QR Code Payments Explained: Will 2024 Be The Year of QR?

The onset of the coronavirus of previous years brought concerns about the risks posed by traditional payment methods, especially those that required contact. As a result, people started looking for contactless, seamless, and secure payment options, like QR code payments.
This could explain why, according to Statista, 18.8% of those surveyed strongly agreed and 27.95% agreed that QR payment usage had increased.
from 25 countries outsourced software development to Relevant
We provide companies with senior tech talent and product development expertise to build world-class software.

The use of QR codes for payment may still be in its onset stages in some countries now, but there are several reasons why more merchants will adopt QR more in the near future.
In this article, you will learn about what QR codes are, how they work, some use cases, and benefits for both the consumers and the merchants.
How does QR code payment work?
The first thing you need to understand about QR (Quick Response) codes is that they are 2-dimensional codes comprising black squares and bars on a white background. When you scan a QR code, a scanner decodes the information in it, which is then used for payments. Read also: Developing a Palm Scanner Solution for Payments Like Amazon One
What are the types of QR codes?
It is important to understand the difference between static and dynamic QR codes.
- Dynamic QR code payments – in this case, the QR code is editable and can contain extra features such as scan analysis and passwords. The decoded info can convey information to the merchant, such as the location of the consumer or the type of scanning device.
Dynamic QR codes also convey the transaction amount, so customers do not have to enter the sum manually. - Static QR code payments – this type of payment contains unchangeable codes that include the payment URL.
When the consumer scans the QR code, they need to add the amount manually. Merchants with static QR codes have one QR code for all payments. They can be created by QR code generator.
What are the QR payment modes?
There are two different payment modes:
- Customer-presented mode means that customers display codes on their devices, and merchants scan them for payment.
- Merchant-presented mode means that merchant display QR codes which customer scans to pay. The merchant can use a payment app to create QR code payments. You can develop this kind of apps with the help of skilled dedicated software development teams.
The QR payment process
The QR process here applies to the merchant-presented mode and can be visually seen in the diagram below.
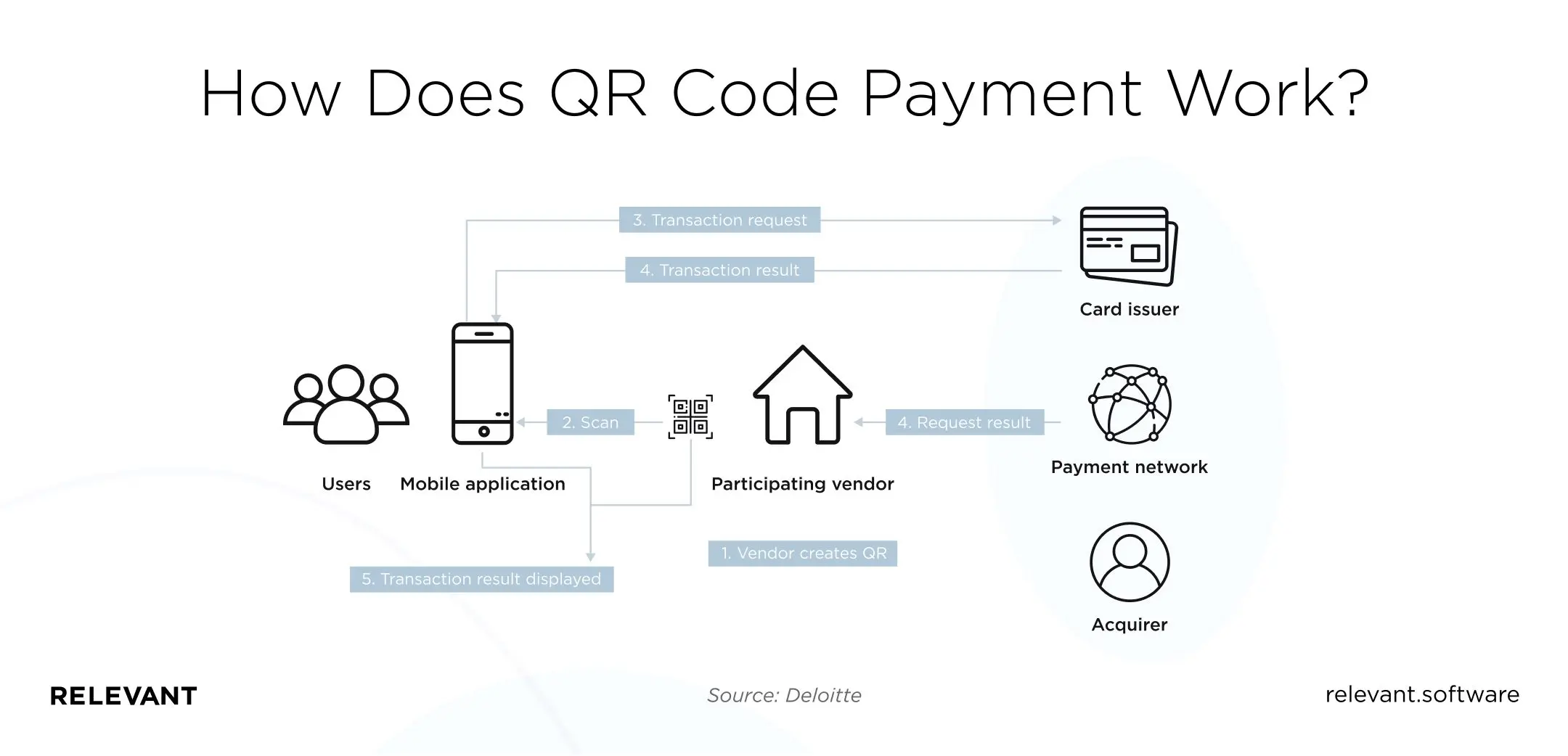
The process is as follows:
The merchant (vendor) creates a QR code which the user can scan for mobile payment. The app makes a transaction request to the card issuer.
