10 Common Web Application Security Vulnerabilities and How to Prevent Them in 2024

Web applications are one of the most common targets for hacking because they provide easy access to a wider audience, allowing malicious code to spread faster. But, alas, many companies seriously think about how to secure the company from web application vulnerabilities only after the incident has already occurred.
Let’s face it; this oversight has a price – for example, a data breach in 2024 is expected to cost the world $9.5 trillion. However, many of these incidents could have been prevented with the proactive and defensive approach to web security.
from 25 countries outsourced software development to Relevant
We provide companies with senior tech talent and product development expertise to build world-class software.
We want to save your money and your nerves. Therefore, we at Relevant have prepared an article about the most common vulnerabilities in web applications and best practices for protecting your web apps from malicious attacks and accidental damage in 2024.
Web Application Vulnerabilities: Why are Web Applications So Vulnerable to Attacks?
Web apps can be attacked for various reasons, including system flaws resulting from incorrect coding, misconfigured web servers, application design flaws, or failure to validate forms. Any web application has at least one vulnerability that hackers can exploit at a higher level.
Such web application vulnerabilities allow criminals to gain direct and public access to databases that contain valuable information (e.g., financial details or personal data), making them a frequent target of attacks.
Cloud containers that package application software with the elements needed to run it have recently been found particularly vulnerable when they are not properly secured or contain insecure elements. The use of open source and reliance on application programming interfaces (APIs) also exacerbate security concerns.
