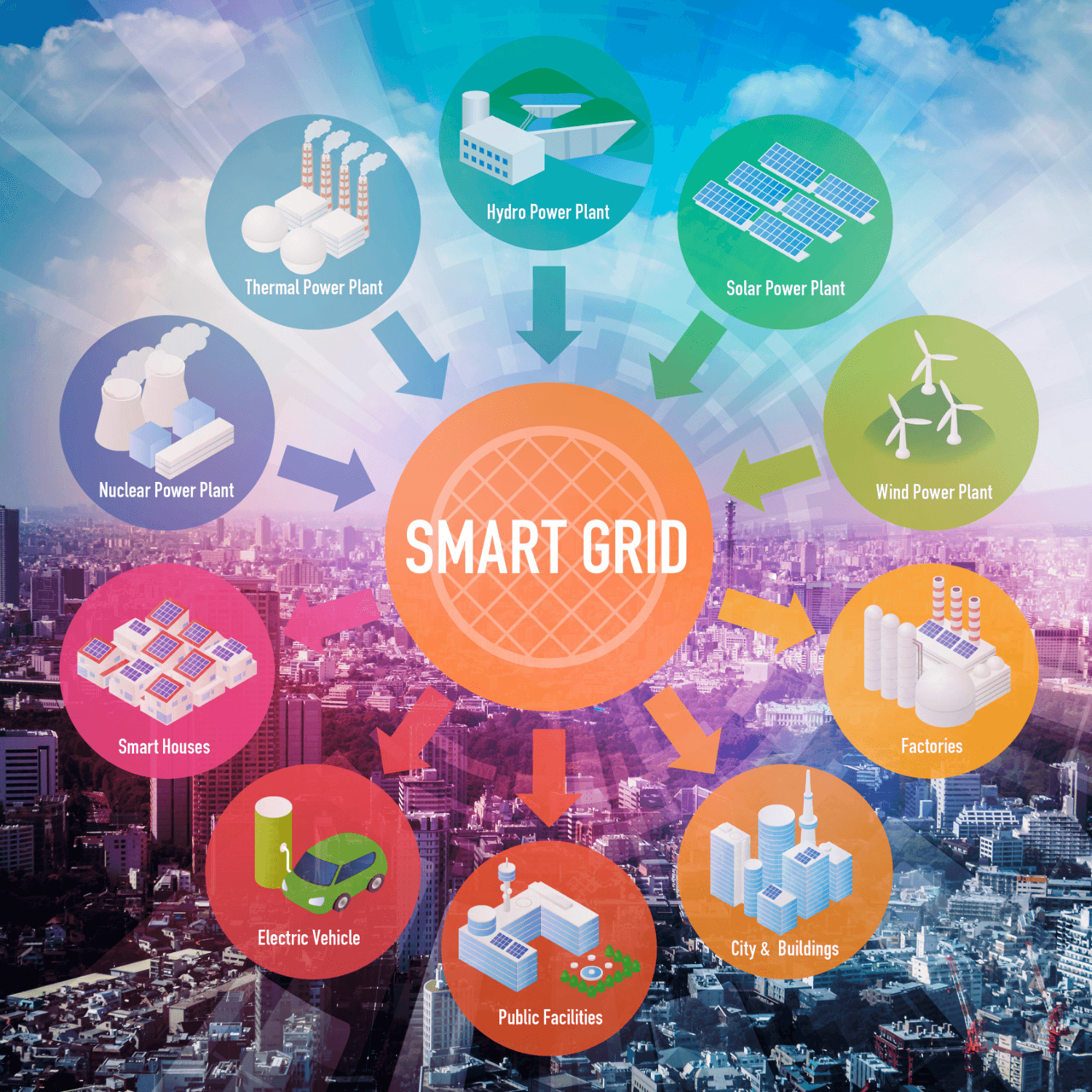
In Europe, Denmark’s island of Bornholm is testing a smart grid system that integrates renewable energy sources like wind and solar power. On top of that, mobile IoT apps let consumers see and control how much energy they are using. It helps make the whole system more efficient and environmentally friendly.
Real-life Applications of IoT in Smart Grids:
- Smart meters and real-time data
- Distributed renewable energy integration
- Self-healing grids and preventative maintenance
- Demand response and dynamic pricing
- Electric vehicle charging optimization
9. IoT Mobile Applications in Hospitality
IoT can greatly improve the way things work in the hospitality and tourism sectors. It can automate many routine tasks and interactions, allowing your staff to focus on more critical issues and boosting the guest experience to the next level.
Take, for example, the Hilton’s Digital Key technology. Through an IoT application on a guest’s smartphone, they can bypass the front desk, select their room, and unlock the door. Moreover, guests can use a mobile app to control room features like temperature, lighting, and even entertainment systems. Thus, they not only added more convenience to their gest but streamlined operations for the hotel and optimized energy usage based on the gathered data.
Similarly, Marriott International is experimenting with IoT to make guest stays more comfortable and hyper-personalized. Their mobile app lets guests change room temperature, lighting, and more to suit their preferences. Restaurants are also turning to IoT apps. Smart refrigerators, for example, can monitor temperature and humidity levels, which helps keep food fresh and cut waste.
Real-life IoT App Examples for Hospitality:
- Smart rooms and personalized comfort (with voice-controlled functions and smart devices like automated blinds or shower controls).
- Enhanced guest services and communication with data-driven insights
- Resource optimization and sustainable practices with energy-efficient rooms
- Seamless check-in and keyless access
What Are the Prospects of IoT Applications
The demand for IoT solutions is growing every day, and so is the number of IoT mobile app developers for hire and software providers.
