Harnessing the Potential of Healthcare Data: An In-Depth Look at the FHIR Data Model

Are your organization still struggling with fragmented healthcare data? Don’t worry because first, you’re not alone. A recent survey shows that 56% of healthcare leaders prioritize interoperability, and another 29% implement interoperability solutions. And second, there is a solution to this challenge. Since traditional approaches often fall short of meeting data security and exchange requirements, organizations increasingly turn to the FHIR data model as the essential tool for this dilemma.
FHIR empowers interoperability, and that’s why it’s rapidly becoming a cornerstone in US healthcare strategy. But why should you care? Because fragmented data isn’t just an IT headache; it’s a roadblock to patient care and operational efficiency. Learn how adopting the FHIR data model can be your first step towards a more integrated, efficient, and patient-centered healthcare system.
from 25 countries outsourced software development to Relevant
We provide companies with senior tech talent and product development expertise to build world-class software.
What is FHIR?
FHIR, short for Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources, is a new standard that addresses the complexities of healthcare data administration and interoperability. Developed by Health Level Seven International (HL7), the FHIR model facilitates the secure and efficient transfer of healthcare information between different establishments and systems. It took the best features of previous HL7 standards. But unlike its predecessors, FHIR also uses the latest web technology, making it easier to implement.
Flexibility and adaptability are the characteristics that set the HL7 FHIR model apart. It employs a set of APIs that allow different healthcare systems to recognize and interpret the data, making it universally applicable. For instance, your hospital might store a patient’s blood type differently than another clinic, and more often than not, this is a ubiquitous situation. FHIR helps you and the clinic you need to share information with to ensure this data can be easily accessed, understood, and utilized.
So, why is FHIR the number one solution to clinical data interoperability challenges? It’s simple because FHIR is built to fit modern web solutions. It supports RESTful architectures that makes it lightweight, scalable, and easy to implement. What’s most important is that FHIR is incredibly secure and meets rigorous industry regulations like HIPAA. So, you can kill two birds with one stone: ensure compliance with laws and achieve the desired data interoperability.
The Importance of Data Interoperability in Healthcare
Many physicians globally found themselves overwhelmed with the increasing amount of patient data generated at a breakneck speed while noticing their healthcare systems becoming more complex. All this calls for an urgent need for standardizing information management and exchange. US health organizations realize it and plan to enlarge their interoperability budgets by up to 20% in 2023 compared to 2022. The main reasons behind this trend are refining patient outcomes and boosting the performance of clinical workflows.

Let’s break it down. Improved data interoperability directly impacts patient care. When healthcare providers can effortlessly access complete, accurate patient records, they can make diagnoses quicker and treatment more effective. No more redundant tests or conflicting medications. Everything you might need is in one place, accessible at the click of a button.
On the operational side, interoperability streamlines clinical workflows. Healthcare professionals can spend less time wrestling with incompatible software and more time focusing on patient care. Due to this, you can not only reduce operational costs but also minimize the risk of errors, contributing to safer, more reliable healthcare delivery.
All this is possible and easily achievable with professional HL7 FHIR service.
FHIR Data Model Components
Comprising a set of standardized building blocks, the FHIR common data model serves as the blueprint for secure and efficient data exchange. It’s a robust and flexible model that can accommodate everything from basic patient records to complex clinical data. Let’s delve into components that make FHIR so powerful and effective standard for today’s healthcare data management.

Resources
At the core of the HL7 FHIR model are FHIR resources, modular components that capture or describe specific healthcare data. Each FHIR resource is a data packet containing an island of coherent information like patient name, address, or medication details. You can easily combine these resources to get a comprehensive view of patient information. The genius of FHIR resources lies in their granularity and interoperability. They can be as simple as a blood pressure reading or as complex as a surgical procedure. Yet, they all speak the same ‘language,’ ensuring seamless data exchange across diverse healthcare systems.
Data Types
The FHIR’s data types define the format and structure for essential healthcare elements, such as dates, numbers, and text. By standardizing these basic units, the FHIR relational data model ensures that reference data—like patient IDs or medication codes—are consistently represented across different systems.
Extensions
These elements add custom attributes to FHIR resources without changing their core definitions. It means you can include specialized data that may be unique to a particular setting or requirement. For instance, an extension may let you attach a lab test result that isn’t part of the standard FHIR resource for lab data. Crucially, these extensions are also searchable and can be integrated seamlessly into FHIR search functionalities. Applying it to your system will allow for precise data retrieval without compromising the stability of the core model.
