How Regular IoT Firmware Updates Can Prevent Security Breaches

Connecting everyday devices to the Internet unlocks real value. Behind every successful IoT software development lies a critical layer that is often overlooked: IoT firmware. It turns hardware into a dependable, secure, and updatable device.
Firmware does more than keep devices running. It adds features through updates, without a hardware swap. For businesses, that means longer product life and better ROI.
from 25 countries outsourced software development to Relevant
We provide companies with senior tech talent and product development expertise to build world-class software.
If you’re new to smart technology, start with what IoT firmware is and why it matters for device functionality. This guide explains basics, architecture, and maintenance at scale.
What is IoT firmware and how does it work?
Firmware is the built-in software that lets a device’s hardware work properly. Stored in the device’s memory, it acts as a bridge between the physical components and the main software. It controls basic startup tasks and complex functions, helping sensors collect data, process it, and communicate with other devices or the cloud.
You’ll find firmware in almost every modern product — computers, phones, home appliances, cars, and many electronic components. Without it, hardware would remain inactive, unable to run tasks or connect with other systems.
Source: Microsoft
IoT device firmware components
Firmware is the invisible engine inside every IoT device. It connects raw hardware to the functions users actually care about. Depending on the device’s complexity, the firmware might range from a simple boot routine to a whole operating system with middleware and security layers.
Core components
- Bootloader: The very first software that comes alive when the device powers up. It configures the hardware, sets memory, and hands control over to the operating system or application.
- Kernel: Often described as the brain of the system. It allocates resources, manages tasks, and coordinates device drivers. While small devices might not need one, many advanced IoT products do.
- File system: Configuration files, logs, and stored data live here. Think of it as the device’s filing cabinet, keeping everything organized.
- Device drivers: The translators between hardware and software. Drivers allow the operating system and applications to use sensors, radios, or displays effectively.
Application-specific components
- Application logic: Here lives the real “purpose” of the device. In a smart thermostat, for instance, this layer would handle temperature readings, apply control algorithms, and manage interactions with the display or mobile app.
- Communication protocols: These protocols enable connectivity in IoT, connecting devices to external systems via Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, Zigbee, and cellular networks.
- Security modules: These ensure the device’s safety and data security through encryption, authentication, and access control. Focusing on security in firmware development helps prevent unauthorized access and protect against data breaches.
- Update mechanism: Firmware updates enhance device performance, add features, and fix bugs, which are crucial for Internet of Things products. Any IoT device firmware update can be downloaded and installed remotely. A reliable update mechanism in place ensures that devices can receive binary files for updates without manual intervention.
Additional components (depending on device complexity)
- Real-time operating system (RTOS): Used in devices with strict timing needs, an RTOS ensures predictable scheduling and efficient resource use, making complex systems more reliable.
- Middleware: This software layer bridges the operating system and applications. It manages data and communication, reducing development effort through reusable services.
- Libraries: Libraries provide ready-made, reliable code for common tasks such as calculations or encryption. They help developers work faster and reduce mistakes.
Note: The number and complexity of firmware components depend on the device’s purpose and capabilities. Simple devices may use only basic firmware, while advanced products often require layered software stacks with third-party modules for added functionality.
How does IoT firmware differ from software?
People often mix up firmware and software, yet they live in different layers of a device. Firmware sits in non-volatile memory on the device itself. It links chips, sensors, and radios to everything above, powers the board at power-on, configures drivers, and governs core behavior. Firmware is rarely updated, and each new version must be carefully tested, as a faulty update can make the device unusable.
Software operates on a higher level. This is where apps, services, and user interfaces run. It adds functionality, connects with cloud platforms, and updates often. If something goes wrong during an update, it’s usually easy to roll back without causing serious issues.
Firmware is the foundation of a building, providing stability and structure. Software is the furniture and décor, shaping how people use and experience the space.
Firmware runs directly from the device’s built-in memory, communicates with hardware, and operates under strict power and memory limits. Software loads from regular storage or the Internet, interacts with users and other programs, and faces fewer restrictions.
Key features of advanced IoT firmware
Advanced firmware turns raw hardware into a secure, reliable, efficient product that keeps improving. It sets trust at boot, protects data in motion and at rest, manages power, and recovers cleanly from faults. It also streamlines fleet operations with observability, safe rollback, and controlled over-the-air (OTA) updates. Below, we break those capabilities into clear functions so the flow from “why it matters” to “how it works” is easy to follow.
