What is IoMT and How to Develop Effective IoMT Solutions

IoT has gone from an idea to an everyday tool. Homes, factories, and vehicles now use connected devices to get real results. In healthcare, the impact is even greater. The Internet of Medical Things connects medical devices, sensors, and software to hospital systems, helping doctors make decisions faster and use resources more efficiently.
So, what is IoMT in practice? Now we describe what this guide delivers: a clear definition of IoMT, a grounded view of today’s market and technology landscape, credible use cases, and the role of IoMT development services in turning strategy into shipped software that clinicians trust and patients actually use.
from 25 countries outsourced software development to Relevant
We provide companies with senior tech talent and product development expertise to build world-class software.
What is IoMT: an overview
The Internet of Medical Things (IoMT) is the healthcare branch of IoT that links medical devices with hospital systems and clinical software. It securely delivers real-time, detailed data from both in-clinic equipment and wearables used at home. Measurements flow into electronic health records, appear in existing workflows, and support decisions both in hospitals and at home.
Here’s how it works. A device captures a reading, the platform validates the data, encrypts it in transit and at rest, and updates the chart as a core pillar of IoMT cybersecurity. The clinician reviews trends, adjusts treatment, and every action is logged with a clear audit trail across complex IOMT projects. When the loop runs smoothly, care becomes faster, more consistent, and easier to measure.
IoMT covers far more than wearables. IoMT devices examples include smart inhalers that track medication use, connected contact lenses that monitor eye pressure, ingestible sensors that confirm dosing, infusion pumps that log usage and raise alerts, and asset tags that locate critical equipment in seconds. Each device sends structured data into existing systems, improving efficiency and safety.
The momentum keeps growing as IoMT companies scale proven models and expand clinical coverage. Patients want care that fits their schedules, providers focus on better outcomes, and leaders aim to raise quality while cutting costs. IoMT enables this when systems follow interoperability standards, data stays protected, and the technology fits naturally into clinical work.
If you need a simple definition, the Internet of Medical Things links medical devices and software to clinical systems so teams act sooner, document faster, and deliver better care with less effort. With that in mind, let’s see how IoMT differs from IoT.
IoMT vs. IoT: A deeper dive into their differences
You can spot the naming difference, but the real gap lies in scope, risk, and regulation. This section explains how IoMT diverges from IoT and why it matters.
What is IoMT, and how does it differ from IoT?
IoMT focuses on clinical care. It connects regulated medical devices to hospital systems and feeds data into decisions in real time. By contrast, IoT spans many other settings with lower risk and lighter oversight. The table below gives a clear side-by-side view.
| Basis | IoMT | IoT |
| Definition | Healthcare subset of IoT connecting medical devices, apps, and clinical systems. | A broad network of connected objects across consumer, enterprise, and industry. |
| Focus | Patient care and provider operations. | Home, mobility, industry, cities. |
| Examples | RPM kits, glucose wearables, connected inhalers, smart pumps, and hospital asset tags. | Smart thermostats, connected cars, factory sensors, city lighting. |
| Data & regs | PHI, strict rules (HIPAA, GDPR), device software controls. | Mixed data, general privacy and safety rules. |
| Benefits | Faster interventions, lower unit cost, audit-ready records. | Convenience, automation, resource efficiency. |
| Security & risk | Very high stakes; errors can harm patients. | Context-dependent; typically lower direct clinical risk. |
| Interoperability | Tight EHR and standards alignment required. | Useful but flexible, standards vary by sector. |
| Growth drivers | Aging populations, chronic disease, rising costs, and medical tech advances. | Smart product demand, urban growth, and industrial automation. |
IoMT: Core elements
IoT in healthcare lifts patient care, strengthens device supply chains, and improves hospital efficiency. Real value appears when devices, connectivity, and software operate as one trusted system. In the sections below, we break IoMT into its core elements.
Medical devices and equipment
Care begins at the edge. Medical devices capture real conditions, give clinicians context, and remove guesswork from diagnosis and treatment.
Wearables
Wearable healthcare IoT devices collect health signals from the wrist or body and feed them into care plans with minimal friction.
