How Can Manufacturers Benefit from an IoT Solution for HVAC?

According to Intel, IoT applications currently amount to more than 200 billion devices, up from just 2 billion in 2006. Among these devices, are HVAC systems which are predicted to reach over USD 28.3 billion by 2025, up from USD 8.3 billion in 2018.

IoT is the internet-based connectivity of sensors and devices that enables the sharing of data and control of electronic gadgets.
from 25 countries outsourced software development to Relevant
We provide companies with senior tech talent and product development expertise to build world-class software.
Today, thanks to IoT, original equipment manufacturers (OEMs) can design digital HVAC assets that can monitor as well as control heating and cooling systems from smart devices. And in addition to the ever-growing convenience features, it’s important to note that IoT helps consumers significantly save energy.
However, while IoT solutions for HVAC increase the HVAC efficiency for consumers, the big question is: what do they bring to the table for the manufacturers?
In this article, we will discuss the benefits, challenges, and intricacies of manufacturing an IoT Solution for HVAC.
What are the reasons for using IoT for HVAC?
As a manufacturer, adopting IoT technology into HVAC systems has numerous benefits. For instance, previously unconnected gadgets can now communicate data with HVAC systems.
HVAC systems will soon be able to modify and regulate themselves without the need for human intervention. In other words, HVAC systems will develop the ability to ‘think’ for themselves.
HVAC systems have algorithms – pieces of computer code – that can learn, adapt, and improvise over time in response to specific events. So, like a human brain, it will assess current situations and take necessary corrective action without the need for human interaction.
When a smart system detects that no one is in a building, it might, for example, reduce ventilation flow, thereby saving energy.
The Honeywell D6 smart controller expands on this approach. Here, the controller may learn how much time the AC takes to reach the desired temperature, adjusting the start-time based on the user’s location. As a result, the required temperature is achieved only when the user enters their home, rather than before.
This is an excellent example of machine learning algorithms that study the behavior of a smart air conditioner and adjust startup times to save electricity.
Challenges of managing the HVAC systems
According to a technological analysis released by the US Department of Energy, residential and commercial buildings account for around 74% of electricity use and 40% of all primary energy use in the United States; of which HVAC systems can account for up to 60% of the building’s overall energy usage.
Despite HVAC systems being only a minor component of the infrastructure of commercial buildings, air conditioning and its distribution across a structure consumes a tremendous amount of energy.
These are some challenges commercial building owners face with HVAC systems.
Adjustment problems
Building managers routinely alter HVAC systems based on trial-and-error adjustments in response to occupant comfort feedback, putting energy savings on the back burner.
Consequence: Discomfort among the occupants.
Traditional thermostats regulate the temperature of a space to a set point. Still, they ignore variables like humidity, airflow, sunlight, and an individual’s activity level.
In large buildings, particularly, residents cannot simply adjust the thermostat and must instead submit a work order, call the building superintendent, and wait for adjustments.
Difficulties of keeping track of the whole HVAC system
HVAC is a multi-element infrastructure with a lot of moving parts. When one of the system’s components fails, the entire system suffers. A dirty air filter, for example, causes HVAC systems to work harder to compensate for the reduced airflow, resulting in system failure over time.
Consequence: Exorbitant electricity bills.
It’s no surprise that illogical electricity usage, inappropriate refrigerant charge, and duct leaks cause electric bill spikes. This is because heating, ventilation, and air conditioning account for up to 40% of energy consumption.
Inadequate HVAC maintenance
Real estate owners often don’t prioritize HVAC maintenance, only attending to it when it is too late. On the other hand, proper tune-ups aid in the early detection of potential problems, optimizing HVAC unit performance and extending its lifespan.
Consequence: Equipment breakdowns and malfunctions.
Heating and cooling loops produce high electricity bills, but improperly working equipment also causes high electricity bills. Therefore, extra resources are devoted to determining the cause of the rise in energy use and fixing the equipment.
Constantly turning on and off the air conditioner
Many people assume an AC should stay on while a space is empty, because restarting later would “burden” the system. In practice, keeping the unit running at a comfort setpoint usually wastes energy because it fights heat gain for hours when no one is in the room. A smarter approach uses scheduling or an occupancy-based setback temperature, then restores comfort shortly before people return.
Consequence: Higher electricity demand and higher emissions. In the EU, renewables covered 26.7% of energy used for heating and cooling in 2024, meaning that most of the supply still comes from non-renewable sources.
How does the Smart HVAC Internet of Things ecosystem work?