Predictable resource location, SQL, and code injections were the top three security breaches, making up 64% of all attacks on web apps and APIs. While the number of DDoS attacks on web apps reduced by 33% in 2023 compared to 2022, the frequency of hostile web app transactions increased exponentially, surging by 500%. Attackers are now focusing more on online apps and their infrastructure, with DDoS attacks moving towards more complex attacks aimed at web applications.
Distribution of critical web application vulnerabilities worldwide as of 2022
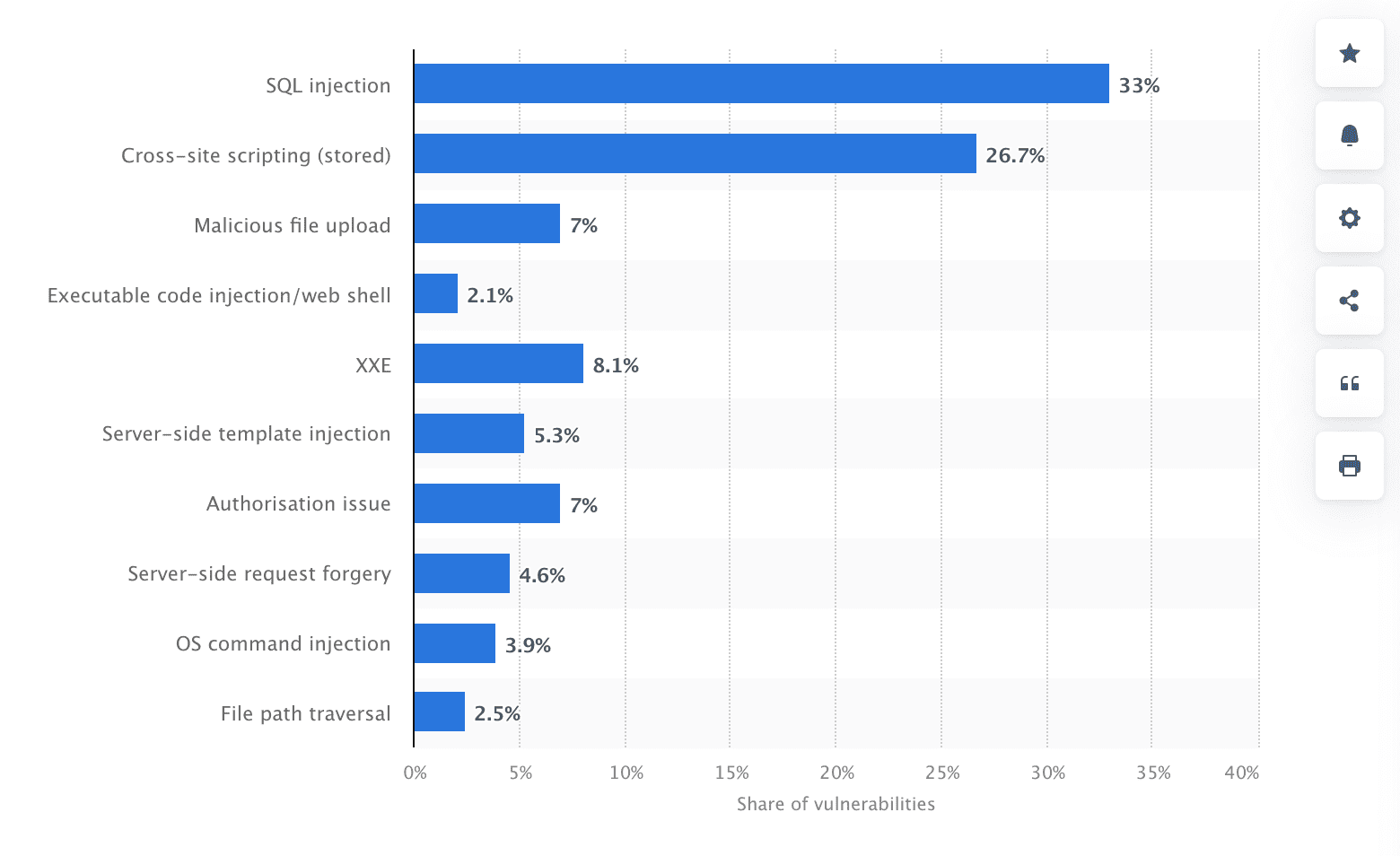
Cybercriminals use compromised sites for various purposes: to spread malware, steal sensitive data, implant unauthorized information, commit fraud, and infiltrate a company’s internal infrastructure. All this threatens the organization’s operation and reputation. Therefore, securing software and eliminating all potential vulnerabilities in a web application is more than just a choice; it’s imperative in 2024.
That’s why further we highlight how to find vulnerabilities in web applications and what to do to mitigate the risks.
OWASP Top 10 Vulnerabilities: General Overview
The Open Web Application Security Project (OWASP), an open-source community, aims to make the web the safest for users by creating an overview of the most prevalent web application vulnerabilities and providing industry best practices to mitigate them.
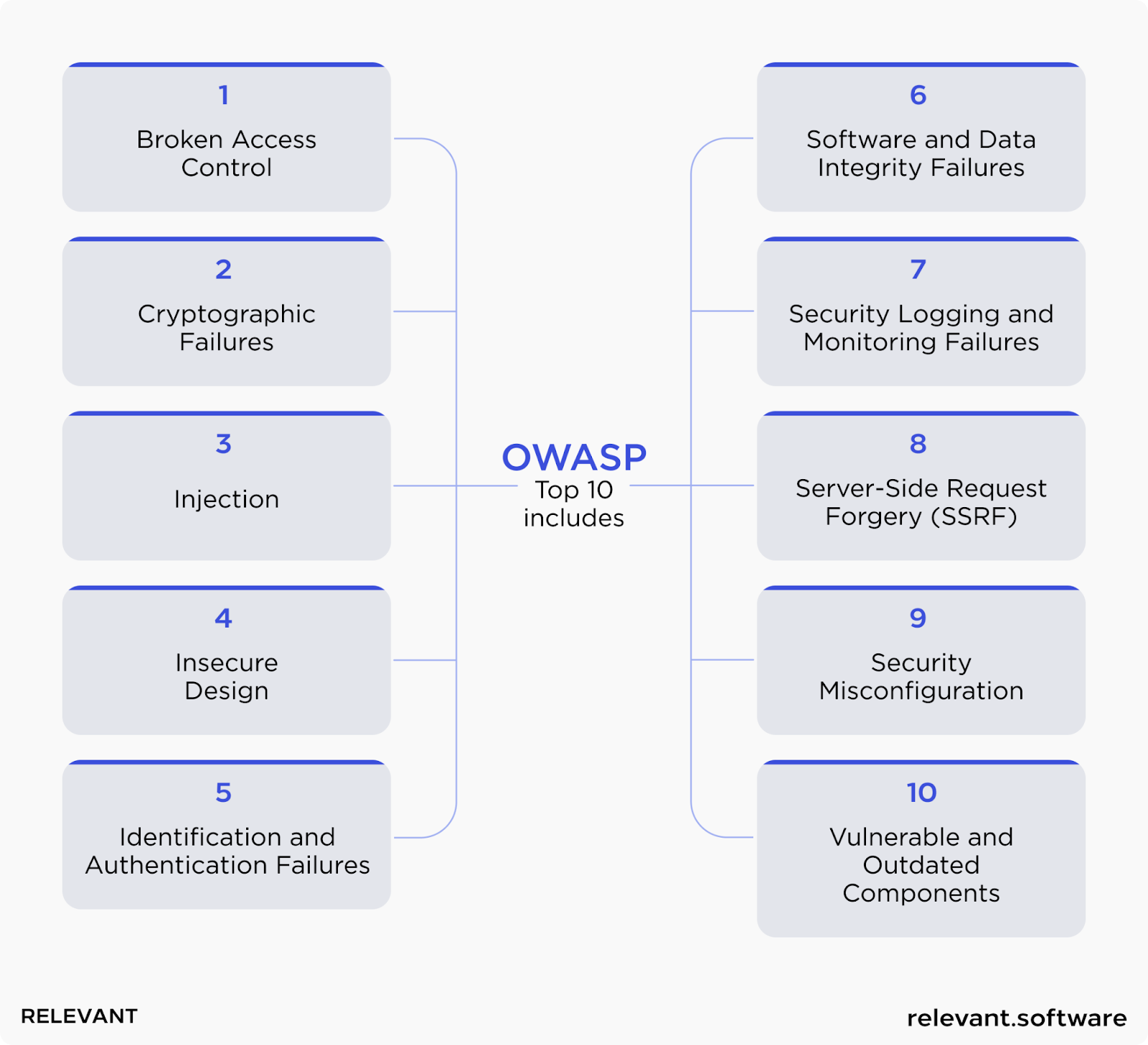
OWASP Top 10 is not just a web application vulnerabilities list. It rates each class of weaknesses using the OWASP Risk Rating methodology and provides examples, attack prevention recommendations, and links for each risk. By examining the Top 10 web application vulnerabilities of OWASP, application developers can take concrete steps to create a more secure application that will help keep users safe when it comes to malicious attacks.