The payment results are transmitted to both the consumer (from their card issuer) and the merchant (from their payment network). The merchant and the vendor can now see the complete transaction results displayed to them.
What are the benefits of the QR code payment system?
There are many advantages of using QR code payments for your business. They include:
- It’s convenient – the vendor can set up the code, and consumers can pay for their products or services anywhere, anytime they want.
- It’s cheap to set up – it is cheaper to introduce QR code-based mobile payment to your business than to add a manual point of sale equipment.
- It’s easy to integrate with new financial instruments and tools – when you receive reputable fintech software development services, you can integrate payment solutions and even add financial instruments like cryptocurrencies.
- It’s fast – QR code online payments or mobile payments are much quicker than many traditional payment methods.
QR-code – a modern tool for payment
While QR codes as a form of payment are just gaining traction in the US, UK, and Latin America, China has been using them for years successfully.
A 2023 survey by the Payment & Clearing Association of China reported a QR code payment penetration rate of 92.7%.
It is fair to say that in this country QR payments have displaced cash as the preferred method of payment. This is true at all levels of business, from street vendors to high-end stores, completely overtaking the use of credit and debit cards.
Therefore, China is rightfully considered ground zero for the QR code renaissance as there is no other country with as much widespread use of QR payments.
According to the Mobile Money Programme, China’s business and consumer mobile payment volumes reached USD 41 trillion.
Approximately 30 percent ($13 trillion) of that amount were QR code payments, mainly through the two main QR code schemes in China – Alipay (founded in 2004) and WeChat Pay (founded in 2011).
However, the rapid rise of QR code payments in China did not immediately translate into use in other markets. Initially, QR codes were indeed frequently considered a low-tech, high-risk solution not worthy of copying. But, the past few years have seen a considerable shift in perception.
In 2016, one of the first significant changes came with Visa launching a mobile payments application in Kenya, effectively challenging the incumbent M-PESA.
By partnering with four leading banks, they launched mVisa, enabling consumers to scan a merchant’s QR code to make a payment. Visa expanded the service, making it live in Rwanda, India, and Kenya, then later in Egypt, Indonesia, Kazakhstan, Nigeria, Ghana, and Vietnam.
MasterCard quickly joined the race by rolling out Masterpass in Tanzania, Rwanda, Ghana, Nigeria, and Uganda.