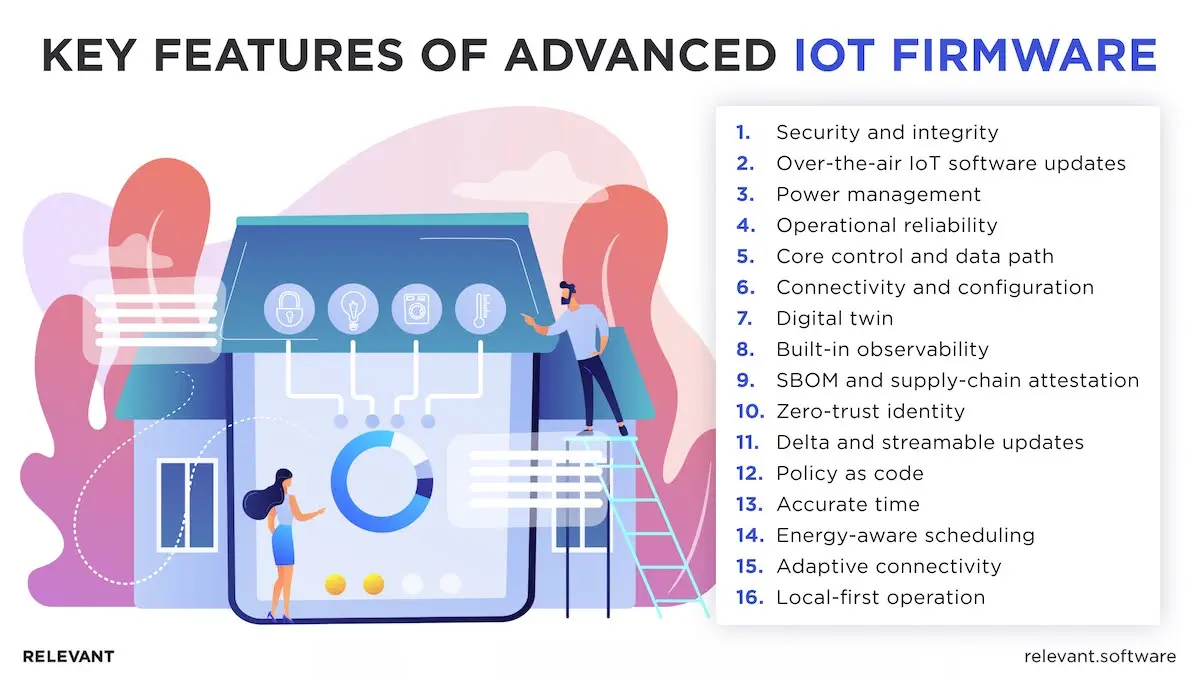
- Security and integrity. A hardware root of trust anchors secure boot. The bootloader, OS, and app image are verified before execution. Continuous integrity checks monitor the system during operation, while encryption protects data at rest and in transit. Secrets stay in secure storage. This is the foundation of strong security.
- Over-the-air IoT software updates. Modern firmware updates are digitally signed, verified, and applied atomically to ensure reliability. Each update is verified before installation and cannot be replaced with an older, less secure version. Updates roll out gradually to small test groups, then to more devices, with checks at every step to ensure everything works properly.
- Power management. Power management helps IoT devices run longer. Deep sleep and standby modes save energy, while radios and sensors activate only when needed. Data is sent in batches using efficient protocols such as BLE or LoRaWAN, allowing devices to remain active longer between charges or maintenance visits.
- Operational reliability. Operational reliability keeps IoT devices stable and recoverable. A watchdog—a built-in timer that monitors the system—automatically restarts the device if it freezes or stops responding. Backup firmware images restore normal operation after a failed update. Detailed logs and remote diagnostics help teams quickly find and fix issues, even when devices are far away.
- Core control and data path. Core control and data-path functions enable the device to operate smoothly. The firmware starts up the hardware, sets up drivers, calibrates sensors, removes signal noise, and controls actuators. It also compresses or groups data before sending it, so only useful information goes to the cloud, saving both bandwidth and costs.
