Role of IoT in Healthcare: Key Benefits, Challenges & Examples

Leaders look for fewer readmissions. Nurses and doctors look for fewer blind spots. Patients hope for fewer unnecessary visits. The Internet of Things in healthcare turns those hopes into practice with timely data and clear, reliable workflows.
Forecasts show the scale of change across connected care. MarketsandMarkets projects the IoT in healthcare market will reach $289.2B by 2028, implying a 17.8% CAGR and signaling sustained investment in connected workflows and remote monitoring. UN DESA reports 703M people age 65+ today and projects 1.5B by 2050, which increases demand for continuous monitoring and safer, automated care.
from 25 countries outsourced software development to Relevant
We provide companies with senior tech talent and product development expertise to build world-class software.
This article explores what IoT in healthcare means for providers and patients. It highlights the most impactful applications, measurable benefits, and the security and integration challenges that must be addressed. It also presents real-world examples and a step-by-step path to building solutions with Relevant Software, an IoT development company that understands both technology and clinical practice.
What is IoT in healthcare?
The Internet of Things (IoT) is best understood as a network of interconnected devices that communicate with each other. Each device has sensors that collect data, which is then shared across systems for analysis and action. Instead of isolated information, you get a stream of live updates that make everyday operations more efficient.
In healthcare, this network is represented by the Internet of Medical Things. It integrates medical devices, software platforms, and hospital infrastructure into a single environment that tracks patient status, guides treatment, and supports daily routines, all while meeting strict standards for accuracy, safety, and privacy.
You’ve probably seen these kinds of technologies before: a wearable patch that sends heart and oxygen data to doctors, an infusion pump that tracks dosage, a smart bed that adjusts to protect the skin, and a vaccine fridge that logs temperature data. Each one automatically reports key information to ensure safety, accuracy, and compliance.
The value does not sit in any single gadget. It appears that when devices identify themselves correctly, gateways transfer data without loss, and the platform applies rules that match how a unit actually operates. The result is fewer blind spots, clearer tasking, and earlier action, with data that stands up to clinical review and operational scrutiny.
Key benefits of IoT in healthcare
IoT technology enables continuous patient monitoring through intermittent checkups. Wearable devices and smart sensors capture vital signs, such as heart rate, SpO₂, and glucose levels, and securely transmit health data to cloud platforms. Healthcare professionals see clear signals at the point of care, while remote patient programs extend medical care without extra trips.

Access and continuity of care
Virtual visits become more effective when remote patient monitoring shares vital health data in advance. A mobile app connects with wearables and home devices to send real-time metrics to clinicians, ensuring consultations begin with accurate facts rather than relying on memory. Routine follow-ups can occur outside clinics, resulting in cost savings, reduced wait times, and enhanced overall care quality.
More precise, more personal
Continuous data collection helps care teams spot long-term trends instead of single readings. AI and machine learning analyze this data in real time to detect risks early. For example, if a patient with COPD (chronic obstructive pulmonary disease) shows a gradual drop in oxygen levels, doctors can adjust therapy before serious breathing problems develop. A cardiac patch can flag heart rhythm changes, and diabetes tools can fine-tune insulin doses. In the end, care plans turn into truly personalized treatments.
Faster, safer response
Connected monitors verify device identity and track safety thresholds, triggering alerts only when necessary. When readings exceed set limits, the system logs the event, prioritizes it, and sends it to the right medical team. Smart beds help prevent pressure injuries, pumps confirm correct medications, and cold-chain sensors keep vaccines safe. The outcome is fewer errors, faster response times, and better patient results.
Operational lift for hospitals
IoT systems enhance the efficiency of healthcare operations. Smart location trackers enable staff to locate medical equipment in seconds, environmental sensors verify operating room conditions, and automated reminders ensure timely maintenance. With real-time data, leaders can make smarter resource decisions, while connected devices automatically update medical records — freeing teams to focus on actions instead of raw data.
Data that reaches the record, securely
Real value emerges when connected devices, gateways, and platforms work seamlessly with electronic health records (EHRs). Cloud systems organize patient data, apply clinical rules, and record results. Robust security measures, such as encryption and strict access controls, protect personal information, allowing IoT adoption to grow without eroding trust.
IoT in healthcare doesn’t replace clinicians; it empowers them. With well-designed IoT systems, hospitals gain continuous visibility into patient health, safer clinical workflows, and measurable improvements that strengthen over time.
