Why You Can’t Ignore Cybersecurity in Fintech
Updated: January 8, 2025
The fintech revolution has done more than change how we handle money—it’s rewritten the rules of finance itself. From mobile banking that fits in your pocket to AI-driven platforms that make investing smarter and faster, fintech has fused technology and finance in ways that were unimaginable just a decade ago. But there’s another side to this story, one that’s less polished, and its name is cybersecurity in fintech.
Beneath the smooth interfaces and instant transactions lies a constant battle, where cybercriminals target vulnerabilities and security teams race to outsmart them. The stakes aren’t just financial; they touch the core of what makes the fintech industry thrive—trust, reputation, and stability.

We provide companies with senior tech talent and product development expertise to build world-class software. Let's talk about how we can help you.
Contact usRead our article if you’re curious about how to address fintech security concerns and build innovative, resilient solutions. Relevant, a fintech software development company, shares insights into crafting systems that don’t just work—they withstand the test of today’s evolving threats.
Table of Contents
Why is cybersecurity critical in Fintech?
Digital transformation has made the fintech sector fast, convenient, and scalable—but also a prime target for cyberattacks. Unlike traditional financial systems, fintech platforms thrive on interconnectedness: APIs that bridge services, third-party integrations, and cloud-first infrastructures. This interdependence is both a strength and a vulnerability.
The more data, including personal details, flows through these systems, the more attractive they become to hackers eager to exploit weak spots. And fintech isn’t dealing with just any data—it’s personal, financial, and often irreplaceable. A leaked credit card number is one thing, but imagine the fallout if an entire customer portfolio is exposed.
The trust economy it’s built on makes fintech security uniquely high-stakes. People don’t just trust fintech platforms with their money; they trust them to protect their identities, savings, and investments. A single breach can shatter that trust, not just for one company but for the broader sector. And it’s not just customers watching—regulators are, too. Compliance isn’t just about checking boxes on data protection laws like GDPR or PCI DSS; it’s about demonstrating resilience in the face of evolving threats.
Cybersecurity in fintech isn’t a feature; it’s the foundation. Without it, the promises of innovation and disruption crumble under the weight of risk. The question isn’t whether fintech companies can afford to prioritize security. It’s whether they can afford not to.
What are the biggest cybersecurity challenges fintech companies are up against today?
Cybersecurity challenges in fintech range from phishing scams that exploit human error to sophisticated ransomware campaigns and data breaches. Add to that DDoS attacks that can take down entire platforms, and it’s clear why robust defenses are no longer optional but essential.
The cost of cybersecurity failures in Fintech
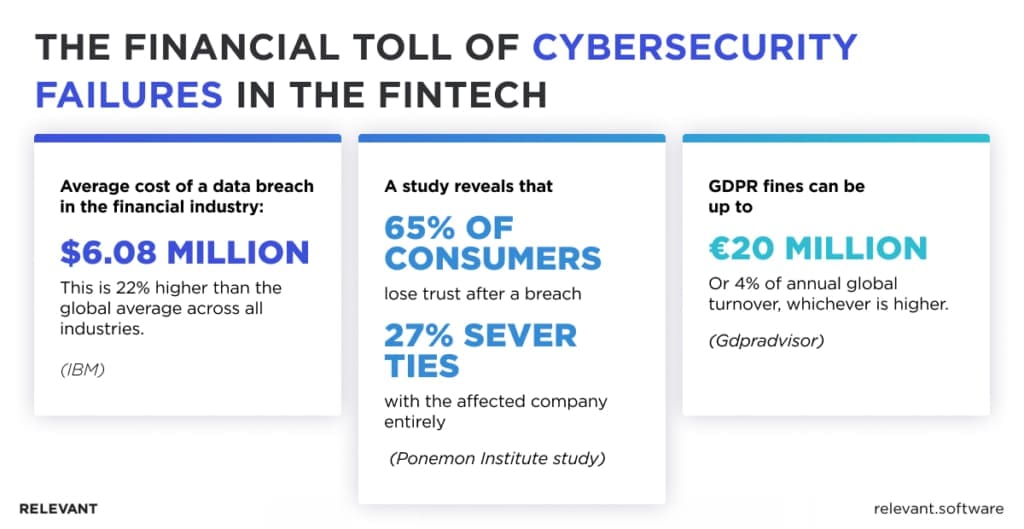
Average cost of a data breach in the financial industry: $6.08 million. This is 22% higher than the global average across all industries, demonstrating the particularly high stakes for Fintech.