OWASP web security list serves as a lighthouse and is updated every few years based on data from security audits and surveys of experts within the industry. On the diagram, you can see the changes in this list from 2017 to 2021.
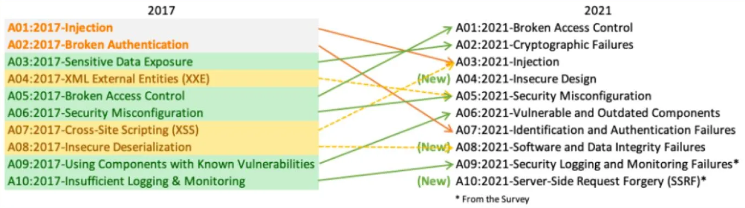
So let’s consider the latest web applications vulnerabilities and ways to prevent them in 2024.
Broken Access Control
At the top of the web application vulnerabilities list is Broken Access Control. Picture a burglar managing to disguise himself and fool the guard dog, or worse, a trusted visitor secretly pocketing the keys. In the digital world, these scenarios might take the form of spoofing or reusing a JSON Web Token (JWT) access control token. It could also involve modifying cookies or hidden fields to elevate privileges or make use of JWT revocation.
But there’s more. Let’s say you’ve got a members-only club, but due to an oversight, the doors are open to anyone and everyone. This is akin to violating the default rejection principle in the digital realm. Administrators should ideally grant access only to those individuals or roles that carry the right passcodes or, better yet, the right capabilities. But alas, a loophole means the doors are wide open, providing a free pass for anyone who stumbles upon it. As you can imagine, such errors can make it a walk in the park for attackers to gain access to their targeted content.
In essence, while access control is our digital guardian, it’s crucial to ensure that it’s foolproof to keep out those with malicious intentions. Our security is only as strong as our weakest link, after all.
