What is IoT: A Connected World Explained

What is IoT (Internet of Things) all about? Technology became mainstream decades ago with the rise of smart homes and devices. Although it might not be as prominently discussed today as AI, its importance remains vital because many modern applications rely heavily on IoT technology. De facto, current IoT software development services have moved beyond basic features such as simple dashboards and remote monitoring to more complex, unique applications for IoT products.
To handle these complex scenarios, you must understand what an IoT device is and how IoT systems are structured. Intrigued? You should be. Awareness of IoT and its technical aspects is key, especially if you aim to develop software for it.
from 25 countries outsourced software development to Relevant
We provide companies with senior tech talent and product development expertise to build world-class software.
What is IoT: A Look at Its Roots
What is IoT, or the Internet of Things? While smart home devices might be the first to come to mind, the concept stretches far beyond our living rooms and boasts a surprisingly long history. While the term itself was coined in 1999 by British technologist Kevin Ashton, the IoT had its first practical application much earlier.
The first known example of IoT in action dates back to 1982 at Carnegie Mellon University, where scientists connected a Coca-Cola vending machine to a computer network. It could report on stock levels and drink temperatures, demonstrating the potential of connected devices a decade before the World Wide Web became public. Even today, the implementation of such an intelligent vending machine seems impressive.

Forty years later, IoT is everywhere. Think about it – cars, kettles, coffee machines, fridges, washing machines, smartphones, and even bread makers often have IoT elements. If there’s a companion app for a product, chances are it’s part of the IoT world.
So, what is IoT technology in simple terms? It relies on three essential components to function:
- Sensors: Various types of sensors can detect sound, vibration, load, motion, water, air quality, and even infrared radiation.
- Networks: They connect these sensors to the Internet via wired or wireless connections to ensure seamless communication.
- Software: It collects, stores, and analyzes sensor data. Additionally, software solutions control and manage the devices within the IoT ecosystem.
More about how to control IoT devices can be found here.
The Brief Explanation of IoT Devices
Well, what is an IoT device? Broadly speaking, it’s any physical item that doesn’t have traditional computing power but typically has built-in sensors to collect data. These items also have actuators that enable them to take physical actions in response to instructions from other devices, software programs, or even people.
Additionally, IoT devices connect to an IoT gateway to share the sensor data they collect. This gateway serves as a central hub, collecting data from all the IoT devices. Sometimes, data is sent to an edge device for local analysis. By analyzing data locally, the amount of data sent to the cloud is reduced, saving bandwidth. The communication protocols and connectivity options these devices use vary based on the specific IoT applications.
Moreover, some IoT systems include built-in AI and machine learning, enabling them to make independent decisions and tackle complex tasks without being online or suffering from cloud-related delays.
Currently, IoT devices are widely used in various fields:
- Human Health: Wearable technology monitors health and fitness, manages chronic diseases, and provides real-time vital sign tracking through IoT healthcare devices. For example, ingestible sensors can transmit health data directly inside the body.
- Residential Use: Smart interactive devices like voice assistants, robotic vacuums, and advanced security systems make life at home more convenient and safer. Respectively, IoT applications help to control lights, thermostats, and security cameras with our voices or a tap on our phones.
- Retail Spaces: In retail, IoT enables efficient inventory management, self-checkout, and personalized promotions, boosting service efficiency and customer experience.
- Corporate Offices: Smart office solutions include energy management systems to cut costs and security systems to ensure safety. These interconnected technologies streamline operations and increase productivity.
- Industrial Environments: Manufacturing plants, hospitals, and farms use IoT to improve operational efficiency and optimize equipment utilization. For instance, sensors built into factories can prevent equipment failures and reduce downtime.
- Specialized Industries: Mining, construction, and oil and gas sectors use IoT for predictive maintenance and safety monitoring. Smart helmets, for example, can continuously monitor workers’ health and safety in hazardous conditions.
- Transportation: IoT in vehicles supports condition-based maintenance, usage-based insurance, and advanced pre-sales analytics. The technology also powers autonomous cars, ships, airplanes, and trains.