References
References serve as the connective tissue within the HL7 FHIR data model, linking disparate FHIR resources to create a cohesive healthcare narrative. With the help of references, you can link related pieces of information, such as connecting a patient’s medication record to their overall profile. This feature is particularly valuable in the FHIR bulk data model, where large volumes of reference data must be processed and linked efficiently. Thanks to these references, FHIR ensures that each data point is part of a larger, interconnected healthcare story.
Identifiers
Identifiers are unique tags that help distinguish each piece of healthcare data. So when you transfer data between different healthcare systems, identifiers remove the confusion that can come from duplicate or similar records. For example, in a multi-hospital network, a patient might have records in various locations. Identifiers help you pull all this information into one complete patient profile. In emergency situations, rapid access to accurate patient data can save lives.
Narratives
In the FHIR model, narratives offer easily understandable summaries that accompany the more technical data of FHIR resources. They give clinicians a brief review of essential information eliminating the need to examine the data’s finer details. When taking the FHIR simplified data model, narratives facilitate the transition of complex healthcare data into practical clinical use. So, healthcare providers can interpret data at a glance, ultimately speeding up patient care and improving its quality.
Meta
Meta elements of the HL7 FHIR model play an administrative role and help manage each FHIR resource. They record vital metadata such as version history, time markers, and security tags. In fact, meta is the identifier of healthcare data that stores contextual information on the data’s latest updates or its accessibility permissions. Thus, meta elements help you keep data safe and reliable and guarantee healthcare experts always receive up-to-date and precise information.
Bundles
Bundles function as digital containers, consolidating multiple FHIR resources to optimize data exchange. Grouping patient records or diagnostic reports, bundles simplify the transmission of varied related data simultaneously. Their utility shines in intricate healthcare situations that demand the concurrent transfer of diverse data types. Hence, FHIR refines the communication procedure, enhancing the efficiency of healthcare data management and making it less prone to errors.
FHIR Data Model Implementation
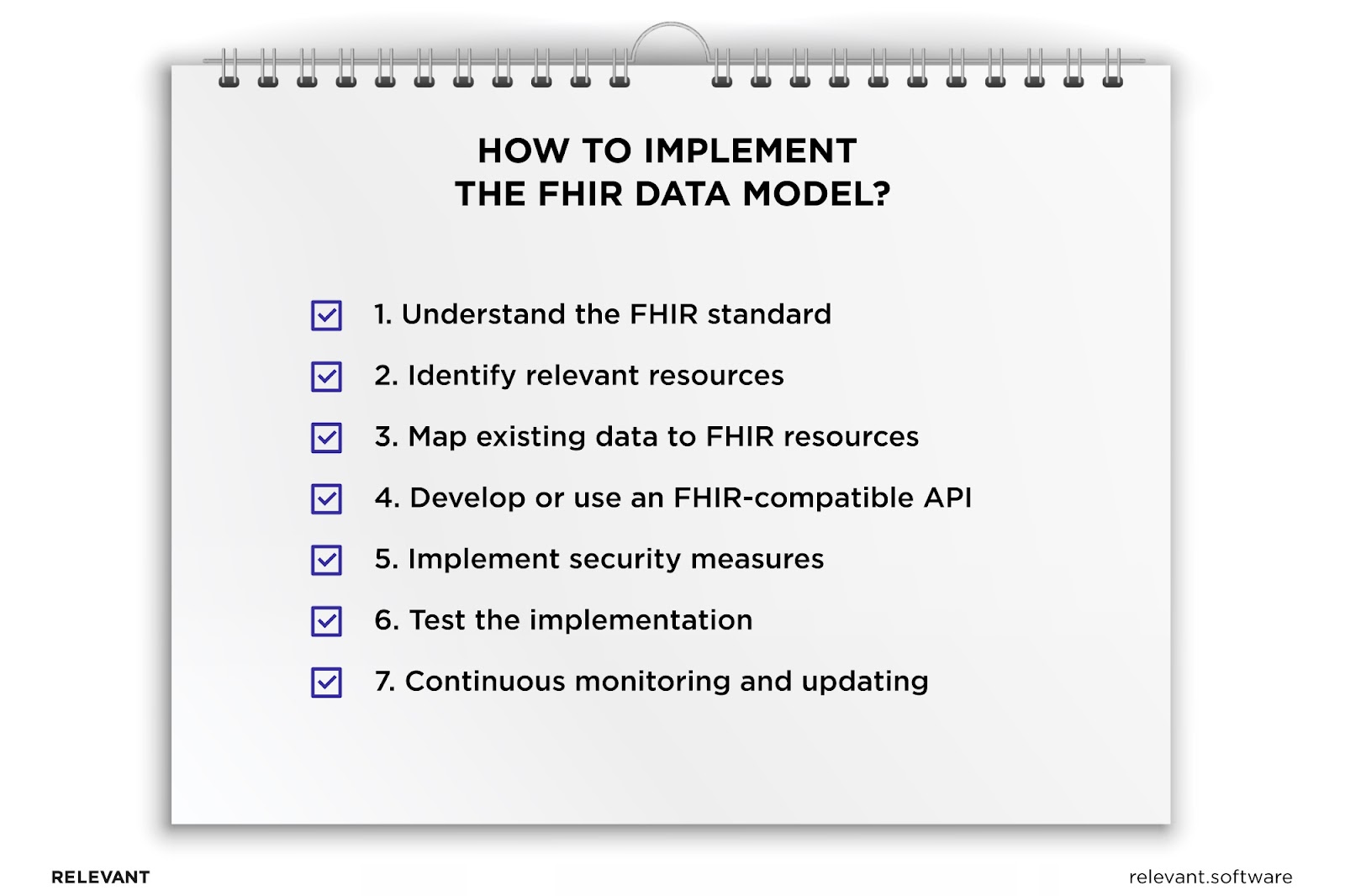
Now, as you get acquainted with the main FHIR components, we can get to the FHIR model implementation process itself. Despite FHIR’s user-friendly and flexible design, the transition demands a degree of expertise, a thoroughly planned strategy, and the alignment of IT infrastructure. Here, we outlined the steps to help you do it properly.
Understand the FHIR Standard
First, you should thoroughly understand the FHIR framework itself to identify how it will interact with your existing systems and what changes will be necessary for a successful transition. Adopting a new set of protocols doesn’t equal embracing FHIR. You should realize the full potential FHIR can bring to your healthcare data management. This knowledge is instrumental for the successful development and integration of your FHIR applications.
Identify Relevant Resources