IoT-based HVAC Solution Architecture
The following elements make up a typical deployment architecture:
- HVAC sensors. They include temperature, motion, light sensors, and so on.
- An actuator that accepts electrical input from sensors, converts it into action, and acts on devices and machines.
- A wireless sensor network that sends data to the gateway and the cloud
- A gateway that allows data to be channeled into the smart HVAC system and establishes bi-directional communications from the device to the gateway and vice versa
- Cloud IoT solutions that allow management of the data collected from the sensors
- Embedded devices, such as smartphones and tablets that enable users to access and manage HVAC IoT devices remotely
- HVAC software for acquiring data from several sensors, processing it as needed, and sending it to the cloud for more analysis.
- The cloud analytics platform for filtering, analyzing, and sharing data with other systems as needed.
- Learning algorithms that utilize database information to help in preventive maintenance, energy optimization, and remote control of HVAC systems. Faults, warnings, and events are also reported to system managers on their smart devices.
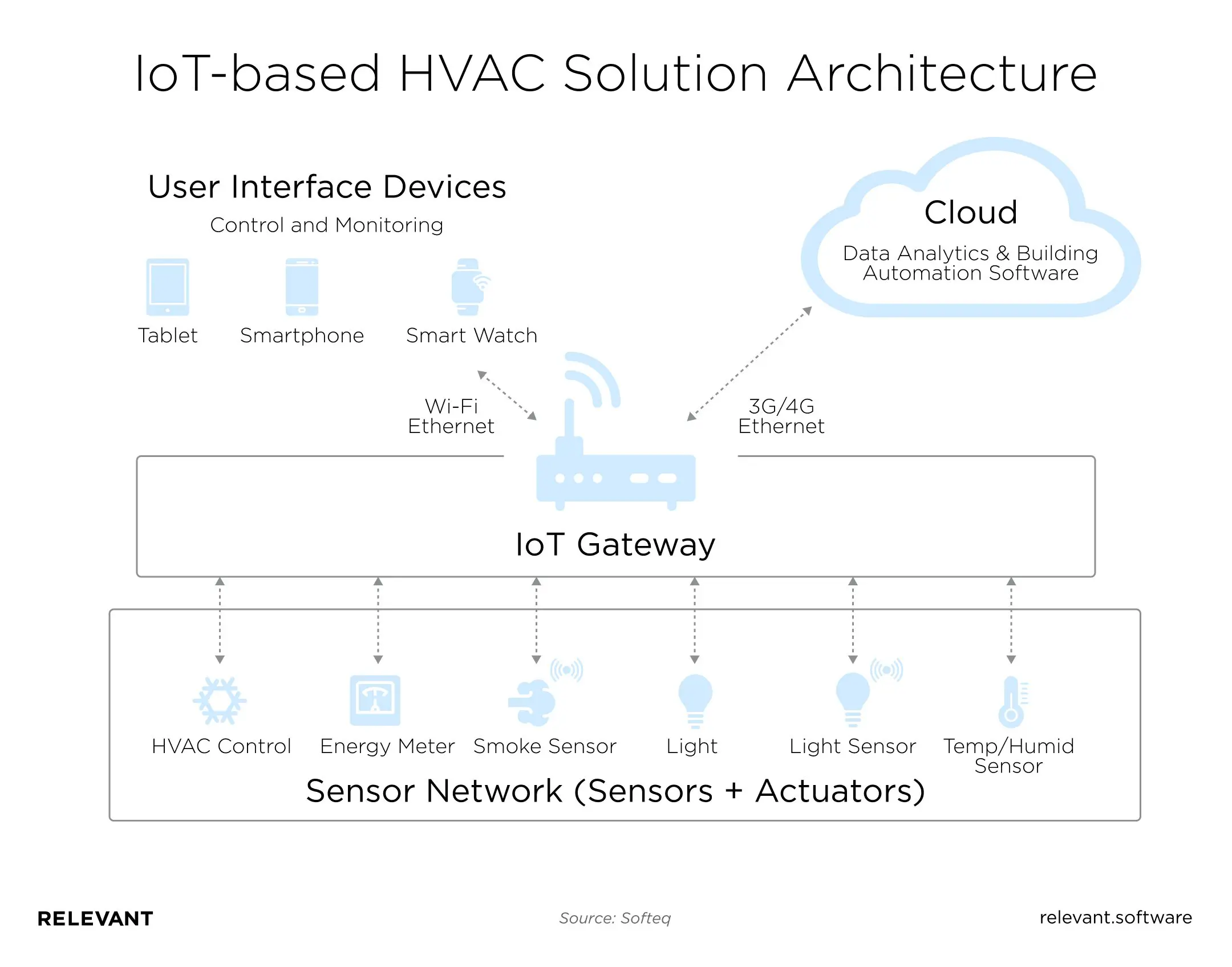
Here’s how the network works:
- HVAC software evaluates data from several sensor locations and stores it in a cloud-based system in real-time.