The consequences of a cybersecurity failure in fintech can be staggering, with financial losses often taking center stage. Breaches caused by various security threats can result in direct theft of funds, costly ransom payments, or the need to invest heavily in cybersecurity measures and remediation efforts post-attack. However, the ripple effects often prove even more damaging. A single high-profile breach can destabilize a fintech company’s operations, disrupt services, and lead to significant revenue losses as customers flee to competitors perceived as safer.
Loss of customer trust can be even harder to recover from than financial setbacks. In fintech, trust is the lifeblood of the business. Customers expect their sensitive financial information—bank accounts, investment portfolios, transaction histories—to be handled with the utmost care. A breach doesn’t just expose vulnerabilities; it signals a failure to uphold that trust. Even years of reliable service can be overshadowed by a single incident, leading to customer churn and reputational damage that could take years to repair. Research indicates that businesses lose an average of 4% of their customer base following a data breach, with far greater losses in sensitive industries like finance. A Ponemon Institute study reveals that 65% of consumers lose trust after a breach, and 27% sever ties with the affected company entirely.
Then there’s the legal fallout. Regulatory frameworks governing fintech security are stringent for good reason, and breaches rarely go unnoticed. Non-compliance with laws like GDPR or PCI DSS can result in hefty fines that can cripple startups and damage established players. (GDPR fines can be up to €20 million or 4% of annual global turnover, whichever is higher.) Worse still, class-action lawsuits from affected customers or partners can pile on additional legal costs and liabilities. For digital finance companies, a cybersecurity failure isn’t just a technological misstep—it’s a financial, reputational, and existential threat.
Key cybersecurity challenges in Fintech
What makes cybersecurity in fintech uniquely challenging is not just the sophistication of the systems but the rapid evolution of both threats and compliance requirements.
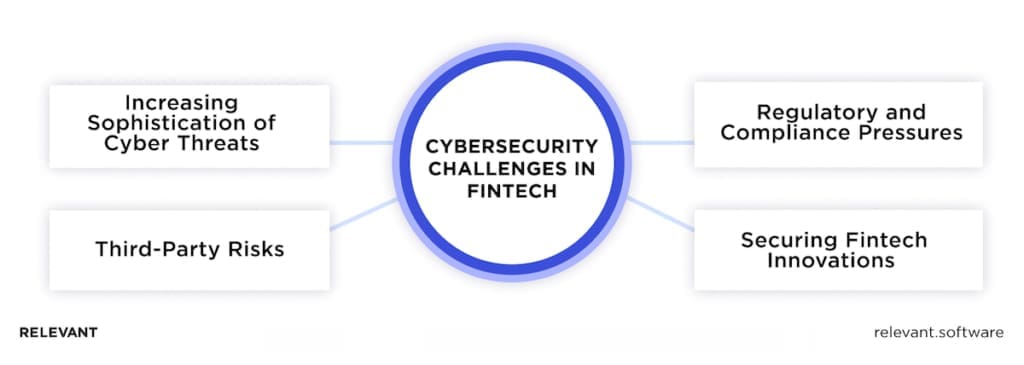
The increasing sophistication of cyber threats
The arsenal of cybercriminals has become far more advanced, placing fintech companies and the security of financial transactions in constant jeopardy. Phishing campaigns, once limited to basic email scams, now use highly targeted social engineering tactics to manipulate employees and customers. Ransomware attacks have intensified, shifting from small-scale extortion to multi-million-dollar demands that threaten firms dependent on seamless operations to process financial transactions. Advanced persistent threats (APTs) act with stealth over extended periods, stealing sensitive data without detection.