- Urban Development: Smart cities utilize IoT for adaptive traffic management, smart meters, environmental monitoring, and efficient resource management. These systems decrease traffic congestion, save energy, and make city living more pleasurable.
- Outdoor Applications: In logistics and transportation, IoT facilitates real-time routing for delivery vehicles, connected navigation for autonomous systems, and precise shipment tracking.
IoT Connectivity Technologies in Use
What is IoT connectivity? IoT technology is a complex system that comprises multiple layers of architecture and a network of web-enabled devices. These devices rely on different IoT connectivity technologies, standards, and protocols, each with unique strengths suited to other use cases.
- Data Distribution Service (DDS): Created by the Object Management Group, DDS is a standard for real-time, scalable, high-performance machine-to-machine (M2M) communication, instrumental in industrial IoT.
- IPv6 over Low-Power Wireless Personal Area Networks (6LoWPAN): Developed by the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF), this standard allows low-power radios to connect to the Internet. It’s used in technologies like 804.15.4, Bluetooth Smart, and Z-Wave, supporting applications in home automation, industrial monitoring, and agriculture.
- Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure (HTTPS): An enhancement of HTTP that provides secure communication over a computer network. This protocol is essential for protecting data during transmission, making it highly suitable for IoT applications that require secure data exchange, particularly when interacting with cloud services.
- OPC Unified Architecture: OPC UA is a robust protocol for machine-to-machine communication in industrial automation. It ensures that data is exchanged securely and reliably, which is critical for maintaining the integrity and functionality of industrial IoT systems.
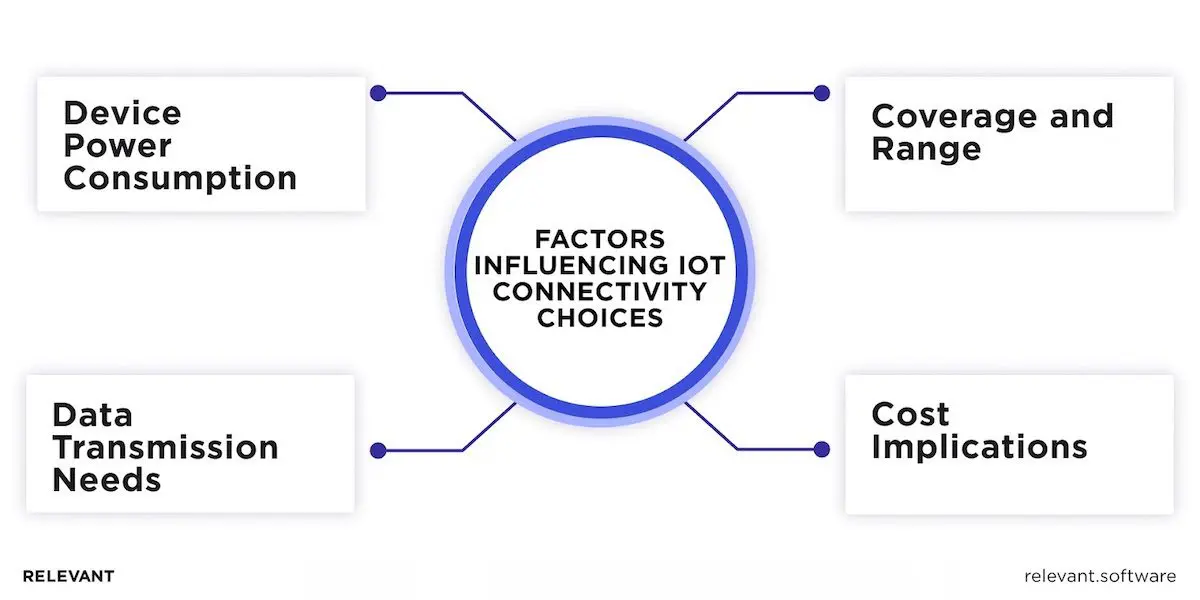
IoT standards typically specify protocols for device communication that govern how data is transmitted and received. The most widely recognized are:
- Constrained Application Protocol (CoAP): Designed by the IETF, CoAP allows low-power, compute-constrained devices to operate efficiently in IoT environments.