- The system is linked to a cloud-based analytics platform, where the data is filtered, gathered, and shared.
- Built-in algorithms use database information to enable preventive maintenance and optimization of monitoring and control of IoT HVAC systems.
- Then, when the software detects anomalous activity, such as power consumption that exceeds the system managers’ established baseline, it sends out dynamic notifications.
These sophisticated controls can reduce HVAC use in unoccupied areas of a building, identify, and resolve malfunctions.
What are the exact benefits of Smart HVAC systems?
When integrated with IoT sensors, the thermostats form the main interface of a smart HVAC system that can help homes and businesses save money on energy and improve productivity.
According to a Cornell University study, employees committed 44 percent more errors and were less than half as productive under cooler temperatures than when conditions were acceptable. If a building’s HVAC system is misconfigured or fails during work hours, less productivity and compromised materials can result in severe financial losses.
Regardless of the challenges, a smart HVAC system powered by IoT can transform how a company maintains its environment.
- Real-time monitoring
Like many other IoT-based pieces of equipment, a smart HVAC system uses smart sensors to constantly monitor and gather data about the system’s state and performance. For example, temperature settings, energy consumption, cooling cycles, and condensation levels may all be collected and shared with system managers, engineers, and technicians to provide them with a complete view of the total health of an HVAC system.
Managers may use these extensive data sets to run a variety of remote diagnostic and predictive maintenance procedures to lengthen the life of their HVAC system and prevent it from breaking down during work hours, which would have a detrimental impact on productivity. - Decreased power consumption
The amount of conditioned (heated or cooled) air delivered throughout a building can be optimized with IoT HVAC controls for a smart building. Smart controls use data from CO2 levels, occupancy, temperature, humidity, static duct pressure, and air quality sensors to optimize airflow. It regulates airflow in one area without ignoring or over ventilating the other.
HVAC systems collect operating data and send it to the cloud regularly. The information is processed in the cloud, which aids in making informed judgments. This allows for more cost and HVAC energy saving. Traditional buildings are inefficient because they release large volumes of CO2, contributing to climate change. - Preventive maintenance
HVAC equipment faces leaks, blockages, and performance drift that can go undetected during day-to-day operations. Automated Fault Detection and Diagnostics (FDD) pairs sensor data with algorithms that compare expected operation to actual behavior, then flags anomalies and ranks them by impact. More advanced FDD can narrow the likely root cause, so teams fix the right component faster and avoid repeat faults.
Microsoft’s smart buildings program at its Redmond campus shows what this looks like at scale. Microsoft reports 125 buildings and roughly 2 million data points, producing about 500 million data transactions per day, which engineers review through a single dashboard rather than manual walk-throughs. In the early rollout, Microsoft reports 6–10% lower energy use, and published summaries of the exact Microsoft figures note that 48% of detected faults were corrected within 60 seconds once the software surfaced the issue.
- Controllability, adaptation, and comfort
Smart HVAC systems are beneficial to business owners and managers for reasons other than peak efficiency, as they provide much improved levels of control. Sensors can monitor temperature, humidity, and airflow throughout a building. They combine this data with external factors like weather forecasts and current utility rates to define the best settings for performance and comfort, ensuring that productivity is maintained, and temperature-sensitive materials are kept in check.
Sensors in a smart HVAC system connected to a wireless network can compare current humidity levels to historical data and weather forecasts to minimize latent heat in the air before it becomes uncontrollable. Instead of responding to changes after they happen, a smart HVAC system may actively create a pleasant environment by learning to adapt its behavior based on present or predicted upcoming situations. - Cross-functionality
IoT solutions for HVAC introduce previously stand-alone equipment into the realm of interoperability. Appliances that were once considered independent from your home are now integrated into the more fantastic “smart home” technology. The key players in this space are home assistants like Google Home and Amazon Alexa, which provide a single entry point for numerous devices to connect and work in combination with several smart systems.