Affected objects:
The implications of broken access control are chilling: compromised sensitive data, users granted permissions way beyond their purview, or even outright account takeover attacks, where outsiders seize control and orchestrate fraudulent transactions.
How to prevent a Broken Access Control:
- Safe coding practices and precautions, like password management and identity verification, are your first line of defense. You should also consider disabling administrator accounts and setting up multi-factor authentication.
- Next, apply access control mechanisms uniformly across your application, akin to making sure every door and window in your web app is secure. This step can help minimize cross-origin resource sharing, keeping unwanted guests out.
- Think of domain models as your property boundaries; they should impose constraints on business applications. This way, you ensure that nobody oversteps their mark.
- Also, you should restrict access to APIs and controllers to alleviate the detrimental effects of automated attacks.
- Remember, alertness is the key. Make sure you’re logging access control failures and alerting administrators as needed.
- Finally, don’t just grant users permission to view, create, change, or delete information. Instead, let your model access controls bestow ownership of records.
Each of these measures you take, each precaution you implement, strengthens your digital fortress, keeping intruders at bay.

Cryptographic Failures
Previously known under the banner of sensitive data exposure, these web application vulnerabilities have climbed the ranks to occupy the number two spot. Here, we’re not focusing on the symptoms but rather the root cause – those little hiccups in cryptography, or even their complete absence, that can inadvertently lay bare sensitive data.
At the core of these failures can lie a spectrum of issues:
- Using weak or outdated encryption algorithms that can be easily broken with modern computing power.
- Improper implementation. Even strong encryption algorithms can fail if they are not implemented correctly. Common mistakes include using default or hard-coded encryption keys, improper storage of keys, or errors in the encryption/decryption process that leave data exposed during transmission or storage.
- Poor key management practices, such as reusing keys across multiple systems or failing to rotate keys periodically.
- Vulnerabilities in cryptographic libraries. Many web applications rely on third-party cryptographic libraries for encryption tasks. Web application vulnerabilities within these libraries can introduce cryptographic failures, especially if they are not regularly updated to patch known issues.
Affected objects:
We’re talking about passwords, email addresses, patient health records, proprietary business secrets, credit card information, and more. Picture this: an application diligently encrypts credit card information using automatic database encryption. All good so far, right? But when this information is accessed, it’s instantly decrypted. This security vulnerability in web applications paves the way for an SQL injection failure to extract the credit card information in plaintext – a field day for any attacker lying in wait.
How to prevent cryptographic failures:
- When storing passwords, use robust, salted, and adaptive hashing algorithms with delay factors, like Script or PBKDF2. It’s akin to not just locking your valuables in a safe but also choosing an intricate lock that’s nearly impossible to crack.
- If you’re transferring sensitive data, avoid outdated protocols like Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP) or File Transfer Protocol (FTP).
- Choose authenticated encryption over simple encryption. It’s the difference between a simple handshake agreement and a legally binding contract – one just offers more security.
- Finally, when it comes to keys, make sure to generate and store them as cryptographically random arrays of bytes. And if passwords are used, replace them with a key using a password-based key generation algorithm.
Injection
An injection flaw is one of the security vulnerabilities in web applications that allow a cyberattacker to slip in malicious code through an application all the way to another system. These injections come in various shapes and sizes, including SQL injections, command injections, CRLF injections, LDAP injections—you name it.
They have a broad impact, compromising backend systems and any other clients tethered to the vulnerable app. It’s like a poisonous vine, spreading its dangerous tendrils far and wide. In fact, code injection (14%) and SQL injection (11%) alone account for a whopping quarter of all web application attacks.
Affected objects:
Injection attacks are a crafty way for cyber invaders to sneak into off-limits areas and hunt sensitive data, all while pretending to be trusted users. The likely targets? The Input Fields and URLs that communicate with the database.
How to prevent injection:
- Prevent injection attacks by validating or sanitizing the data submitted by users. Think of it as having a meticulous doorkeeper who rejects suspicious visitors (validation) or cleans up anything dubious they might bring (sanitizing).
- Use an API that avoids the interpreter entirely or employ a parameterized API. Alternatively, you can shift towards tools that offer object-relational mapping. It’s like opting for a safer route to your destination.
- Implement positive server-side input validation. Consider it a double-check system, ensuring that only the correct data gets through.