- Advanced Message Queuing Protocol (AMQP): A protocol for business messaging, AMQP provides a platform-agnostic way to send and receive messages. It ensures interoperability between different systems and is often used in financial services and enterprise messaging.
- Long-Range Wide Area Network (LoRaWAN): This protocol is designed for wide-area networks and supports large-scale deployments, such as smart cities with millions of low-power devices.
- Zigbee: An IEEE 802.15.4-based specification, Zigbee is a low-cost, low-power wireless mesh network standard. It is used in a variety of applications, including home automation, intelligent energy, and medical data collection.
- MQ Telemetry Transport (MQTT): Lightweight and efficient, MQTT is ideal for control and remote monitoring applications, especially on devices with limited resources.
- Bluetooth Smart. Next up is Bluetooth Smart, previously known as BLE (Bluetooth Low Energy). This isn’t a single protocol but a suite of them, and it doesn’t assign IP addresses to devices. Although it’s a newer technology, it’s found in nearly every connected consumer product that needs to communicate directly with a smartphone or other personal computing device. It offers high data throughput with minimal power usage, making it an essential connectivity option for most markets.
Various frameworks support the development and management of IoT applications:
- Amazon Web Services (AWS) IoT: A cloud computing platform that allows smart devices to connect and interact securely with the AWS cloud and other devices.
- Microsoft Azure IoT Suite: A robust set of tools that helps users connect with their IoT devices, analyze data in multiple dimensions, transform it, and visualize it for better business decisions.
- Arm Mbed IoT Platform: An open-source solution for IoT development on Arm microcontrollers that offers a connected, scalable, and secure environment, complete with a wide array of tools and services.
Security Considerations
The IoT ecosystem operates in a highly hostile cyber environment. Ensuring robust security should be the primary concern before selecting a communication standard. Here are some important ones:
- TLS/SSL (Transport Layer Security/Secure Sockets Layer): Encrypts communication between devices and servers.
- IEEE 802.1X: Port-based Network Access Control (NAC) for wired networks.
- WPA (Wi-Fi Protected Access): Security protocols for Wi-Fi networks.
How Does IoT Work?
While the components of IoT systems can vary depending on the application’s size and purpose, most share standard features such as data collection mechanisms and sensors. An IoT sensor captures real-world data and converts it into information that other devices can interpret.
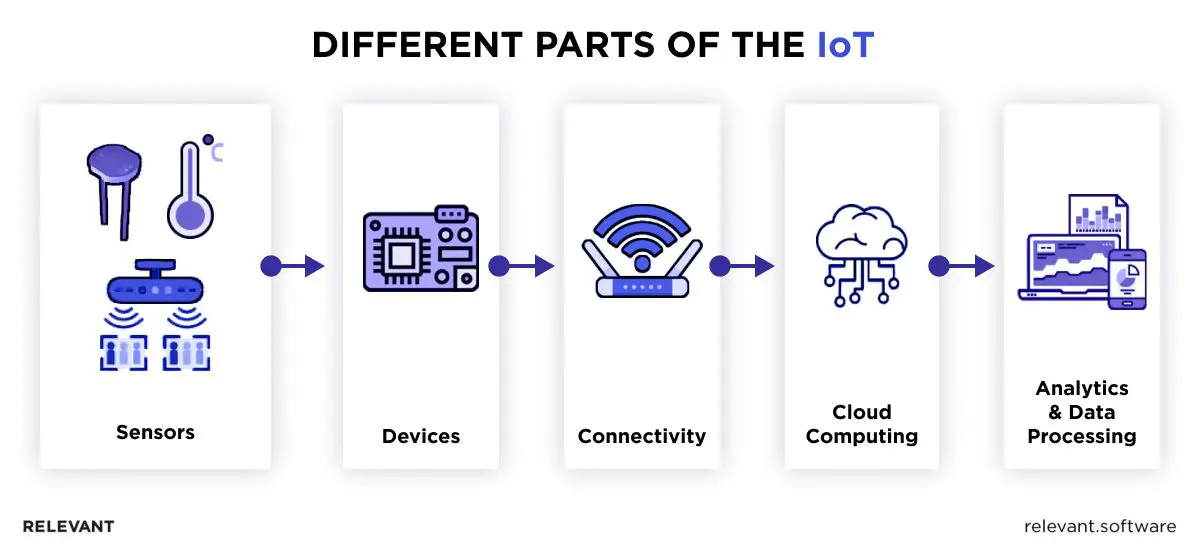
Getting a handle on it is pretty straightforward when broken down into its main parts. Any IoT system functions through five main steps:
Data Gathering
How does IoT work? IoT devices equipped with sensors measure and collect data on temperature, humidity, motion, light, and other conditions. For instance, a smart thermostat collects temperature data to keep your home space comfortable. This constant stream of data is the ground of any IoT system.