To do that, analyze and sort the existing types of data your healthcare system handles daily. Once done, you should align those data categories with the appropriate FHIR resources, which are designed to manage certain data facets. Choosing the appropriate FHIR resource for each data category will help you build a more agile and interoperable healthcare system where data is represented in a usable format. Moreover, keeping up with the latest FHIR developments will further improve your system responsiveness and data-sharing capabilities.
Map Existing Data to FHIR Resources
In this stage, the task at hand is to synchronize your current healthcare data elements with the FHIR resources to convert data into the FHIR format. The goal here is to facilitate fluid data exchange and interoperability while retaining vital information. This mapping process turns your healthcare data into a common, universally understood language.
We recommend using FHIR conversion tools for this purpose, as they can accelerate and automate the process, reducing the likelihood of errors. Generally, since data mapping can be complex, given its sensitive nature, engaging FHIR experts will help you avoid common pitfalls and save time and resources in the long run.
Develop or Use an FHIR-compatible API
Analyze your existing healthcare data systems to identify gaps and opportunities for integration. Once you have a clear understanding of your data silos and other issues you need to resolve, you have two options: develop a custom API that aligns with the FHIR data model or adopt a pre-existing one. The choice will depend on the complexity of your platforms and the resources at your disposal. While custom APIs give you solutions designed specifically for your needs, a pre-existing API can be a cost-effective and quick solution to achieving interoperability.
In any case, you should ensure that the API you’ve chosen can handle the types of data you plan to exchange. Also, perform testing to confirm that the API integrates smoothly with your existing infrastructure.
Implement Security Measures
It’s a non-negotiable step for safeguarding all the healthcare data you’ll manage and share. So, what does it involve? At the bare minimum, you should:
- Set up robust authentication protocols that often involve multi-factor authentication to verify the identity of users accessing the system;
- Apply data encryption both in transit and at rest to protect sensitive healthcare and clinical data from unauthorized access or breaches;
- Establish access controls to define who has permission to view, edit, or delete specific data. Usually, it refers to role-based access control, where different levels of permissions are granted based on job roles;
- Perform audit trails that log all interactions with the data to provide a transparent record of who accessed what and when.
By strengthening your FHIR implementation with these top-tier security measures, you’ll protect data and enhance the reliability of the entire healthcare delivery process.
Test the Implementation
This phase involves rigorous quality assurance checks, including unit tests, integration tests, and end-to-end tests to validate that all components work as intended. Here, you should focus on ensuring data accuracy, system interoperability, and security compliance. Rather than simply finding bugs, you should concentrate on the whole system to confirm that it can handle real-world healthcare scenarios effectively. During this phase, you should mitigate potential risks and roadblocks to ensure your FHIR solution is functional and at its best capacity in a live healthcare setting.