- Smartwatches: Compact health hubs that track heart rhythm, activity, sleep, and on-wrist ECGs for clinical review.
Fitness trackers: Record steps, distance, energy use, and recovery patterns to establish activity baselines. - Continuous glucose monitors: Provide round-the-clock glucose readings for better diabetes control without fingersticks.
Monitors
Monitors collect ongoing data so clinicians can see patterns instead of one-time snapshots.
- Blood pressure monitors: Track systolic and diastolic trends for cardiovascular risk assessment and therapy adjustments.
- Pulse oximeters: Measure oxygen saturation for respiratory care and surgical monitoring.
Connected medical devices
Networked equipment extends beyond wearables, sending precise telemetry for continuous follow-up.
- Smart inhalers: Track medication use and inhalation technique to help people with asthma or COPD (chronic obstructive pulmonary disease) manage breathing problems and prevent flare-ups.
- Digital pills: Ingestible sensors confirm medication intake and improve adherence.
Smart pacemakers: Provide real-time rhythm data for targeted clinic interventions.
Connectivity layer
Connectivity transforms signals into usable clinical data. Its reliability, reach, and security determine whether information arrives accurately and on time.
Wireless communication
Short-range and local links connect bedside devices and wearables efficiently with minimal power consumption.
- Wi-Fi: The hospital workhorse connecting monitors, pumps, and imaging systems to clinical networks with quality-of-service controls.
Bluetooth low energy: Reliable short-range communication for wearables and bedside devices with minimal battery drain.
Cloud services
Cloud platforms store and process device telemetry securely, turning data streams into actionable insights.
- Data storage: Encrypted repositories with access controls and retention policies for PHI and device data.
Data analytics: Stream and batch engines that detect alerts, trends, and key performance indicators for clinicians and operations teams.
Networks
Wide-area networks ensure data keeps flowing beyond hospital walls and into mobile and remote care settings.
- Cellular (4G/5G): Provides connectivity for ambulances, home care, and remote clinics with priority lanes for critical traffic.
LPWAN: Long-range, low-power connections for asset tags and remote monitors at minimal cost.
Software applications
Software converts raw signals into clinical and operational value. Seamless integration removes noise and reduces rework.
Data Analytics
Analytics platforms transform continuous data into early warnings and better treatment plans.
- Detects trends and outliers across data streams.
- Predicts deterioration or adherence risk using historical and real-time data.
Supports immediate, evidence-based treatment adjustments.
Patient monitoring apps
These apps display the right metrics at the right time, enabling proactive and remote care.
- Show vital signs in context for timely clinical action.
- Support chronic and rural patient monitoring.
- Create personalized plans using continuous health data.
Medical software
Specialized mHealth app development solutions enhance diagnostics, recovery, and operational efficiency.
- Diagnostic tools: Assist in image and waveform analysis with audit-ready outputs.
- Rehabilitation apps: Deliver structured recovery programs with measurable progress.
Operational systems: Manage inventory, scheduling, and asset use to cut waste and delays.
IoMT is more than a set of gadgets. It works as a connected ecosystem. Built on validated devices, secure transport, standards-based data exchange, and purpose-driven software, it raises care quality, lowers cost, and scales with confidence. So, as you can see, strong medical software is the bridge that turns IoMT signals into choices clinicians trust.
The types of IoMT in healthcare
What is IoMT across various healthcare settings? Each application area, from in-hospital and in-home use to on-body and community-wide solutions, uniquely benefits from the capabilities of IoMT.
In-hospital IoMT
Monitors capture vitals in real time and trigger timely alerts. Nurses see trends on one screen instead of walking between beds. Imaging systems automatically add device data to reports, reducing errors and repeat scans. Asset tags show the nearest pump or wheelchair, so staff stop searching. Doctors can see how patients move across wards and operating rooms and use that insight to remove bottlenecks.
In-home IoMT
Every morning, a patient slips on a blood pressure cuff and presses start. Within seconds, the results appear at the clinic. Later that day, a pulse oximeter detects a small dip in oxygen, and a nurse calls to check in before it becomes serious. What could have turned into an ER visit ended with a quick adjustment at home. With telehealth, a short video chat replaces a long, tiring trip to the doctor.