- Connectivity and configuration. Connectivity and configuration ensure devices stay connected and consistent. The firmware handles Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, cellular, Zigbee, and Thread connections with stable pairing, quick reconnection, and smooth data transfer. Device identity, settings, and feature controls are securely stored and kept in sync with cloud policies to prevent errors or data corruption.
- Digital twin. A digital twin is a virtual version of the physical device stored in the cloud. It reflects the device’s current settings and status in real time. Teams can use it to test updates, adjust configurations, or try new policies safely, without affecting the actual device until everything is confirmed to work correctly.
- Built-in observability. Built-in observability means the firmware continuously collects and organizes key data about how the device performs. Metrics, traces, and structured logs give engineers clear visibility into system health. This helps them confirm service levels, spot problems early, and plan capacity based on real performance data.
- SBOM and supply-chain attestation. SBOM and supply-chain attestation make firmware more transparent and secure. Each release includes a signed list of all software components and their origins. This helps identify and block risky parts before deployment, speeds up compliance checks, and strengthens overall supply-chain trust.
- Zero-trust identity. Zero-trust identity ensures that every device and session is verified before access is granted. Each device uses its own certificate and short-lived credentials linked to secure hardware. If a device is compromised, its access is instantly revoked, protecting the rest of the network from unauthorized activity.
- Delta and streamable updates. Delta and streamable updates make firmware upgrades faster and lighter. Instead of downloading a full new version, devices receive only the parts that have changed. This reduces data use, shortens update times, and keeps large fleets of devices responsive throughout the process.
- Policy as code. Policy-as-code means device rules are managed the same way software is. Access permissions, data retention settings, and update schedules are stored in versioned files. Teams can easily review, test, and revert policy changes, ensuring consistency and control across all devices.
- Accurate time. Accurate time is critical for reliable device operation. Secure NTP or PTP protocols keep clocks synchronized and check for drift or errors. Precise timing supports scheduled tasks, validates security tokens, and ensures trustworthy audit logs.
- Energy-aware scheduling. Energy-aware scheduling helps devices balance performance with power efficiency. Tasks are timed according to strict energy limits. Radios send data in short bursts, sensors activate only when needed, and the system still meets performance goals while conserving battery life.
- Adaptive connectivity. Adaptive connectivity keeps devices online wherever they are. Using eSIM and eUICC technology, devices can automatically switch between mobile carriers without physically swapping SIMs. This prevents connection loss, reduces roaming costs, and ensures updates and data transfers continue smoothly.
- Local-first operation. Local-first operation ensures devices keep working even without an internet connection. Core functions run offline, and data is stored temporarily on the device. Once the network returns, the data syncs automatically, so users experience slower performance instead of full outages.
Related – How to build an IoT dashboard.
Why firmware matters in IoT systems
Firmware is the control tower for connected hardware. It brings the device to life, initializes components, and ensures that the code that runs at startup runs. It establishes secure links, validates sensor input, and routes the right data to the right destination.
Security starts here. Verified boot blocks untrusted code. Modern encryption protects data at rest and in transit. Keys and identities stay protected, so only trusted peers connect.
Performance and stability do too. The firmware schedules time-critical tasks, puts radios and sensors to sleep when idle, and recovers cleanly after faults. It keeps core features working during outages and syncs when the network returns.
Over the lifecycle, firmware manages identity, configuration, and updates. It supports safe OTA rollouts with health checks and rollbacks. That keeps fleets consistent as they scale and as standards evolve.
Without strong firmware, devices feel fragile. With it, even small form factors deliver dependable, long-lived value.
Firmware updates in IoT devices
What is firmware update in IoT? Firmware updates keep IoT devices secure, stable, and up to date. They fix bugs, close security gaps, and add new features without needing to replace or manually service each device.
Most modern IoT systems use over-the-air (OTA) updates, which send new firmware remotely. This saves time and maintenance costs, especially for large device fleets. But updates must be carefully managed to avoid issues such as failed installs, power outages, or poor network connectivity.
Reliable systems use dual-bank storage so devices can safely roll back if an update fails, and delta updates send only the changed parts of the code, saving bandwidth. Staged rollouts start with a few devices before expanding fleet-wide, helping catch issues early.
At Relevant Software, we build firmware update systems that make IoT devices secure, easy to maintain, and ready for the future.