Continuous Monitoring and Updating
Your job doesn’t end once you implement the HL7 FHIR data model. It’s an ongoing commitment. Regularly conduct system audits, analyze performance metrics, and assess security to maintain a compliant, secure, and efficient system. As healthcare practices and technology progress, actively update your FHIR solution to retain its relevance and practicality. The continuous monitoring and updating cycle will help you keep your healthcare data systems in good shape.
These major steps described in brief will help you understand the FHIR model implementation process. For more insights and detailed information on how to do it, check our FHIR implementation guide.
FHIR Data Model in Practice
Now, let’s switch from concept to concrete solutions. Real-world FHIR applications are already demonstrating its power to break down data silos and improve patient outcomes. Let’s review them in detail.
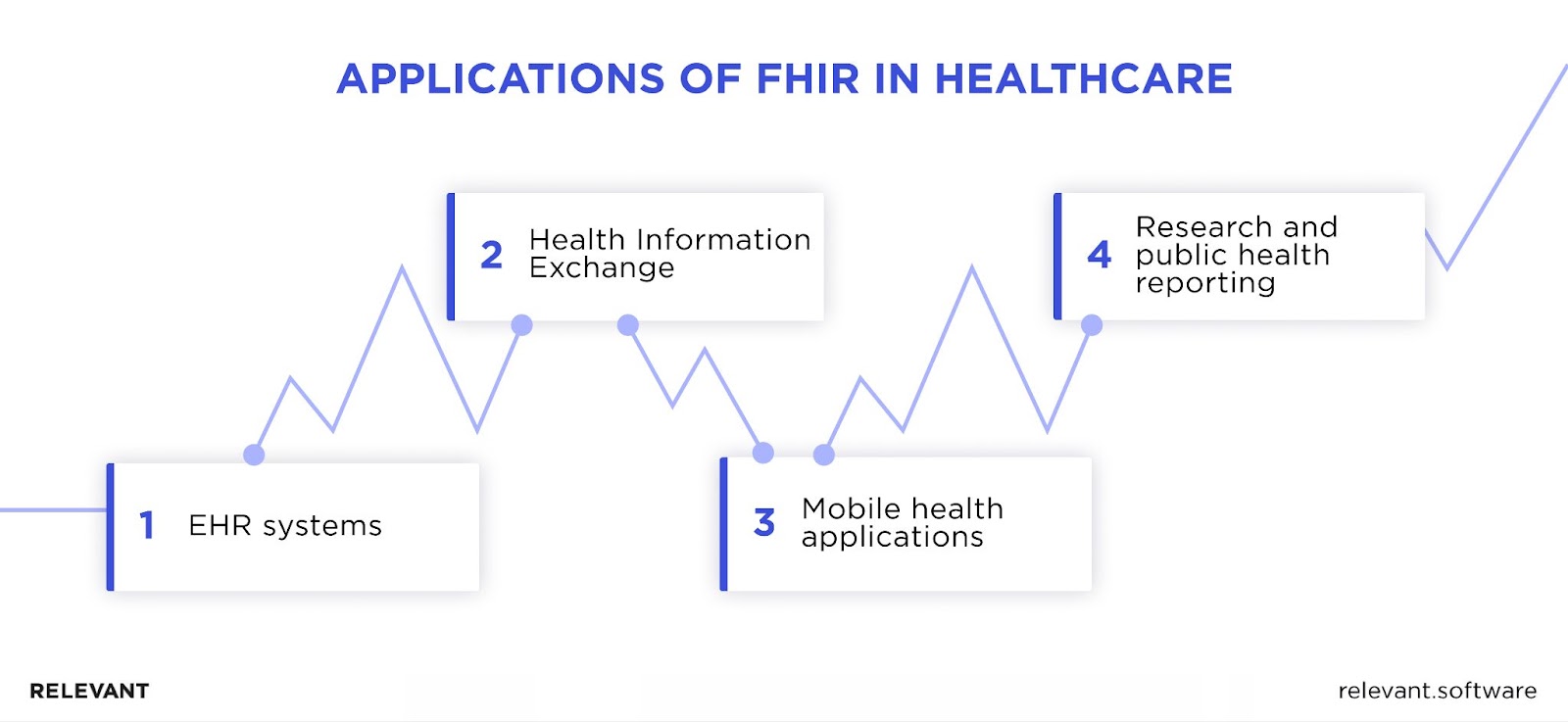
EHR Systems
Given their central role, it’s only logical that Electronic Health Record (EHR) systems are the primary platforms where healthcare organizations look to implement the FHIR data model. EHRs house a comprehensive array of patient data, from medical histories and lab results to medication and treatment plans that require a secure exchange. FHIR standardizes how healthcare data is stored, accessed, and shared in EHR systems. It replaces the patchwork of legacy systems and data formats with a unified, extensible structure. What’s more, when combined with SMART on FHIR technologies, you can integrate various medical applications directly into your EHR system.