Data Processing
After collection, the gathered data needs to be processed. That is where IoT devices use powerful processors and advanced algorithms to turn raw data into useful information. Often, the data must be sent to centralized systems or cloud platforms for more complex analysis. How does IoT work under the hood? Our blog’s IoT architecture guide has all the insights you need.
Data Exchange
For IoT devices to be effective, they need to share the data they collect. This happens through widely used communication methods such as Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, or cellular networks. The best option for usage depends on the unique requirements of the concrete IoT application, particularly the range and data transfer speed needed.
Data Storage and Management
All the data generated by IoT devices needs to be stored securely and managed efficiently. This is usually done through cloud storage solutions or on-site databases to ensure that the data remains accessible and secure. For a thorough overview of one of the leading cloud services, be sure to check out the AWS IoT core guide.
Data Utilization
Finally, the processed data is put to use. For example, a smart home system can adjust lighting and heating based on your daily activities, or a factory can predict equipment failures before they occur, saving time and money.
As noted above, data processing and analytics often happen in data centers or the cloud, but that’s not always feasible. For critical devices like industrial shutoffs, the time it takes to send data, process it, analyze it, and get instructions back can be too slow. That’s where edge computing steps in. With smart edge devices, data is aggregated, analyzed, and responded to locally, reducing delays. These devices also connect upstream to send data for further processing and storage.
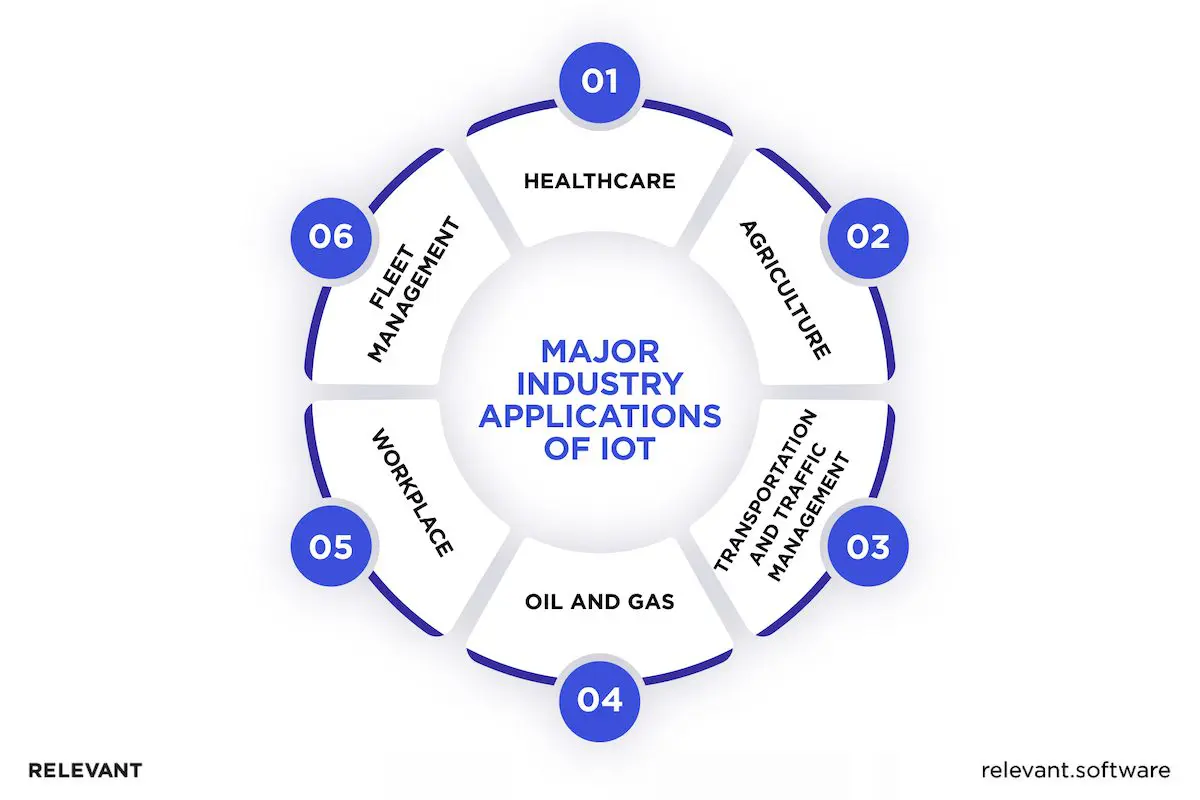
The Major Industry Applications of IoT
The Internet of Things (IoT) extends beyond smart home gadgets and touches every industry, making operations much more efficient and responsive. From healthcare to transportation, IoT brings practical benefits that improve daily life and business processes.
IoT in Healthcare
What is IoT’s potential in healthcare? There’s a real sense of optimism, and for good reason. Healthcare IoT development lays the groundwork for:
- Smart Healthcare Systems: Using IoT, these systems connect devices to monitor patients in real-time, manage chronic illnesses, and offer personalized treatment plans. For example, IoT wearables can monitor vital signs and alert doctors to issues immediately, enabling quick medical intervention.