Voice-activated air conditioning controls, for example, are already a relatively frequent feature. Programmable thermostats and smart AC controllers, such as the Cielo Breez Plus, show you how to control AC using it by linking to home assistants and controlled either by voice commands or as part of a much more complex routine or skill. - Streamlined maintenance
Another advantage of using a cloud-based solution for building system control is the ability to remotely monitor, operate, and modify it. The software would allow the building owner to monitor equipment performance statistics, record faults, and arrange a repair appointment. In addition, the technician would watch the same performance data and any faults both on and off-site, making maintenance visits more efficient. Some IoT mobile apps even allow you to transmit error messages straight to other service providers. - Energy efficiency
Now this is the cycle, climate change increases demand for temperature control buildings, and the energy required exacerbates the problem. But, facility managers can provide a better tenant experience at a cheaper cost and with less environmental impact by understanding how energy is utilized to provide the proper building conditions given factors such as weather, occupancy, etc. - Healthy buildings
Temperature, humidity, CO2, VOC, air pressure, and occupancy are all characteristics that significantly impact employee productivity and well-being. Luckily, you can monitor them using sensors. Staff concentration is affected when CO2 levels rise, but with real-time monitoring, airflow can be tailored to the needs of the staff. - Predictive maintenance
Continuous monitoring of energy consumption, fan speeds, alert circumstances, filter differential pressures, and other parameters is available with HVAC IoT solutions. They give you the information you need to address maintenance challenges before they become problematic. - Better facility management
Consistent, real-time data about your PACs by site and customer allows you to manage your facilities from a single location and deliver the service levels that your customers expect. - Сost reduction
By using IoT solutions for HVAC, you can identify the areas that require investment, ensuring that you don’t waste money. - Key to future readiness
HVAC IoT solutions are incredibly flexible, cost-effective to scale, and easily adaptable to include more use cases. This extends its advantages beyond your organization to other possible business objectives.
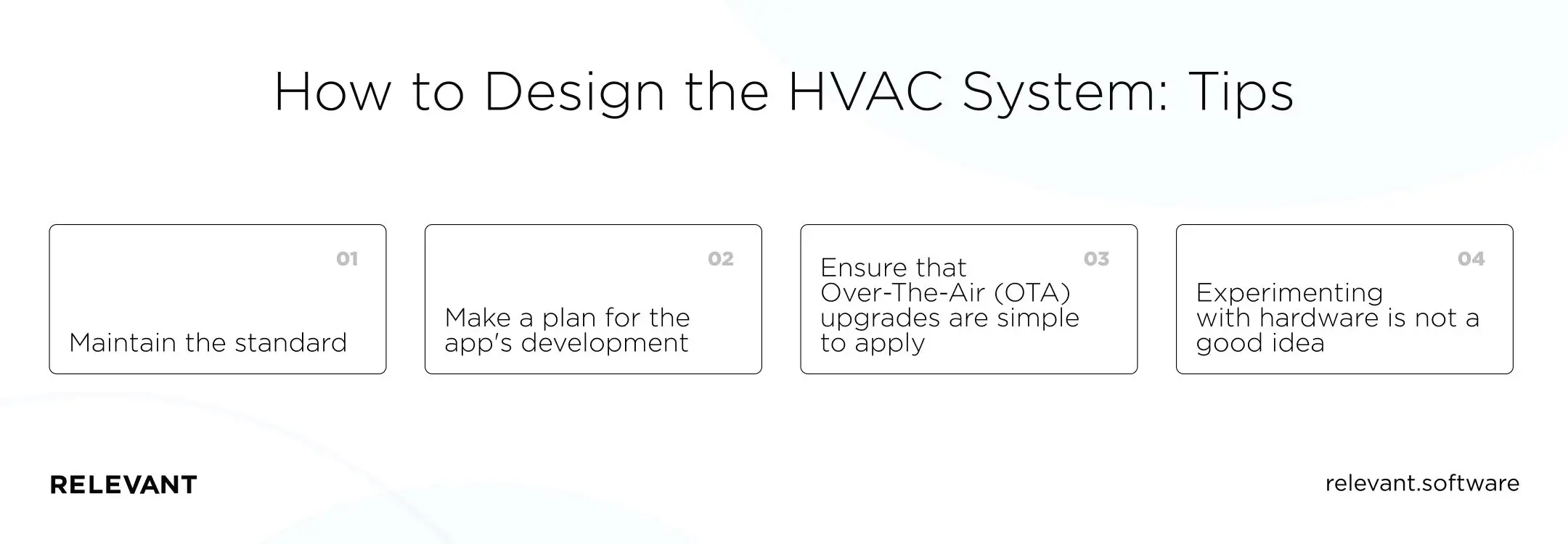
How to design the HVAC system the right way?