Best practices for IoT firmware development
If updates feel stressful, you do not have a process. This section gives you one. The goal is simple: fewer surprises, steadier uptime, and results you can measure. Use our checklist below to turn releases from guesswork into a repeatable playbook.
Define measurable goals
Set clear targets so everyone knows what success looks like. Track metrics for security, reliability, and cost. Aim for a 99.5% update success rate, a mean time to recovery (MTTR) under 10 minutes, improved battery life, and a defined daily data budget per device.
Test on real hardware
Develop and test on the actual devices you plan to ship. Automate builds and tests using CI/CD. Include real-world scenarios like power loss, weak Wi-Fi, low memory, or sensor noise. Run static analysis, memory checks, and attach a Software Bill of Materials (SBOM) to every build for traceability.
Optimize for power, visibility, and offline work
Save power by putting radios and sensors to sleep until needed. Capture logs and metrics to track Service Level Objectives (SLOs). Design the system to handle outages — store data locally and sync safely once the device reconnects.
Prepare your team and processes
Make sure operators know how to monitor and recover devices. Always keep a rollback option ready. Track firmware versions, update success rates, and connectivity health across your fleet. Treat firmware like a living product with its own roadmap, not a one-time project.
The IoT firmware update process (step-by-step)
Updates should be calm and predictable. Below, Relevant Software experts explain the approach we use to keep risk low and uptime steady. You will learn what to focus on, what to avoid, and how to make each release repeatable and auditable without slowing the business.
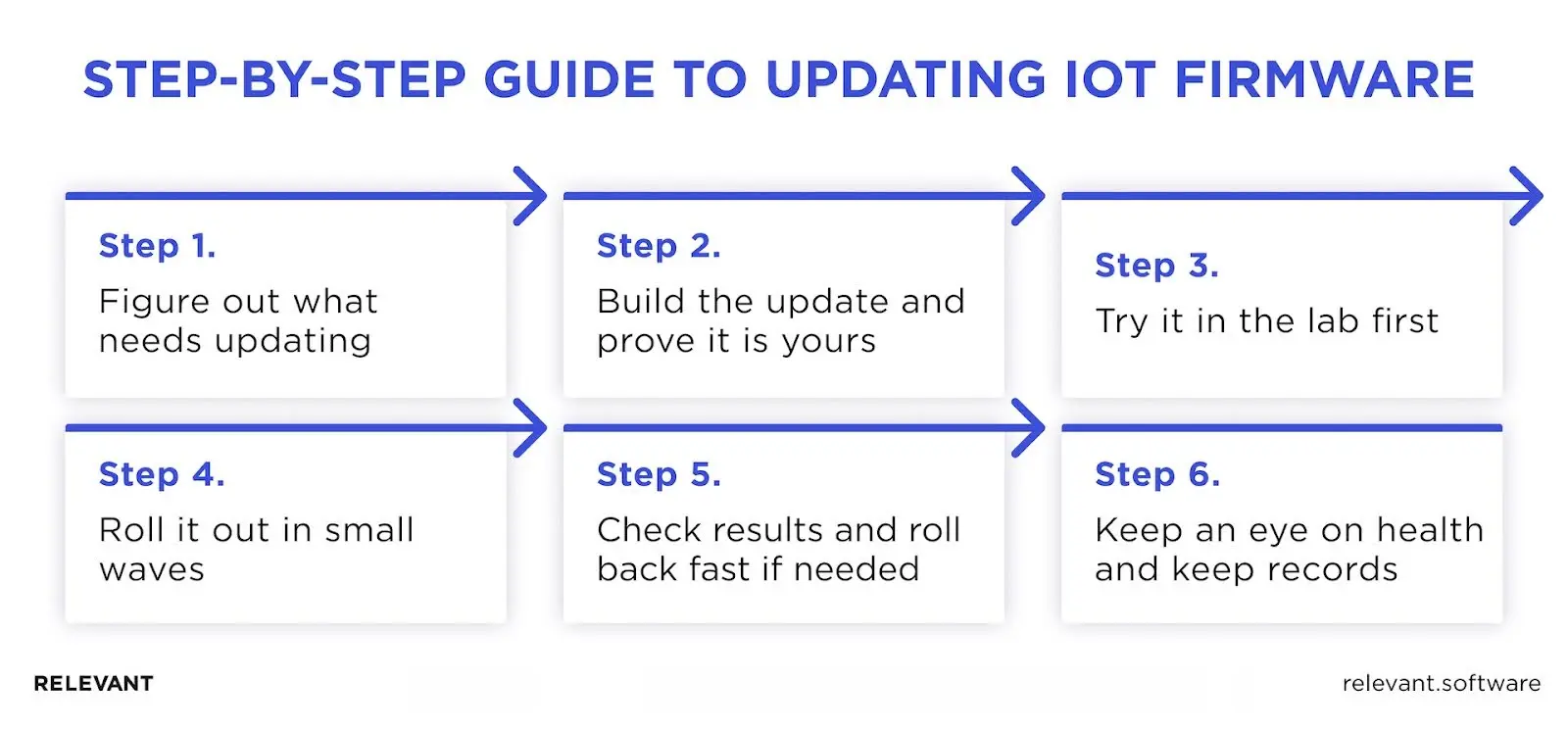
1) Figure out what needs updating
Start with a complete list of device models, current versions, and available storage. Check network type, hardware limits, and known issues. Note dependencies or minimum versions that may require an intermediate update before the main rollout.