AI-powered attacks now push the boundaries further. Cybercriminals have embraced AI to take their methods to the next level. They create malware that changes to bypass security and fake identities that slip past fraud detection. These tactics use the same innovative tools that financial firms rely on to compete, making it even harder to keep financial transactions safe.
Third-party risks
In an ecosystem fueled by collaboration, third-party risks are a constant concern. Open banking and the integration of external vendors expose innovative finance platforms to vulnerabilities beyond their direct control. APIs, which act as the connective tissue between services, can become weak links if not properly secured. A single unsecured API can grant malicious actors a backdoor into sensitive systems, compromising not just the fintech provider but also its partners and customers.
Managing these risks requires a delicate balance—leveraging the benefits of third-party integrations while implementing rigorous oversight to ensure that external vulnerabilities don’t jeopardize the entire operation. However, many digital finance providers find it difficult to maintain consistent security standards across a network of interconnected systems.
Regulatory and compliance pressures
The regulatory environment for fintech is anything but simple, highlighting the importance of cybersecurity in banking sector operations. Frameworks like GDPR, PCI DSS, and PSD2 demand strict compliance to meet industry standards. These regulations cover critical areas such as data protection, transaction security, and user authentication, forming the backbone of cybersecurity in fintech. While essential for safeguarding customer trust, these rules can place a heavy burden on operations, particularly for startups working with limited resources.
The complexity grows with constant changes in these requirements. New laws emerge to address unforeseen risks, and companies must adapt rapidly. Non-compliance is not an option in the financial sector—it results in fines, audits, and reputational damage. Efforts to stay ahead of regulatory demands remain a major challenge, particularly for companies operating across multiple jurisdictions.
Securing fintech innovations
The very innovations that make fintech exciting—blockchain, cryptocurrencies, decentralized finance (DeFi), and AI—also introduce unprecedented cybersecurity challenges. Blockchain’s reputation for security is well-deserved, yet vulnerabilities in smart contract coding have enabled attackers to siphon millions from DeFi platforms. Cryptocurrencies, too, face risks from exchange hacks and wallet breaches in recent years.
AI-driven algorithms, a cornerstone of fintech innovation, are not immune either. Attackers can manipulate training data or exploit algorithmic biases to disrupt services or gain unauthorized access. Digital banking enterprises must balance progress with security, ensuring advanced solutions do not create new risks.
Essential cybersecurity strategies for Fintech
The demand for advanced cybersecurity solutions in banking has never been higher. As technology reshapes financial services, risks tied to sensitive data and vulnerabilities in system integrity increase. Tackling these challenges requires more than a basic checklist for fintech app security—it demands proactive measures and a layered approach that adapts to evolving threats.

Implementing zero-trust architectures
In the evolving landscape of fintech, trust is not assumed—it is verified. Zero-trust architectures follow the principle of “never trust, always verify,” requiring constant validation of every user, device, and application that attempts to access a system. This strategy reduces the risk of insider threats and lateral movement within networks.
For fintech companies, implementing zero-trust involves micro-segmentation to compartmentalize sensitive data and applications. For instance, accessing payment processing systems may involve multi-factor authentication (MFA), endpoint verification, and real-time behavior analysis, whether the request comes from an internal team member or an external vendor. This approach strengthens cybersecurity in banking, ensuring robust protection of critical assets.
Advanced threat detection and response
Cyber threats evolve faster than most organizations can react. To stay ahead, financial technology startups use machine learning (ML) and artificial intelligence (AI) tools to identify unusual patterns in real-time. A sudden spike in transactions from an obscure IP address or a login attempt from an unfamiliar device? ML identifies and flags it. These systems thrive in high-velocity environments where human oversight would be too slow.
Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) systems add a vital layer to cybersecurity in banking by gathering logs and alerts from across the organization. These systems go beyond passive data collection and offer clear insights, highlight vulnerabilities, and trigger automated responses to incidents. Paired with ML, SIEM creates a defense that evolves to counter new threats.
Data encryption and secure authentication
Encryption isn’t just a technical checkbox—it’s a lifeline for cybersecurity in banking and Fintech. With data constantly moving between users, applications, and cloud environments, end-to-end encryption ensures that sensitive information—whether it’s payment confirmations, login credentials, or account balances—stays unreadable to unauthorized individuals. This critical measure significantly reduces the risk of data breaches, providing a robust shield against cyber threats.
Authentication stands as the next critical line of defense in cybersecurity in fintech. While multi-factor authentication (MFA) has become standard, fintech companies are taking security a step further with biometrics. Features like facial recognition, voice authentication, and behavioral patterns such as typing speed offer both enhanced protection and a seamless user experience. People want their accounts secure, but they also expect convenience—achieving both is the ultimate goal in today’s fintech landscape.
Secure application logic
Here’s a lesser-discussed reality: no matter how secure the perimeter, poorly designed application logic can unravel everything. A single unchecked input field or an overlooked API vulnerability can create a backdoor for attackers. Regular code reviews, rigorous penetration testing, and secure coding standards are the only ways to prevent such lapses. It’s not glamorous work, but it’s essential. A fintech app that fails here is like a vault with an open window—impressive on the outside but wide open to exploitation.
DevSecOps
In cybersecurity in fintech, security isn’t something you tack on at the end—it’s a fundamental part of the development process from day one. DevSecOps integrates security into every stage of the software development lifecycle (SDLC), which ensures that vulnerabilities are addressed early and often. It’s not just about finding bugs—it’s about creating a culture where developers think like hackers and act like engineers.
Tools for finding code vulnerabilities are helpful, but they aren’t enough on their own. Real security comes from teamwork. Security experts must work alongside developers, embedding protection into every phase of development. This partnership ensures that the drive for speed and innovation never undermines the integrity or safety of the final product.
Continuous security training for staff
Here’s the harsh reality: even the most secure systems can fail because of a single careless click on a phishing email. This is why employee education is not optional—it is essential. Lessons must move beyond dull presentations and focus on practical, real-world examples: how to recognize a phishing attempt, steps to take when an attack is suspected, like checking the email with an SPF lookup, and the risks posed by weak passwords, which often serve as open doors for hackers.
Training sets the foundation, but more is needed to fully protect cybersecurity in fintech. True change occurs when companies build a culture where every individual understands their role in security. Giving employees the confidence to question unusual requests or report suspicious activity turns them into active defenders. It’s not about instilling fear or suspicion—it’s about fostering a shared sense of responsibility and vigilance. Awareness paired with accountability creates a workforce that strengthens every layer of the system.
Best practices for Fintech companies
The importance of cybersecurity in financial services isn’t theoretical—it’s existential. Fintech firms navigate a complex ecosystem where they are entrusted with both customer funds and trust. Protecting sensitive data and tackling cybersecurity threats are their core responsibilities. By leveraging insights from resources like the Journal of Information Security, fintech companies can adopt best practices to fortify their defenses and protect what matters most—customer trust, regulatory compliance, and operational resilience.
Conduct regular security audits
In an environment where attackers evolve their tactics, static defenses fail to keep up. Positive Technologies reveals that 93% of enterprise networks are vulnerable to external attacks, which shows the critical need for penetration tests to address weaknesses before exploitation. The Verizon DBIR reports that 83% of breaches stem from exploited vulnerabilities, stressing the urgency of patching systems promptly and conducting regular audits to maintain security.
Penetration tests are not just a formality; they act as real-world stress tests for systems, uncovering weaknesses that automated scans overlook. Beyond periodic audits, ongoing oversight provides another layer, detecting unusual activity such as abnormal logins or unauthorized API access before these issues grow into full-scale breaches.