Here are a few tips on designing an IoT-enabled HVAC system:
- Maintain the standard. The first step is to connect your devices to the cloud. Even if you’re a startup, you may eventually need to work with worldwide clients who want cloud-to-cloud connectivity with other IoT systems. When creating HVAC solutions, utilize open native libraries and a cloud architecture responsive to specific data forms to ensure that they are easy to integrate.
- Make a plan for the app’s development. Some executives believe that remote control of HVAC appliances via mobile or web apps is an afterthought when, in fact, it should be incorporated into every stage of linked product development. The app’s capabilities must be planned ahead of time, and these questions must be answered from the start: Will users be able to control many stand-alone HVAC systems from the app’s dashboard? Will the ability to manipulate things from afar be restricted for security reasons? What happens if your internet connection goes down or your device’s battery runs out? Have we put in place a method to gather and update local behavior when offline?
- Ensure that Over-The-Air (OTA) upgrades are simple to apply. One of the primary benefits of the Internet of Things, and a distinguishing feature of connected devices, is that they continue to improve after the installation is complete. Ensure you design a technique for fast adding new features to HVAC equipment and that the system can be changed to meet the client’s requirements without unnecessary delay. However, don’t overlook safety precautions. Employ all state-of-the-art protection mechanisms, and the security system must be updated as needed via OTA communication.
- Experimenting with hardware is not a good idea. Regarding networking protocols and connectivity, don’t leave any box unchecked: don’t save a few dollars by using substandard Wi-Fi chips from an unreliable provider. Instead, you want your HVAC system’s wireless connectivity to have a comprehensive networking stack. The easiest way to accomplish that is to use the quality hardware that most leading smartphones already have. Premium hardware will also aid in delivering high-level security and the prevention of short wireless range and compatibility issues.
How can Relevant help you grow your business?
As an experienced IoT software development company, Relevant offers top-notch IoT software solutions, so we can quickly grasp your requirements and apply the right technology to grow your business.
It is our mission to provide a scalable architecture for your IoT software to bridge the gap between people and devices by:
- Data collection and management
We can connect to sensors, beacons, and connected devices to collect data and provide visualizations, analytics, and information modeling. - IoT app development
At Relevant, we harness the power of connected things by providing consumer-centric user experiences to show data and control devices. - Providing back-end infrastructure & integration
We also develop a cloud-based infrastructure that powers the front-end to store data and connect to, monitor efficiently, and manage your IoT devices.
At Relevant, you can also hire a dedicated development team who has employed the technology for projects, such as Sensor Innovation and Airthings.
Wrapping up
With increasing growth in the industry, more businesses recognize the benefits of converting to a smart HVAC system to help decrease energy costs, ensure workplace productivity, and preserve temperature-sensitive items. Since energy consumption is expected to rise, system designers must develop their IoT-enabled smart HVAC systems to remain competitive in the evolving commercial HVAC industry.
Relevant provides adaptable IoT Big Data solutions that fully utilize IoT infrastructure. As a result, we simplify the complicated device management problem by providing businesses with a single point of control to manage their energy-efficient HVAC systems.
To learn more about utilizing IoT in the development of a smart HVAC system or implement your own IoT project, contact us at Relevant today.
FAQs
How is IoT taking over the HVAC industry?
According to Intel, the Internet of Things is predicted to grow breakneck speed, reaching a peak of 200 billion devices in 2020, up from just 2 billion in 2006. The market for smart HVAC controls was worth over USD 7 billion in 2017, and it is expected to expand at a 19 percent CAGR from 2018 to 2024. By 2024, global shipments are estimated to exceed 250 million units.Specifically, IoT helps track vibration, airflow, pollutants, number of occupants, weather conditions, and more within the HVAC industry. In addition, monitoring key stress indicators and remote analysis improves troubleshooting and makes preventive maintenance easier to establish.What are the advantages of IoT in HVAC?
IoT HVAC system has the potential to transform how a company maintains its environment. These are some of its advantages:– Real-time monitoring– Decreased power consumption– Preventive maintenance– Controllability, adaptation, and comfort– Streamlined maintenanceHow can I find the right IoT software development firm?
To get the best services, you can consider outsourcing to Ukraine. Relevant is a software development agency based in Ukraine where you may hire experienced remote developers. We have a dedicated team of professionals with appropriate technologies and IoT software solutions tailored to your needs.Contact Relevant today to get a quote on your IoT project and hire a software development team.

Hand-selected developers to fit your needs at scale! Let’s build a first-class custom product together.