Health Information Exchange (HIE)
HIE establishes the rules and policies for the secure exchange of healthcare information across diverse healthcare systems, providers, and payers. The logical question may arise: How does HIE differ from FHIR? Well, HIE answers for ‘what’ and ‘why’ of healthcare data exchange, and FHIR is about the ‘how’ of this process. HIE focuses on the governance, policy, and use-case requirements for data sharing. In contrast, FHIR supplies the technical guidelines to realize these exchanges in a standardized manner.
Therefore, using FHIR can expand the capabilities of HIEs. For instance, it can simplify real-time access to patient records and clinical data, which in turn improves the quality of care and decreases the likelihood of medical errors. Moreover, you can connect telehealth services or wearable devices to the healthcare data ecosystem.
Mobile Health (mHealth) Applications
mHealth applications are convenient means for real-time monitoring, telemedicine consultations, and personalized treatment plans available on our mobile devices. Following FHIR standards, mHealth apps deliver users extensive insight into their health data, which they can quickly and securely share with their doctors. On top of a better user experience, you’ll be able to provide more coordinated and effective care. If you’re looking to develop such an interoperable mHealth solution, the expertise of a healthcare software development company like Relevant Software might just be what you need.
Research and Public Health Reporting
This medical domain can probably benefit the most from adopting the FHIR data model. Implementing a standardized approach to gathering, storing, and sharing healthcare data will help researchers access and examine large datasets. Epidemiological studies, clinical trials, and health policy planning, where data accuracy is vital, stand to gain from it. FHIR empowers public health agencies to track disease outbreaks, monitor population health, and coordinate emergency responses with heightened efficiency. For researchers, it simplifies the data extraction and analysis process, thus accelerating the progress of medical innovation.
FHIR Data Model: Final Thoughts
The strong architecture and emphasis on interoperability make the FHIR data model an essential asset for everyone related to healthcare, including doctors, researchers, and policymakers. It brings uniformity to healthcare data management, improving patient care while simultaneously driving advancements in medical research and public health initiatives.
Adapting to this change may be a substantial undertaking due to a lack of the required skills and knowledge. By partnering with Relevant Software, you can save resources, time, and nerves while ensuring your systems operate according to the HL7 FHIR data model. If you want to implement FHIR or build a new FHIR-compliant healthcare solution from scratch, you can always rely on our healthcare IT consulting services to get the necessary assistance.
FAQ
What are FHIR profiles?
FHIR profiles are special rules that explain how to use FHIR resources in different clinical scenarios. They set clear standards for data elements, their structures, and coding systems to secure consistent and accurate data exchange. Profiling helps you create detailed specifications of the content models, workflows, and services to support concrete use cases. And as each FHIR implementation is unique, so are the resource use cases. As such, profiling is a vital part of FHIR that boosts interoperability.What is the role of profiles in the FHIR data model?
They tell healthcare systems how to arrange and use FHIR resources correctly in particular clinical settings. They help in organizing data elements, applying certain coding, and maintaining high data quality during transmission. What’s more, profiles allow customizing the FHIR model to meet the unique requirements of various possible healthcare scenarios. It could be clinical care, research, and more.What are the differences between the FHIR data model and older healthcare standards?
FHIR is a modern solution to healthcare data interoperability, contrasting sharply with older HL7 V2 and V3 standards. You can implement and adapt FHIR to various healthcare situations much more easily as it leverages commonly used web-based technologies. The support of widely applied JSON and XML formats is also beneficial as it facilitates smoother data management. Unlike older standards that often require specialized software for data exchange, FHIR’s RESTful architecture works with current web technologies without a hitch. So it’s faster and less expensive to deploy.How does FHIR integrate with EHRs?
Standard data formats and RESTful APIs are the main drivers of real-time data exchange. Thanks to HTTP and JSON technologies, developers can easily connect EHR systems with other health apps. Once they integrate with FHIR, sharing any kind of healthcare information becomes effortless. The FHIR model also supports CRUD (Create, Read, Update, Delete) operations, which is beneficial for establishing dynamic interaction with healthcare data. Moreover, you can add custom elements to include specialized or unique data in your EHR system.

Hand-selected developers to fit your needs at scale! Let’s build a first-class custom product together.