2) Build the update and prove it is yours
Generate the new firmware image using a clean, automated build pipeline. Sign it, attach a Software Bill of Materials (SBOM), and include provenance details for traceability. Write simple release notes with step-by-step installation instructions for operators.
3) Try it in the lab first
Test the update on real devices, not just in simulations. Make sure each device starts correctly, reads its sensors, and stays connected to the network. Then try breaking things on purpose by cutting the power during installation or weakening the Wi-Fi to see how the system recovers. Watch how much power and memory the firmware uses, and let tests run overnight to catch problems that only appear after long use.
4) Roll it out in small waves
Start by sending the update to a small group of test devices. Watch how they work and fix any issues before updating more devices. When everything looks stable, roll it out to everyone. Use two firmware versions (A/B setup) so devices can safely switch back if something goes wrong. Keep secure boot enabled at all times to ensure updates remain safe.
5) Check results and roll back fast if needed
Track installation success, crash-free operation, and key user actions. If metrics fall below acceptable thresholds, initiate an immediate rollback to minimize risk and restore normal operation fast.
6) Keep an eye on health and keep records
After releasing the update, monitor its performance in real-world use. Track the time each update takes, the number of retries, any impact on battery life, and possible errors. Keep detailed notes about the version, approval, release date, and the devices that received it. Clear documentation makes audits easier and helps future updates in remote IoT device management run more efficiently.
Our IoT case studies
Want proof from our engineers? Review these two projects to see how we design, deliver, and optimize connected systems.
Case 1: Remote sensor management
Sensor Innovation hired our team to upgrade its remote sensor platform for humidity and leak detection across industrial and residential sites. We rebuilt the dashboard, added interactive building maps, enabled mobile use in the field, and applied weather-aware alert filters.
The system now shows detailed sensor conditions and generates clear reports. Results: accuracy up 45%, false alarms down 40%, full coverage, 6,500 sensors across 500+ sites, and 25% better scalability. The client praised structured work, clear communication, and on-budget delivery.
Case 2: Real-time air quality at scale
Airthings asked us to rebuild its global air quality dashboard for real-time insight at scale. Devices in 7,000+ buildings and 1,000+ professional accounts needed instant data with a smooth interface.
We delivered customizable dashboards with drag-and-drop tiles, clear device and sensor views, threshold alerts, and CSV export. The new Mapbox map uses clustering and server-side rendering to remove lag.
Results: 100% real-time visibility, faster maps, and confident decisions across a fleet that exceeds one million units. The client praised our expertise, fair rates, responsive process, and reliable delivery.
IoT firmware: bottom line
Need a clear plan for connected products? Our IoT consulting services help you move from idea to stable operation without the guesswork. We start with discovery and a light audit of devices, networks, and risks. Then we shape a practical roadmap for firmware, OTA strategy, security, and compliance.
You get choices explained in plain language, timelines you can run, and KPIs that show progress. Our IoT development company partners with your team to prototype, test on real hardware, and prepare a safe rollout with monitoring and rollback. Simple goal, steady results: faster releases, fewer outages, and devices your users can trust. Contact us!


Hand-selected developers to fit your needs at scale! Let’s build a first-class custom product together.