- Remote Monitoring: IoT technology enables remote patient monitoring, making healthcare more accessible and efficient. Wearable devices like smartwatches and fitness trackers send real-time data to doctors, enabling remote health surveillance. Get the full scoop in our article about IoT impact in healthcare.
- Enhanced Patient Care: For example, smart insulin pens and continuous glucose monitors help diabetes patients better manage their condition. With accurate data from these devices, treatment plans can be adjusted on the fly.
- Operational Efficiency: IoT benefits go beyond patient care; it also enhances operational efficiency in healthcare facilities. Smart sensors track equipment usage and anticipate maintenance needs, minimizing downtime and ensuring critical devices remain functional. This results in improved resource management and significant cost savings for hospitals and clinics.
But it’s not all smooth sailing, though. While IoT undoubtedly offers many benefits for the health sphere, it also comes with its fair share of challenges. Issues such as data security, device interoperability, and the need for a robust infrastructure can make integration very challenging. We’ve experienced firsthand the hard work it takes to overcome these obstacles and detailed them in our article on the challenges of IoT in healthcare.
IoT in Agriculture
What is IoT in agricultural settings? IoT-enabled solutions help farmers increase productivity and better manage resources. Here is an outlook:
- Smart Farming Solutions: With IoT in agriculture, innovative farming methods are now possible. Sensors in the field monitor soil conditions, providing valuable data to help farmers decide on irrigation and fertilization. This improves crop yields and conserves resources.
- Livestock Monitoring: IoT devices are also used to monitor livestock health and activity. With wearable sensors, the location, movements, and vital signs of animals are easily tracked. This allows farmers to detect illnesses early and ensures their livestock remain healthy, thereby reducing losses and improving farm productivity.
- Automated Equipment: Another significant application of IoT in agriculture is automated equipment. Tractors and other machinery equipped with IoT devices can perform tasks such as planting, watering, and harvesting with minimal human intervention. This automation enhances efficiency and cuts down labor costs.
- Data-Driven Decisions: Farmers use data from IoT devices to make much more informed decisions. For example, weather sensors give precise forecasts, helping farmers schedule their activities. Similarly, data analytics can predict crop diseases and pest infestations, which enables proactive measures to protect crops.