Gartner predicts that global spending on IoT software and services will reach $1.4 trillion by 2027. This figure shows how much companies believe in the opportunities of IoT mobile apps. In fact, 53% of executives are using IoT solutions now, 24% plan to deploy them in the next 12 to 24 months, and 18% are thinking about using them.
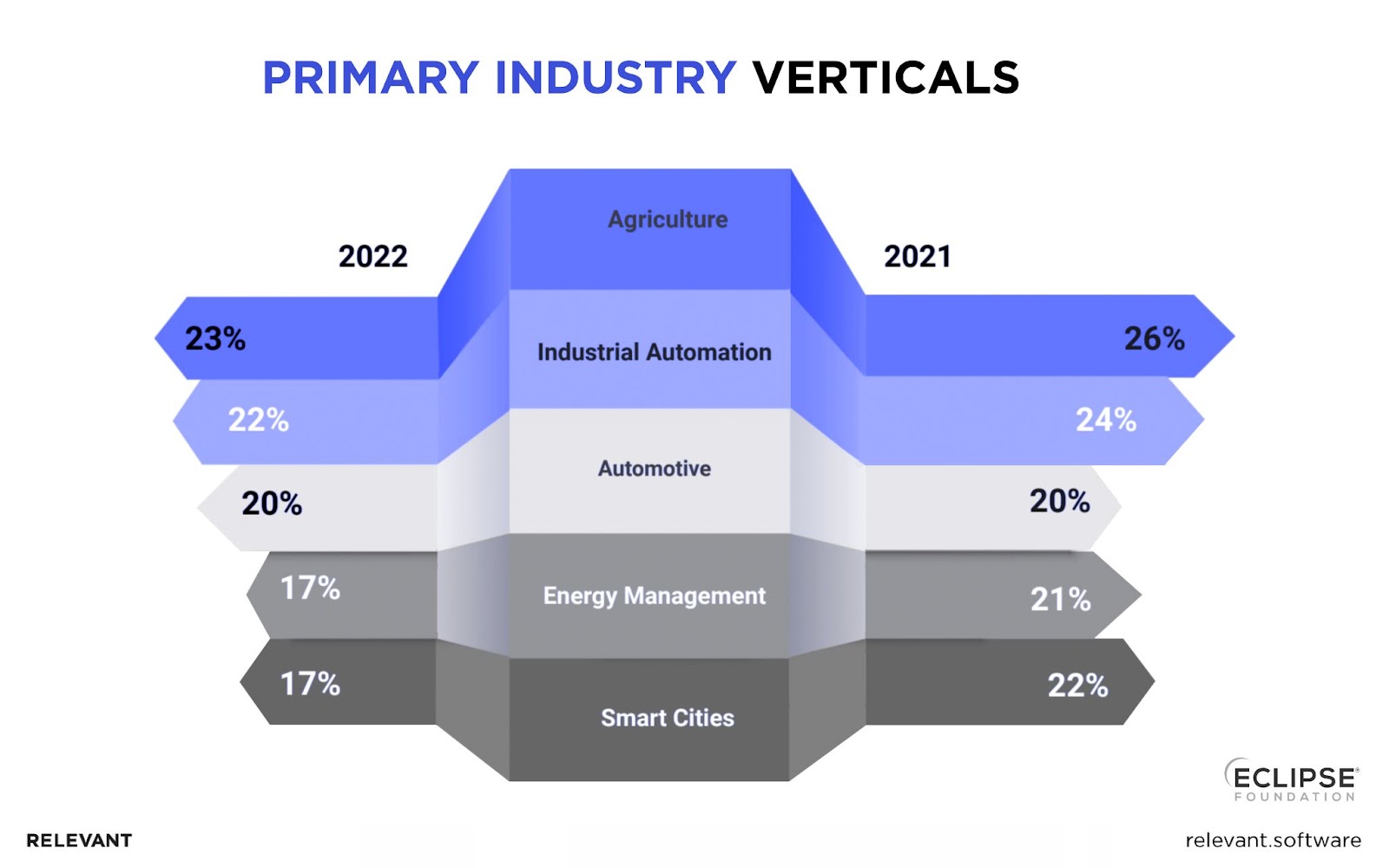
What’s driving this growth? A closer look at the industries reveals that Agriculture (23%) is leading the way in terms of IoT adoption. Industrial automation is closed behind at 22%, followed by the automotive industry at 20%, and energy and smart cities at 17%.
These statistics highlight that the demand for IoT mobile app development is on the rise, and the potential for innovation is virtually endless.
Start Building Your Mobile IoT App
As you now know the numerous opportunities and benefits of IoT applications across different industries, the next logical step is to consider how your organization can join this wave of progress.
As an experienced IoT development company, we at Relevant Software get ready to create a unique IoT solution for you. We offer a lot of advantages, such as:
- Exceptional User Experience: From the outset, we prioritize the usability of IoT apps, understanding that an app’s success hinges on user-friendliness.
- Diverse Expertise: We handpick a team of developers for each project, ensuring they possess the most suitable skills and experience.
- Robust App Security: We are committed to ensuring the highest level of security for your mobile IoT app data, safeguarding it at every stage.
- Scalable Solutions: Your IoT application will scale with zero compromises in quality, including adding new features or integrations and supporting various devices.
Willing to be at the forefront of technological innovation? Contact us today and get an estimation for your IoT project.
FAQ
Our core services:
Do you want a price estimate for your project?
Do you know that we helped 200+ companies build web/mobile apps and scale dev teams?
Let's talk about your engineering needs.
Write to us