- Use constraints like LIMIT within SQL queries to prevent colossal data exposure during a SQL injection.
- Lastly, avoid showing detailed error messages that could be a gold mine for an attacker.
[e-book id=”8445″]
Insecure Design
This category, newly introduced to the OWASP Top 10 vulnerability list, hones in on design and architectural flaws that pave the way for increased security threats. Imagine the painstaking effort put into the perfect implementation of security controls and risk mitigation, only to have it all undermined by foundational design flaws. Even the most expertly crafted security measures can’t hold up if the underlying structure is flawed. Surely, savvy attackers will sniff out and exploit these web application vulnerabilities sooner or later.
How to prevent design weaknesses:
- Collaborate with Relevant experts to establish a secure development lifecycle. Think of it as engaging top-notch architects and engineers for your digital skyscraper, ensuring it’s built with robust security and privacy controls.
- Use threat modeling for access control, rigorous testing, application logic, and core flows. Picture it as the rigorous safety checks a new skyscraper must pass, scrutinizing every nook and cranny for potential weaknesses.
- Perform penetration testing to detect any security loopholes – from the source code and database to the back-end network. By discovering design weaknesses before they become critical, you will ensure a robust and secure online presence for your business.
- Incorporate security terminology and controls in user stories. It’s like using a language everyone understands, ensuring all stakeholders are on the same page when it comes to security.
Identification and Authentication Failures
In a digital world that’s becoming increasingly complex, authentication failures are relatively common security vulnerabilities in web applications. If your web app’s user identification, authentication, or session management functions are not accurately implemented or adequately secured, it could open up a can of worms.
The very essence of these web application vulnerabilities lies in the delicate balance of granting access to legitimate users while barring entry to unauthorized entities. Any misstep in maintaining this balance, like relying on weak authentication methods, mishandling session tokens, or neglecting security measures for password recovery processes, can serve as an invitation to malicious actors.
Affected objects:
Authentication vulnerabilities in a web application can include brute force attacks, where hackers attempt numerous password combinations until they hit the jackpot. Or it could be inadequately hashed and salted passwords that are much easier to crack. Data leaks involving user account details, poorly set timeouts leading to sessions left open longer than necessary, or even something as seemingly harmless as weak passwords such as ‘password1’ or ‘admin1234’ are all web application vulnerabilities ripe for exploitation.
How to prevent authentication vulnerabilities:
- Implement multi-factor authentication, providing a solid wall of security. Thus, even if a cybercriminal cracks a user’s password, they’d still need to bypass another protection.
- Develop and implement rigorous password rules and mandate periodic updates. This approach could differ between a secure fortress and an open house.
- Properly set session timeouts and password security in your database. Only leave sessions open as long as necessary.
- Adjust authentication requirements based on the risk associated with the access request. For example, accessing sensitive financial records might require additional verification steps compared to less sensitive information.
- Implement single sign-on (SSO) to reduce the number of times a user needs to authenticate, thereby decreasing the potential attack surface for cybercriminals. SSO systems can be fortified with strong authentication measures, ensuring that accessing multiple resources requires only one set of credentials, managed securely.
- Use AI and machine learning algorithms to analyze user behavior patterns and detect anomalies that may indicate unauthorized access attempts. For instance, a login attempt from a geographical location vastly different from the user’s typical patterns can trigger additional verification steps or alert administrators.
Software and Data Integrity Failures
It’s one of the most common vulnerabilities in web applications. You wouldn’t eat food without knowing its source, would you? The same principle applies to web applications that leverage modules, extensions, or repositories from Content Delivery Networks or unverified sources. Without thoroughly checking these sources’ integrity, you’re opening the door wide for malicious code, unauthorized access, and potential compromise.
Affected objects:
Today, most software delivery pipelines include an auto-update functionality. This handy feature helps keep your software fresh, downloading and applying updates seamlessly, often without the need for explicit permissions. However, while this is undoubtedly convenient, it’s also a golden opportunity for cyber attackers.
They can, for example, execute a Man-in-the-Middle attack to inject harmful code into the pipeline during an update process. Suddenly, what should have been a routine update becomes a Trojan horse, delivering corrupted payloads right into your application installations.