Applications of IoT medical devices in healthcare
IoT in healthcare replaces guesswork with continuous context. IoMT devices, secure platforms, and clear workflows lift patient care, support healthcare providers, and cut waste across hospitals and clinics. Below are the most impactful IoT applications in healthcare that the Relevan Software team has seen today:

Smart medical devices and wearables
IoMT devices track heart rhythm, SpO₂, glucose, temperature, and blood pressure with clinical-grade accuracy. These IoT devices in healthcare feed a secure platform that flags risk, updates records, and guides action. Patients gain insight into the impact of their lifestyle, while healthcare providers adjust therapy without an office visit.
Telemedicine and remote monitoring
Healthcare IT solutions expand telemedicine by extending care beyond hospital walls. Continuous remote monitoring sends vital signs before a call begins, so virtual visits start with real data instead of memory. Doctors can track patterns over time and adjust treatment immediately. Patients in rural areas or with limited mobility avoid unnecessary travel while still receiving timely guidance and quick intervention when alerts indicate risk.
Hospital operations and asset management
IoT in hospital management boosts reliability and efficiency across facilities. Smart trackers help staff find equipment like pumps, wheelchairs, and monitors within seconds. Environmental sensors monitor temperature, humidity, and air quality in operating rooms, while smart meters adjust lighting and HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning) systems to reduce energy costs. Real-time patient-flow data also helps manage triage and bed assignments during busy periods, cutting wait times and preventing overcrowding.
Medication management and adherence
Smart pill bottles and dispensers track when patients take their medication and alert caregivers if a dose is missed. Clinicians can review these adherence patterns alongside treatment outcomes to adjust therapy when needed. This type of healthcare IoT system helps prevent unnecessary emergency visits and strengthens chronic care programs where timing and dosage are critical.
EHR integration and workflow automation
The real value emerges when IoT data connects directly to the medical record. Gateways verify each device, platforms apply clinical rules, and the system updates the EHR with clear, actionable tasks. Care teams respond to precise instructions instead of raw data. Detailed audit trails safeguard patient information and ensure complete documentation for quality and compliance programs.
Predictive analytics and early warning
Continuous data from IoT healthcare devices allows advanced analytics to detect risks before they become problems. Deterioration scores can increase before symptoms appear, equipment can signal the need for maintenance before it fails, and inventory forecasts can align with actual usage. This demonstrates the true value of IoT in healthcare, as leaders base their decisions on outcomes rather than assumptions.
Supply chain and cold-chain integrity
IoT sensors verify that vaccines and biologics remain within safe temperature ranges from storage to delivery. Combined real-time location tracking and temperature logs help prevent spoilage and expedite root-cause analysis when issues arise. Compliance teams receive accurate reports that meet regulatory standards.
Security and compliance by design
Every healthcare IoT solution relies on strong security. Device and user authentication, network segmentation, encryption of data in transit and at rest, and continuous monitoring protect patient information while keeping systems reliable. Solid security safeguards help protect patient information, keep systems available, and earn trust—especially when delivering healthcare software development services.
These Internet of Things healthcare applications raise access, improve safety, and streamline operations. They also lay the foundation for the future of IoT in healthcare, enabling modular platforms, edge inference, and private 5G to scale without rewrites.
Top challenges of IoT in healthcare and ways to overcome them
IoT in healthcare delivers clear benefits, yet the same connectivity that powers remote monitoring and smart wards also introduces new risks. Grounded on Relevant Software’s expertise, this section explains the core challenges across security, interoperability, scalability, and governance, and provides workable steps that protect care quality.