On-body IoMT
Wearables serve as an early warning system. A smartwatch can spot an irregular heartbeat and suggest a heart check. A glucose monitor alerts users to rising sugar levels, and the app helps them adjust before it becomes a problem. Athletes use heart rate data to track recovery, while people in long-term care get gentle reminders that help them stay on schedule and feel supported.
Community IoMT
Care doesn’t stop at the hospital door. Ambulances send ECGs and vital signs to the emergency team before they arrive, so doctors are ready to act. Mobile carts bring pop-up clinics to schools and community centers. In remote areas, telehealth kiosks connect patients with doctors and can even dispense approved medication after ID checks. Sensors travel with vaccines and medical supplies to confirm they stayed at the right temperature throughout the journey.
Benefits of IoMT for healthcare
The Internet of Medical Things belongs to the wider IoT but serves clinical decisions first. It links devices, sensors, and hospital systems so data moves with intent. In a mature setup, signals arrive on time, preserve integrity, and land where teams decide care.
Improved patient care
IoMT turns raw readings into a complete, real-time view of a patient’s health. Wearables report heart rate, glucose, and activity, while ingestible sensors confirm dose, and home kits extend observation beyond the ward. Clean transfer into the EHR creates a single view. With AI models for prediction, teams spot risk earlier, adjust therapy sooner, and lift outcomes across routine care and public programs.
Lowered per-patient costs
Once home and hospital connect, location stops driving expenses. Remote oversight keeps stable patients out of beds, shortens necessary stays, and reduces repeat admissions. Inside facilities, asset and supply tracking tightens inventory and aligns staffing with demand. These mechanics, not slogans, create measurable savings as adoption scales.
Improved patient experience
Care feels simpler when people use familiar devices and data flows without extra steps. Results appear during the visit rather than inside a separate portal. Clear language, helpful prompts, and timely feedback cut uncertainty. Behind the scenes, aligned workflows make care feel faster and more personal instead of more technical.
Reduced burden on practitioners
IoMT removes search and rework. Fresh data reaches the chart within minutes, and decision support highlights what changed rather than flooding teams with noise. Rounds move faster, documentation gets lighter, and escalation paths remain clear. Strong security and HIPAA-aligned controls sustain trust with patients and payers.
Bottom line: Effective IoMT focuses on reliable collection, secure transport, and standards-based integration. With that foundation in place, healthcare teams act sooner and waste less, which improves outcomes while costs fall.
IoMT real-world impact: A look at case studies
If you wonder what is IoMT in real cases, the proof lives in clinics and homes. The examples below show IoMT in action, where connected devices feed real-time data into decisions and deliver earlier interventions, fewer readmissions, and smoother operations.
1. Remote patient monitoring
With connected sensors and secure remote patient monitoring software, clinicians gain a continuous, real-time view of their patients’ health every day. The benefits of remote patient monitoring show up in practice: earlier interventions, fewer readmissions, and calmer clinics.
Real-life example: A clear IoMT use case in cardiology with measurable results is Boston Scientific’s LATITUDE NXT. It monitors patients with implanted cardiac devices at home and streams data to clinicians. In the PREDICT-RM analysis, remote monitoring lowered mortality by 33% and reduced all-cause hospitalizations by 19%.
2. Smart inhalers for asthma patients
Smart inhalers for asthma patients demonstrate another impactful application of IoMT. By integrating these inhalers into a smart healthcare system using IoT, patients can receive real-time feedback on their usage, adherence, and environmental triggers.
Real-life example: Propeller Health’s sensor snaps onto common inhalers and syncs with a smartphone app. In a Dignity Health program, asthma-related ER visits fell 54% within a year, and combined ER and hospital events fell 57% after enrollment.
3. Connected insulin pens
Managing diabetes requires accurate dosing. Connected insulin pens record each dose, sync with continuous glucose monitors, and help prevent mistakes. They make insulin adjustments safer and more precise.
Real-life example: Novo Nordisk and Medtronic introduced pens that capture dose and timing, then sync with CGM systems. Patients and clinicians view one timeline and set precise adjustments. IoMT technology turns scattered data into a single, actionable picture.