Other nations, like India, Sweden, Denmark, and South Korea, have increasing mobile payment adoption rates, followed by the US, Norway, Canada, and Japan not far behind. China’s visitors to Japan helped influence them to adopt and use QR code payments, and now they rank third in adoption rates.
In Europe’s QR payment adoption efforts, they are setting up collaborations between their mobile wallets and China’s Alipay. In Singapore, there are specifications for e-payments that assist merchants in getting QR codes through a central infrastructure.
By 2026, mobile payments sit at the center of everyday commerce, not on the edge. Juniper Research expects digital wallets to reach 5 billion users worldwide in 2026, pushing wallets into “default behavior” territory in many markets.
Industries that use QR codes as a payment method
So what industries do use QR codes? Here are some examples:
- Utility companies – Companies that offer utility services are embedding QR codes into their consumers’ bills. The consumers scan the QR code on their bill and then proceed to make the payment.
- Restaurants – For example, they can link QR codes to social media accounts or feedback pages. QR code is also a great tool to provide customers with access to the restaurant’s menu, so they can review it whenever they want.
- Street vendors – QR codes are popular among street vendors. They can print a QR code for each item on their menu, so their customers can read the descriptions and make a payment easily.
- E-ticketing services – E-ticketing services allow customers to select the event or mode of transport they want to use and pay for the tickets with QR codes.
QR Code payments companies
What are the examples of business applications of QR codes?
- Yoyowallet – this application offers many services to their customers and the retailers using them actively. Not only do they allow the customers to make payments, but they can also receive coupons and collect loyalty points in the app. Retailers can analyze their customers’ data and send them tailored marketing offers.
- BharatPe – this Indian-based QR solutions company was founded in 2017. They have an iOS and Android application that allows users to make payments to different types of merchants, from restaurants to taxis, directly from their bank account.
- Snap Scan – this app allows users to make payments in one of two main ways. They can load money to the apps or link their cards, then scan a code to pay with.
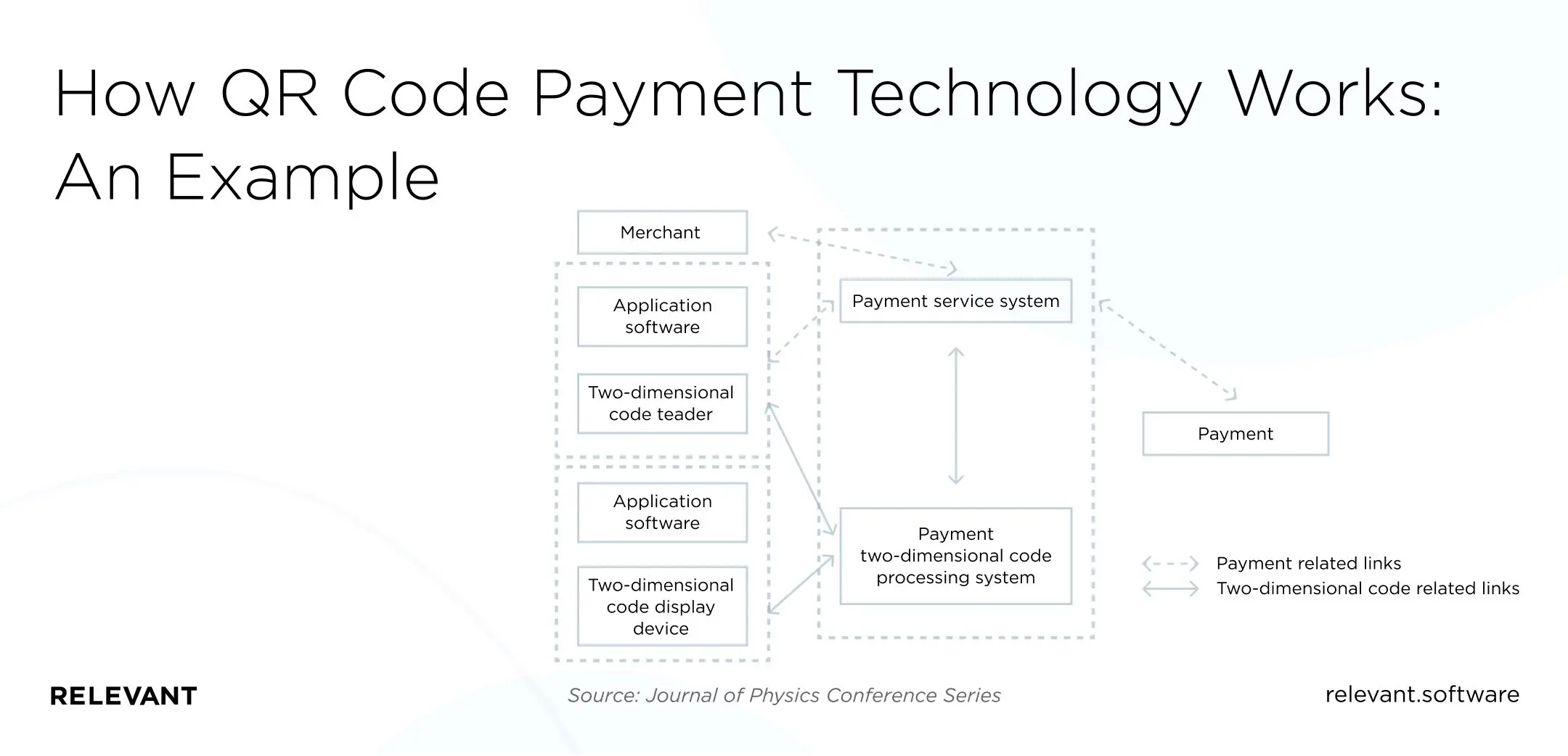
How QR code payment technology works: An example
Let’s say you have a merchant that sells groceries. They have a payment processing system that allows users to pay with a QR code and can also scan QR codes generated by the user.
The user will therefore buy their groceries directly depending on their preferred mode.
Impacts and implications of key QR trends