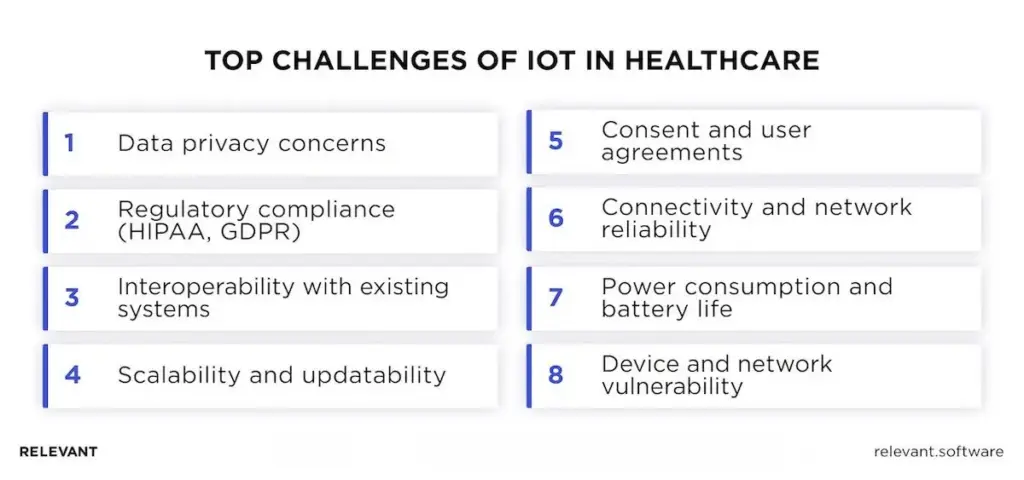
Data privacy concerns
IoT in healthcare turns protected health information into a live stream, raising the stakes for custody and control. The goal is precise patient care without exposing sensitive data across devices, gateways, and clouds.
Risk: Devices collect protected health information. Each transfer raises exposure.
Fix: Encrypt data both in transit and at rest, apply least-privilege access rules, and record every read and write action. Map all data flows and classify PHI to ensure security controls match actual risk.
Regulatory compliance (HIPAA, GDPR)
Rules define how the Internet of Things in healthcare systems handles personal data across borders and vendors. Compliance must live in the architecture, not in a policy binder.
Risk: IoT devices and platforms handle personal data across borders, where privacy rules differ by region.
Fix: Embed privacy by design. Keep a clear data inventory, ensure Data Processing Agreements (DPAs) and Business Associate Agreements (BAAs) are in place, and define retention policies. Demonstrate compliance with audit trails, Data Protection Impact Assessments (DPIAs), and regular vendor evaluations.
Interoperability with existing systems
Value is realized when IoT applications in healthcare write clean data into EHRs, CMMS systems, and analytics systems. Without shared models, the Internet of Things healthcare stack stalls at the interface.
Risk: Inconsistent data models and incompatible interfaces prevent IoT systems from writing data back to the EHR.
Fix: Adopt FHIR or HL7 standards wherever possible. Implement a translation layer to standardize device data and route it reliably to the EHR, maintenance, and analytics systems. Validate all data mappings through unit tests before deployment to ensure smooth integration.
Scalability and updatability
A limited pilot may run smoothly, but scaling to thousands of devices exposes design weaknesses. True healthcare IoT solutions must update, self-recover, and expand without interruptions.
Risk: As the device fleet grows, manual updates and support requests multiply.
Fix: Use over-the-air updates, phased rollouts, and organized device groups. Track firmware versions and certificates in a configuration management database (CMDB). Build for horizontal scalability across gateways and the rules engine to maintain performance at scale.
Consent and user agreements
Trust drives adoption. Patients must see how data moves, why it helps patient care, and how to opt out, or the strongest platform will face resistance.
Risk: Patients cannot see how data moves or why it matters.
Fix: Use plain-language consent forms, clearly state the purpose for data use, and make revoking access easy. Show what data is collected and where it goes directly within the patient portal.
Connectivity and network reliability
Clinical workflows rely on stable connections between IoMT devices and healthcare platforms. Systems designed to handle network loss, jitter, and congestion ensure that critical data still arrives when it’s needed most.
Risk: Coverage gaps or dropped connections disrupt real-time patient monitoring and care.
Fix: Use redundant network paths such as Wi-Fi, LTE/5G, or private APNs. Implement local buffering with store-and-forward capabilities and apply Quality of Service (QoS) rules to prioritize clinical traffic.
Power consumption and battery life
If power fails, patient monitoring can stop instantly. Devices designed for long battery life and simple replacement routines keep data flowing without overloading staff.
Risk: Low battery power interrupts monitoring, leading to data loss.
Fix: Use low-power chipsets, duty-cycling, and battery health monitoring. For critical equipment, include wired power options or hot-swap battery systems to maintain continuous operation.
Device and network vulnerability
Every IoT healthcare device introduces an identity, a key, and a pathway. Weak defaults or flat networks turn convenience into exposure, which is why healthcare IoT security starts at the edge.