4. Wearable ECG monitors
Traditional ECG workflows miss what happens between appointments. A wearable or pocket ECG captures medical-grade readings anytime and sends them directly to clinicians. Heart rhythm issues are detected sooner, treatment decisions happen faster, and patients avoid unnecessary visits.
Real-life example: AliveCor’s KardiaMobile pairs with a smartphone to record a medical-grade ECG in 30 seconds. The app flags irregular rhythms such as atrial fibrillation and shares the trace with a clinician, enabling quicker intervention and fewer complications.
5. Critical equipment monitoring
Consider the potential impacts of power outages, system failures, or even cyber attacks on healthcare facilities. No healthcare organization can afford such incidents, which could compromise patient safety and operational efficiency. To mitigate these risks, they turn to advanced IoT solutions.
Real-life example: Philips e-Alert watches equipment health and notifies staff at the first warning signs. This allows hospitals to schedule maintenance in advance and prevent unexpected downtime. It’s a simple example of how IoMT improves hospital operations: fewer disruptions, greater safety, and smoother care delivery.
These examples show one clear lesson: when device data reaches clinicians quickly and through reliable systems, care improves and operations run smoothly. In the next sections, we’ll explain how to build IoMT solutions that deliver the same results on a larger scale.
How to develop effective IoMT solutions
IoMT solutions development requires specialists who understand healthcare’s strict standards, connected devices, and data flow. Hospital floors are demanding environments where every second counts, and software must perform flawlessly from the start.
Relevant Software’s expertise helps our team build IoMT systems that truly work in real clinical settings. Now we describe the steps our team follows to turn complex medical requirements into reliable connected solutions.

1. Start with clear goals and limits
We start by defining what success looks like, such as faster response times, fewer readmissions, or smoother staff workflows. At the same time, we set clear rules for privacy, safety, and budget to keep every decision transparent from the start.
2. Understand real clinical workflows
Our engineers study how staff actually work, seeing where data appears in the EHR, who reviews it, and how actions follow. Then we simplify the process and assign clear responsibilities so that information supports faster clinical decisions.
3. Choose the right devices and data setup
We test and validate medical sensors across settings such as home, ward, and ICU, evaluating their accuracy, hygiene, battery life, and reliability. Then we design data flow using identifiers, patient consent, and HL7, FHIR, and DICOM standards to make sure all systems communicate clearly and records stay consistent.
4. Build for reliability and security
We design systems that stay up even when networks fail. Local data collectors, secure APIs, and backup queues ensure care continues offline. Security is built in from day one: every connection is encrypted, every device verified, and every update signed and tracked.
5. Stay compliant and audit-ready
Our process follows global medical software standards (IEC 62304, ISO 13485, ISO 14971, IEC 62366) and integrates HIPAA, GDPR, and FDA or MDR requirements based on device class. Every data flow and update is fully traceable for audit readiness.
6. Test, measure, and improve
We simulate devices, run continuous integration with safety checks, and monitor latency, data quality, and uptime. This lets us measure reliability, not just assume it.
7. Integrate analytics with safety oversight
When we add AI or predictive analytics, our team tests each model using real clinical data to ensure it performs accurately. We also monitor performance over time and keep a backup plan ready in case we need to revert to a previous version. Every model is carefully documented and tracked.
8. Run operations with clear accountability
We set service-level goals for uptime and data freshness, maintain on-call playbooks, and monitor device health in real time. Before scaling, we run pilots with measurable results, showing clear impact on care quality, staff efficiency, and patient outcomes.
9. Keep systems safe and stable after launch
Our team reviews every update carefully, assessing risks and applying quick fixes when problems arise. We maintain an up-to-date risk log and track all software versions to keep the system secure and stable as it develops.
Our healthcare case: facilitating the ordering of custom prostheses and orthotics
Össur is a global leader in prosthetics and orthopedics with decades of clinical trust and a footprint across hospitals and clinics worldwide. The company wanted to replace plaster casts and paper forms without slowing care. Manual molds took hours, moved across borders, and still produced uneven fits. Clinics also faced weak connectivity, so any new process had to work offline and migrate existing data safely.