How to prevent potential threats:
- Digital signatures can serve as a trusted stamp, confirming that the data or software comes from the original sources without any meddling.
- Secure your CI/CD workflow and ensure adequate segmentation, access control, and parameterization. This shields your code’s integrity during configuration and deployment operations, essentially building a fortress around your code.
- Perform rigorous integrity checks. If you need to send unsigned or unencrypted compilation data to untrusted clients, ensure you’ve conducted a comprehensive integrity check or digital signature. This step can help detect any alterations or duplications of the data, giving you an extra layer of security.
Security Logging and Monitoring Failures
Without the right tools to track your web application vulnerabilities, you’re essentially navigating blind. Hence, logging and monitoring provide essential accountability, give you a clear view of what’s happening, trigger incident alerts, and serve as a vital aid for forensic investigations. If these systems fail, it’s similar to turning off the ship’s radar – your ability to detect and react to breaches is severely compromised.
Affected objects:
Without sufficient monitoring, logging, or reporting, your web application becomes an open target. Attackers can exploit web vulnerabilities in any part of the application stack, with potential impacts ranging from minor disruptions to devastating breaches.
Preventing Logging and Monitoring Malfunctions:
- Keep Detailed Logs. Log all authentication, access security, and server-side data validation issues. Ensure these logs carry adequate user details to identify dubious or deceitful accounts. More importantly, these logs should be stored long enough to support thorough investigations if needed.
- Use Standard Log Formats. Make sure that your logs are generated in formats that your log management systems can handle. This ensures compatibility and makes log analysis and management easier.
- Have a Solid Recovery and Incident Response Strategy. Adopt established strategies like NIST 800-61r2 or a newer version. This provides a robust framework for handling incidents effectively.
- Set Up Effective Monitoring and Alerts. Detect and react to suspicious activities quickly with real-time monitoring and instant alert systems. Quick response is crucial in the face of potential breaches.
- Encrypt Your Log Data. Protect your log data with strong encryption. This safeguards your monitoring systems from intrusions or cyber threats.
Server-Side Request Forgery (SSRF)
It’s a deceptive cyber exploit that tricks a web application into sending a fake request to an unintended location. What’s particularly disastrous about this attack is that it can even penetrate secure bastions guarded by VPNs, firewalls, or network access control lists. This ability to sneak past defenses makes SSRF a major threat among common web application vulnerabilities.