Risk: Default passwords, outdated firmware, and flat network structures expose systems to attacks.
Fix: Assign unique credentials to every device, enable secure boot, use signed firmware, and rotate keys on a schedule. Segment networks to isolate devices and contain potential breaches.
The security of the Internet of Things for healthcare deserves its own section and a deeper look, because the stakes include protected health information and the safe operation of life-critical systems.
IoT in healthcare: What are real-life examples?
Real results matter more than presentations. The following Internet of Things healthcare examples illustrate how leading providers are already operating at scale. Each one shows how connected devices feed data directly into clinical workflows and demonstrates how these IoT use cases in healthcare deliver measurable, proven outcomes.
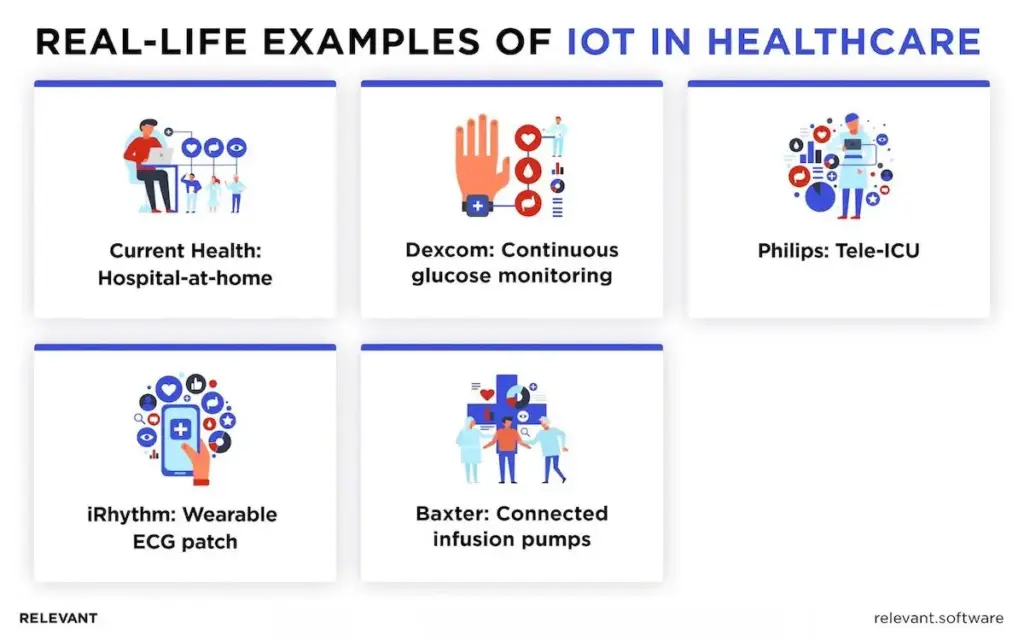
Dexcom: Continuous glucose monitoring
Dexcom G7 is a connected continuous glucose monitor that streams readings to phones and clinician dashboards, showing time-in-range and trend arrows. With real-time data, care teams adjust therapy between visits, reducing hypoglycemia risk and improving diabetes control.
iRhythm: Wearable ECG patch
iRhythm’s Zio patch continuously records ECG data for up to fourteen days, then securely uploads the encrypted results for analysis and physician review. This enables earlier detection of atrial fibrillation and other arrhythmias, improves triage decisions, reduces diagnostic uncertainty, and integrates seamlessly with electronic health records.
Philips: Tele-ICU
The Philips eICU connects intensive care beds to a centralized monitoring center that tracks waveforms and vital signs across multiple hospitals. When early signs of deterioration appear, remote specialists can intervene quickly and provide on-site staff with real-time support. Health systems using this model have reported lower mortality rates and shorter ICU stays thanks to continuous, expert oversight.
Baxter: Connected infusion pumps
The Baxter Spectrum IQ is a connected infusion pump that validates medications against hospital drug libraries, supports wireless updates, and automatically records data in the medication log. Built-in safety checks detect incorrect infusion rates, while analytics uncover usage patterns that enhance medication safety, improve nursing efficiency, and strengthen compliance during audits.
Current Health: Hospital-at-home
Current Health supports hospital-at-home programs through an FDA-cleared wearable, connected sensors, and a central hub that sends vital signs directly to care teams. Clinicians can review patient trends before virtual rounds, adjust treatments earlier, and safely discharge patients sooner. This approach lowers readmission rates and increases patient satisfaction among eligible groups.