QR code merchant payments are becoming more and more popular. In this section let’s look at some of the main trends in QR code merchant payments focusing on their key implications and impacts.
The need for Internet connectivity
For this service to function effectively, you need internet connection. Some countries willing to implement this QR technology cannot do so due to this requirement. However, there is a notable effort towards improving coverage in such areas
Government interest and intervention are growing
In the past, the governments and regulators did not care about the merchant payment sector that much. However, times are changing. Now governments of many countries, especially the developed ones, want to reduce the use of cash to mitigate the circulation of counterfeit notes.
The other crucial objective is improving financial literacy and inclusion, fueling efforts to increase the banked population.
To make digital payments more preferable, regulators aim to reduce non-cash merchant payment costs. The governments know that the increased money traceability more tax revenues for the country.
Increase in smartphone penetration
QR code payments are not possible without a smartphone. The popularity of QR is growing in tandem with smartphone penetration. This is why QR code technology is very widespread in the Asian markets, particularly in China.
The smartphone penetration is still slowly growing in Africa, with the feature phone still more popular due to its relative affordability.
To mitigate this challenge, regions with low smartphone penetration need to have access to affordable devices that allow them to use QR codes for payments.
QR code strategic implications
The fast rise of QR codes for payments has many implications for banks and card schemes, just like other industry players.
Organizations should conclude how to play and come up with new methodologies rapidly to remain in the game. Shifting towards interoperability is one impact.
Though Alipay and Tenpay in China utilized exclusive QR codes, just as the primary variants of mVisa, utilization of interoperable QR code payments is developing.
These interoperable arrangements carry colossal productivity to traders and better adaptability for banks.
Card schemes, for example, Alipay and WeChat Pay that have exclusive QR code payment services, should decide whether to move towards full interoperability to offer a consistent installment experience worldwide or keep on attempting to protect their turf by offering restrictive arrangements.
Another critical effect of QR codes could be their impact on near-field communication (NFC) payments. While Apple Pay and Samsung Pay, just as other “Pay” arrangements have taken off with an incredible following, genuine utilization of NFC contactless services has regularly been low.
Besides, traders, for the most part, need to introduce a contactless card reader or update their POS terminal to acknowledge NFC payments.