What amplifies the danger of SSRF is that an attacker can perform an internal reconnaissance attack and collect internal information about a target network secretly. They exploit the trust placed in the web app by internal systems and search for any sensitive areas and web application vulnerabilities that can be easily exploited.
Affected objects:
During an SSRF attack, a cyber intruder can manipulate a server, forcing it to access internal services within an organization’s digital fortress. In more complex scenarios, these malicious actors could maneuver the server to link to external systems, risking the leakage of sensitive info such as login credentials.
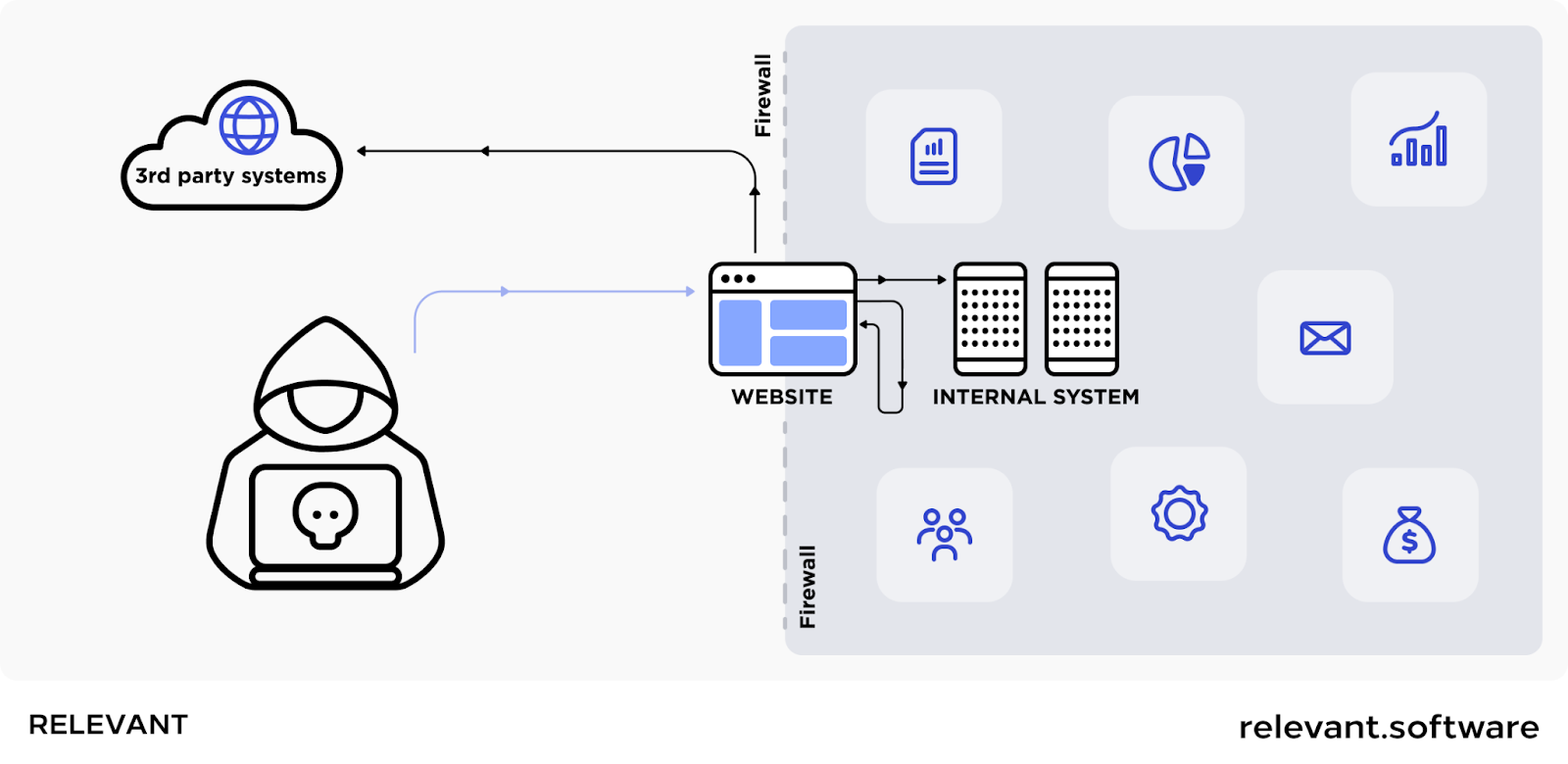
How to prevent SSRF:
- Divide your network into different sections, each with its specific role. Thus, by separating the remote access features into distinct networks, you can efficiently mitigate the damage an SSRF attack can inflict.
- Also, set your firewall settings to a “deny by default” stance or establish network access control rules that block all web traffic, save for necessary internal exchanges.
- Finally, always stay alert and question the legitimacy of URLs. This vigilance can provide a safeguard against insidious attacks such as DNS redirection and “time of check, time of use” situations.
Security Misconfiguration
It happens when your safety protocols aren’t set up correctly or contain mistakes. These not-so-obvious bugs tear open security gaps, leaving your app, its valuable data, and, yes, your entire organization exposed to the dangerous world of cyberattacks or hacking. These web application vulnerabilities are easy targets for cybercriminals.
Affected objects:
Everything from unpatched weak spots, unused pages, unguarded files or directories, dated software, and even running software in a state where it’s laying all its cards on the table – debug mode. Discovering a misconfiguration should set off alarm bells. It becomes essential to sprint towards a security audit, examining any signs of attacks or breaches.
How to prevent security misconfigurations:
Start with ensuring you follow secure construction principles. This involves:
- Synchronizing the development, operational, and QA environments. This facilitates different user privileges and paves the way for automatic deployments to keep your applications battle-ready and defend against any impending attacks.
- Sweeping away any unused features and frameworks. Imagine clearing out any unnecessary stuff lying around your fortress that could provide cover for your enemies.
- And last but not least, establishing a solid platform stripped of unnecessary frills – no unneeded features, components, or even shiny demos or extensive documentation that might increase the chances of weak configuration spots.