IoT in healthcare: future trends
The future of IoT in healthcare is moving toward smarter edge devices, stronger networks, and seamless integration with core clinical systems. Hospitals will expect IoMT devices to send only relevant and reliable data directly into the EHR, eliminating the need for additional dashboards. Security will focus on verifying identities and protecting data paths, ensuring patient information stays confidential while care becomes faster and more efficient.

Edge intelligence at the point of care
Edge intelligence brings decision-making closer to the point of care. Gateways near the devices will analyze data, detect anomalies, and filter out noise before sending information to the cloud. This approach shortens alert response times and provides healthcare teams with clearer, more reliable insights during demanding shifts.
Private 5G and resilient connectivity
Large healthcare campuses will deploy private 5G networks to ensure stable coverage across ICUs, operating rooms, and logistics areas. Dedicated priority channels for clinical data and smart buffering will preserve vital information during short outages or maintenance, keeping critical systems continuously connected.
Interoperability by default
Data payloads follow FHIR standards, shared vocabularies ensure consistent meaning, and open APIs eliminate the need for custom integrations. IoT healthcare systems reliably and scalably send structured data to EHRs, maintenance systems, and analytics platforms, regardless of vendor. As a result, integration teams can focus on improving workflows instead of constantly troubleshooting connections.
Hospital-at-home that scales
Hospital-at-home programs will move past pilot stages as connected device kits, virtual check-ins, and automated supply deliveries become more advanced. This approach reduces readmission rates and provides patients with continuous monitoring and clear, reliable escalation paths that clinicians can trust.
IoT in the healthcare industry: Final thoughts
IoT in healthcare is already part of daily practice. Monitors, wearables, and connected medical devices stream data that clinicians can trust. The result is better patient care, lower waste, and decisions based on continuous signals rather than occasional checkups. As the healthcare IoT ecosystem expands, its true value will depend on seamless integration, clear accountability, and measurable results that withstand scrutiny.
Teams that act early gain a lasting advantage. The best way to begin is with focus — select one high-impact workflow, validate EHR integration, and define clear ownership across clinical, biomedical, and IT teams. Based on Relevant Software’s experience, this targeted approach improves safety, enhances visibility, and scales smoothly as adoption grows.
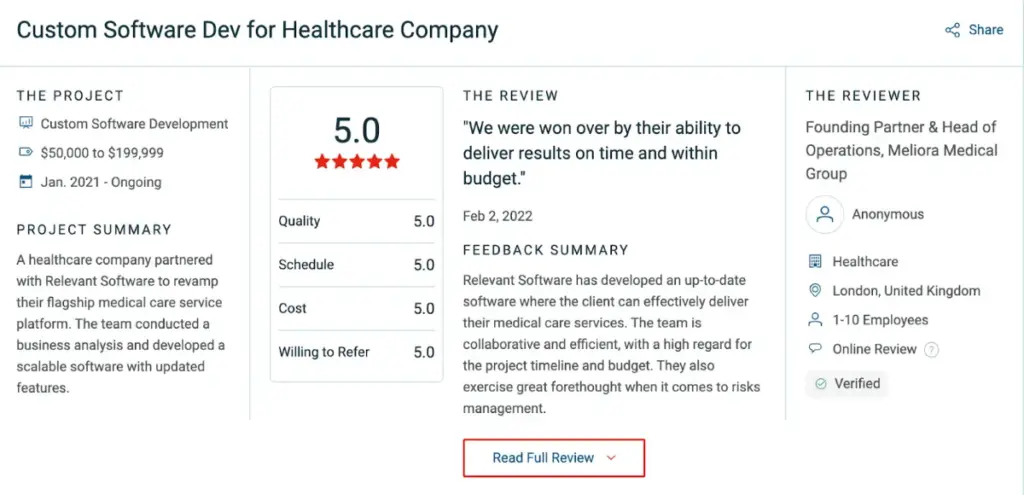
Thinking about bringing IoT into your hospital? We can help you make it happen — safely, efficiently, and with measurable results. Our clients’ feedback and top Clutch rating speak for themselves. Explore our medical IoT development services to see how we partner with healthcare leaders or reach out to discuss a solution tailored to your hospital and patients.


Hand-selected developers to fit your needs at scale! Let’s build a first-class custom product together.