Build a robust incident pesponse plan
No system is entirely immune to breaches or failures, even with the strongest defenses in place. A detailed incident response plan ensures that when issues arise, the response is swift, strategic, and effective. Key steps, such as isolating affected systems, assessing the scope of the incident, and transparently communicating with stakeholders, help minimize the fallout. A well-structured plan prioritizes fast recovery to cut downtime and limit financial or reputational damage.
The IBM Cost of a Data Breach Report (2024) found that organizations with incident response (IR) teams and plans in place contained breaches significantly faster. Specifically, they found that organizations with incident response teams and plans contained breaches in an average of 230 days, compared to 330 days for those without. That’s a difference of 100 days, highlighting the significant impact of having a plan.
Use AI in cybersecurity solutions
Cybersecurity has entered a new era with AI at the helm. With its ability to flag irregularities in data and act precisely, AI has redefined what it means to protect systems and sensitive information.
- Uncovering Threats: AI identifies malicious behavior, exposing attacks like phishing and malware with speed and accuracy.
- Fraud Prevention: AI spots irregular transactions and blocks unauthorized access to safeguard financial and personal data.
- Endpoint Protection: AI monitors devices across networks to ensure security against breaches.
- Threat Intelligence: AI analyzes global data to provide insights into emerging vulnerabilities and attack methods.
- Risk Mitigation: AI isolates compromised systems and neutralizes malicious actions to limit damage automatically.
AI doesn’t replace human expertise but strengthens defenses by providing speed, precision, and adaptability. With the increasing sophistication of cyber threats, leveraging AI becomes a necessity for building proactive and adaptive cybersecurity defenses.
Partner with cybersecurity experts
Outsourcing critical cybersecurity needs to specialists ensures access to cutting-edge expertise without the overhead of maintaining in-house teams. Experienced cybersecurity specialists, like our team at Relevant, provide more than tools—they deliver tailored strategies designed to tackle the specific challenges of the fintech industry. Collaboration with third-party auditors and regulators strengthens regulatory compliance efforts and builds a foundation of trust with customers and partners alike.
Insights to consider:
- 60% of financial technology firms now use external partners for cybersecurity, a number expected to grow as threats increase.
- Third-party vulnerabilities account for 56% of fintech-related breaches.
- 79% of financial CISOs have reported that threat actors are utilizing more sophisticated cyberattacks annually, emphasizing the need for expert collaboration.
Our FinTech success stories
At Relevant, we don’t just deliver software—we create platforms that inspire trust and meet the demands of a rapidly changing industry. Each project reflects our deep understanding of fintech product development and addresses the toughest fintech cybersecurity challenges along with compliance, security, and innovation. Let’s take a closer look at two standout examples:
Swift Onboard
The idea that security and usability don’t mix is outdated, and Swift Onboard is proof. It handles one of fintech’s toughest challenges—getting new customers onboard fast while meeting compliance demands—by blending advanced technology with a simple, user-focused design.
FirstHomeCoach
Buying a home comes with enough stress; safeguarding sensitive data shouldn’t add to it. FirstHomeCoach shines by leading users through the home-buying process with a focus on data protection. Whether users calculate mortgage options or store sensitive documents, they can trust their information remains secure.
Build secure FinTech solutions with Relevant
At Relevant, we recognize that cybersecurity in fintech is not merely a requirement—it is the cornerstone of trust and a critical driver of sustainable growth. Security is not an afterthought in our process; it is deeply integrated into the architecture of every solution we deliver. Whether it is IoT integrations, AI-driven algorithms, or customer-facing platforms, our managed cybersecurity services allow you to withstand real-world threats.
Contact us to make a fintech future secure, innovative, and grounded in trust.
FAQ
Our core services:
Do you want a price estimate for your project?
Do you know that we helped 200+ companies build web/mobile apps and scale dev teams?
Let's talk about your engineering needs.
Write to us