Vulnerable and Outdated Components
Most online applications are built using third-party frameworks. So, your app may contain unknown codes that can lead you down a rabbit hole of unexpected events, such as accent control violations, unauthorized access, SQL injections, and other threats.
Affected objects:
If the software is insecure, outdated, or unsupported, you unknowingly open doors to web application security vulnerabilities. Imagine your app as a complex ecosystem consisting of various elements – the application or web server, the operating system, applications, database management systems (DBMS), APIs, other elements, libraries, and runtimes. When any part of this ecosystem becomes compromised, it can lead to a cascade of troubles.
How to prevent risks from weak and obsolete components
Based on our expertise in software development, we strongly recommend the following preventative measures:
- Always acquire your components from official, trusted sources via secure channels.
- Be wary of elements and modules that have stopped providing security updates for older versions or don’t function as they should. If patching is impossible, consider developing virtual patches that can monitor, spot, or shield against identified vulnerabilities in a web application.
- Remove any unnecessary features, directories, components, items, or documents.
While the OWASP Top 10 vulnerability list provides a robust framework for improving web application security, it shouldn’t be-all and end-all. Yes, it heavily emphasizes server-side security, but many of today’s attacks target the client side. In other words, it’s vital to maintain a 360-degree security vision. Consider the Top 10 vulnerabilities by OWASP as a starting point and complement it with strategies tailored to your needs.
Let Relevant Secure Your Web Application
Although application software development and frameworks are becoming increasingly secure, attackers find new ways to attack their weak points. Deployment isn’t the end of the road – security experts must always be on their toes, finding and fixing all possible web applications’ vulnerabilities. The efficacy of these fixies depends on their awareness of cyber threats and the application of strong security practices.
If you lack sufficient resources to defend your web application against cyber attacks, you can outsource it to managed security service providers like Relevant. Our experience in cybersecurity – from architecture and design to delivery and operations, has enabled us to protect apps, infrastructure, and processes for clients from various industries, including fintech, SaaS, and IoT. Contact us if you are searching for a reliable security partner to empower your digital world.
FAQ
What is a vulnerability?
Mistakes are made, even in building and coding technology, often termed bugs. Though not all bugs pose a threat, bad actors can manipulate many. Vulnerabilities can be leveraged to force the software to act in a manner it’s not intended, such as gathering information about the current security defenses in place.What are the solutions to prevent web application vulnerabilities?
You can apply four techniques to detect security loopholes in web applications.– Static Application Security Testing (SAST) scans source code for security vulnerabilities and threats at multiple stages of development, including committing new code to the codebase and creating new releases.– Dynamic Application Security Testing (DAST) can test an application deployed to a staging or production environment and run its code to check for vulnerabilities.– Interactive Application Security Testing (IAST) solutions combine dynamic testing (like DAST tools) with static analysis (like SAST tools) to help identify and manage security risks in web applications.– Penetration testing is a technique that combines human security expertise with dynamic scanning tools to find vulnerabilities in web application security mechanisms.What is container security?
Containers can create major security issues if not managed correctly. Perceive the following security guidelines:– When creating a container, always use trusted base images, and scan them for vulnerabilities before using them.– Use the secrets mechanism in Docker or Kubernetes to store sensitive info.– Never hand out root access. A container with root access is like an all-access pass – if a bad actor breaches it, they’ve got the keys to the container. – Always define a user in your images, and steer clear of using a “privileged container” option in Kubernetes like it’s a dart thrown your way.– Ensure that containers can only access other systems if it’s absolutely essential. – Run containers in a secure subnet and avoid putting them on the Internet unless it’s utterly necessary.How can I find vulnerabilities in web applications?
There are many tried and tested approaches to securing your web applications. For example:– Check the source code to discover known vulnerabilities such as SQL injection flaws, cross-site scripting (XSS) vulnerabilities, etc.– Use the web application scanner to scan your web app for common vulnerabilities.– Run a penetration test to exploit known vulnerabilities and see if they are present in the app.– View logs to find evidence of attack attempts.– Utilize network traffic monitoring to detect any suspicious activity as a brute-force attack on an application.

Hand-selected developers to fit your needs at scale! Let’s build a first-class custom product together.