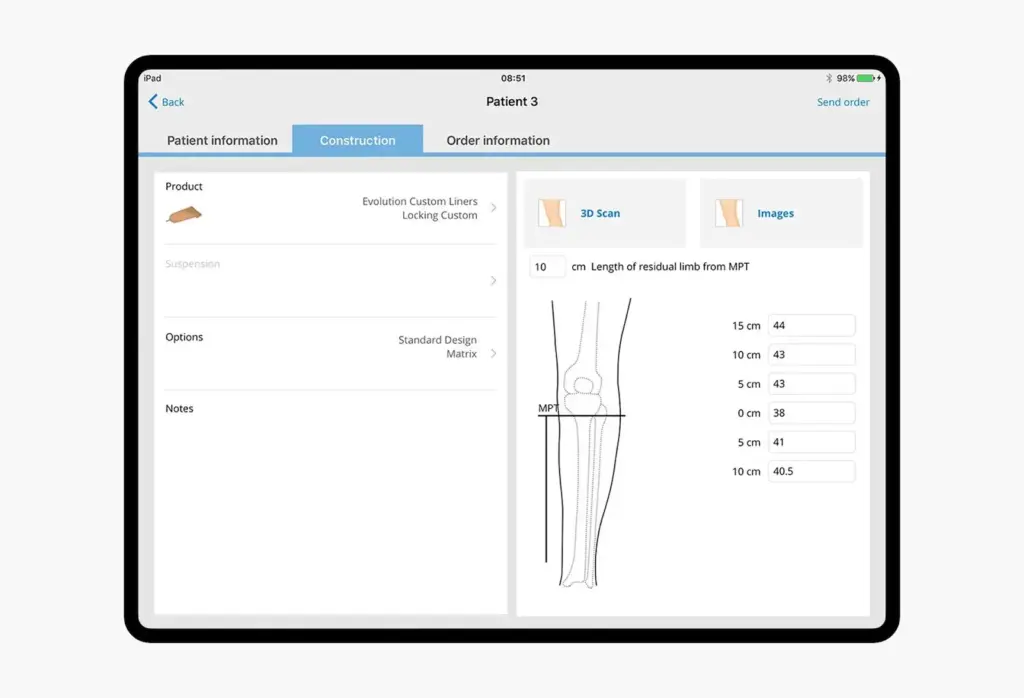
Itera, Össur’s partner, invited Relevant Software to upgrade two iOS apps for knee braces and custom prosthetics. The goal was clear: enable clinicians to measure, configure, and submit accurate orders in minutes, even when the Internet is weak.
To achieve this, we unified the experience so that both apps operate as one system. SmartMeasure now guides brace selection and records exact knee parameters through a clear, stepwise flow. In parallel, Össur Custom Solutions manages sockets and liners while preserving patient context end to end. Finally, we integrated Structure Sensor 3D to capture transtibial geometry with high fidelity. Clean digital scans replace casts, and the courier step disappears.
In addition, we built an offline-first architecture that stores data locally and syncs to Azure once online. We also refactored critical modules, raised performance, and executed safe data migration. Real-time status now shows every order from submission to fulfillment.
As a result, measurement and order entry finish in under five minutes. Overall processing drops from days to hours, and shipping delays disappear. Clinics gain cleaner data, fewer errors, and a better fit for braces and sockets. The platform runs reliably across regions, supports 100% offline order completion, and scales to new sites with minimal effort.
Bottom line: Internet of Medical Things
IoMT now means better care, not bigger fleets of devices. Smarter sensors feed clean, real-time data into clinical systems, so teams see risk sooner, act faster, and tailor care across hospitals, clinics, and homes.
We help you turn that promise into working solutions through our healthcare software development services. We connect devices, secure data flows, align HL7 and FHIR, build analytics and MLOps, and meet HIPAA, GDPR, ISO 13485, and IEC 62304. If you want a partner who delivers, not promises, we are ready to help. Contact us!
.


Hand-selected developers to fit your needs at scale! Let’s build a first-class custom product together.