Industry players may have to reevaluate their payments technique considering the new QR code choices. However, handset makers may have to consider how to manage NFC if QR code utilization starts to extend quicker.
All the more extensively, QR codes could massively affect monetary consideration and bank liability products. One of the troubles for merchants in distant regions has been utilizing digital cash, regardless of whether they have a plastic card or a telephone.
POS terminals were too costly to install in adequate numbers to make card or even mobile payments suitable.
Presently, QR codes give dealers a modest and straightforward approach to acknowledge digital payments.
When QR code installment acknowledgment becomes more comprehensively accessible, it will be simpler for shoppers to utilize the cash they store on their smartphones.
Whatever occurs, QR codes have opened up a considerable number of choices for additional payments more rapidly than many individuals expected.
Therefore, just as other payments industry players, banks should audit their procedures quickly to exploit this fast-rising payments initiative.
What types of payment solutions can you build with a skilled software development company?
If you want to add a QR payment option to your store, you can hire remote developers to help you implement your payment project ideas. Here are examples of what they could do for you;
- You can get an integrated QR-based payment system that connects the user’s bank account to your payment wallet, all with the scan of a code.
The users can be sure that none of their bank information was disclosed to the merchant, while the merchant can connect other services like loyalty points and cash registers to the systems. - Financial app development typically requires developers to work on backend solutions and others on front-end solutions for financial apps.
Developers can help you add systems to your current online and mobile applications that allow your users to add or remove money from their cards to make payments. - Programmers can build integrated systems that allow users to save, deposit, pay, and get other services all under one system.
- Experienced tech specialists can help you migrate your financial services infrastructure to the cloud so that you can deliver your services even beyond your borders.
There may need to be changes made to the service delivery rules depending on the new region’s e financial rules, but you can take advantage of the already established infrastructure. - Programmers can develop an attendance management system. The QR codes can track visitors’ movements and control access granting to users depending on what they paid.
One of the best things about modern software development approaches is that you can hire a great tech team from anywhere in the world.
So whether you’re thinking about Ukraine outsourcing or augmenting your team with a Polish programmer, you can do that and build a great app in accordance with your budget and needs.
Are QR Codes the future of cashless payments?
The benefits derived from using QR codes coupled with the ongoing movement towards secure cashless modes of payment suggest that QR code payments will become even more popular in the future.
According to Juniper Research, the number of QR code users is expected to grow to 2.2 billion in 2025. The US is expected to see a 240% increase in users from 2020 to 2025, which could be partly spurred on by introducing of QR code payment in Paypal.
The Relevant Case Study
Momice had a unique problem. As an event management company that uses software to simplify the organization of meetings and conferences, they needed a way to accurately and constantly keep track of attendance at events.
Therefore, they decided to solve this problem with a mobile application – the app that would allow greeters to scan the tickets of attendees.
After a thorough research, Momice decided that Relevant Software was the perfect candidate for their project. Our team built an app each for iOS and Android according to their specifications—the app needed to be simple, intuitive, and easy to use.
Key features included:
- A QR code scanner
Every Momice event ticket comes with a unique QR code. The Momice app uses the code reader to check guests in and out. - A name badge printer
Each QR code contains a guest’s personal information. This is used to create a personalized name which is printed with a mobile printer when greeters scan tickets. - An attendance report
The QR code information is sanitized and sent to the server. The event’s attendance report is then updated in real-time and can be viewed inside the app.
Relevant Software helped Momice users get very accurate reports on event attendance. Additionally, the unique printing feature facilitates easy networking among guests.
Summary
QR codes are having their momentum. It is not an exaggeration to say that this technology can revolutionize the online and mobile payment fintech industry.
If you want to integrate a contactless payment solution, develop a scan-to-pay app, build a payment system, or implement any other fintech projects, Relevant Software is the perfect place to get started.
We offer a range of fintech services, including payment solutions integration or payment system development.
Our team is made up of professional software engineers and experts in the field who are dedicated to delivering high-quality work for our clients at an affordable price.
If you would like more information on any of these services, please don’t hesitate to contact us today!


Hand-selected developers to fit your needs at scale! Let’s build a first-class custom product together.