IoT in Transportation and Traffic Management
IoT makes transportation systems more innovative and more efficient, improving safety and reducing congestion. So, what is IoT, and how does IoT work in the transportation field? Let’s look.
- Intelligent Traffic Control Systems: IoT sensors at key points, such as intersections and roadways, gather real-time data on traffic conditions and accidents. This helps adjust signal timings, reduce wait times, and improve overall traffic flow. To see this technology in action, check out the article IoT in traffic management.
- Real-Time Monitoring and Management: With IoT devices, transportation systems can be monitored in real-time. GPS-equipped vehicles and smart sensors supply their locations, speeds, and route data. This information helps traffic management centers respond quickly to incidents, deploy emergency services more effectively, and keep traffic running smoothly.
- Predictive Maintenance: Sensors on vehicles and infrastructure monitor the condition of roads, bridges, and tunnels. They can predict when maintenance is needed, preventing breakdowns and reducing downtime. This lowers costs and guarantees safer travel for everyone.
- Public Transportation: IoT also enhances public transportation systems. Innovative ticketing solutions, real-time tracking of buses and trains, and personalized travel information make commuting more convenient and efficient. Thereafter, travelers receive delay notifications and find the quickest paths to their destinations.
- Traffic Decongestion: IoT solutions can even reduce traffic congestion. Connected cars communicate with each other and traffic systems to find the best routes, avoid bottlenecks, and improve traffic flow. This cuts travel time, fuel use, and emissions.
- Enhanced Safety: Transportation safety is a significant priority, and IoT enhances it in many ways. Collision detection, alerts about hazardous conditions, and automated emergency responses are some of the technologies that make roads safer for everyone.

IoT in the Oil and Gas Industry
By focusing on efficiency and safety, IoT brings to this critical sector. Curious about how IoT works in this field? Let’s dive deeper into what is IoT in oil and gas.
- Enhanced Efficiency: IoT devices monitor equipment and infrastructure in real time, providing valuable data to optimize performance and predict maintenance needs. For example, sensors can detect when machines operate inefficiently and alert maintenance teams before a breakdown occurs, saving time and costs.
- Proactive Safety: Sensors located in critical areas can detect potential hazards, such as gas leaks or equipment faults, and promptly alert operators. This swift reaction helps prevent accidents and protect workers. Real-time monitoring enables you to mitigate risks, such as shutting down equipment or evacuating areas, to prevent harm. The constant flow of data helps identify potential dangers early, allowing issues to be addressed before they escalate.
- Resource Management: Efficient resource management is one of the most significant benefits of IoT in this industry. By tracking supply levels and usage rates, IoT helps companies manage resources more effectively, reducing waste and ensuring smooth operations. This technology greatly supports sustainable practices and enhances overall operational efficiency.
IoT in the Workplace
What is IoT`s impact on the workplace? By connecting all existing devices and systems, IoT helps streamline operations, reduce manual tasks, and ensure a much safer environment for employees. Here’s what IoT can bring:
- Boosted Productivity: IoT devices help automate tasks and provide real-time data, making operations run more smoothly. For example, sensors on equipment can alert you when maintenance is needed, which helps prevent downtime and keep everything running efficiently. IoT in workplace helps everyone work more effectively.
- Greater Safety: IoT significantly boosts workplace safety. Wearable devices track worker health, detect potential hazards, and alert staff to dangers. Innovative systems monitor environmental factors like air quality and temperature, ensuring a safe workspace.
- Optimized Space Utilization: IoT helps businesses manage office space more effectively. Sensors track room usage and occupancy, which allows better layout optimization. This turns workspaces into a much more comfortable and productive environment.
IoT in Fleet Management
What is IoT in fleet management and telematics? In fact, this technology helps companies run their operations more smoothly and efficiently.
- Better Operations: With IoT, fleet managers can track vehicles in real time, monitor routes, monitor fuel use, and observe driver behavior. This detailed oversight helps cut costs and maintain stable operations. Got questions? Check out the IoT fleet management overview.
- More innovative Logistics: IoT provides insights into logistics, shipment tracking, and delay prediction. Sensors monitor the condition of goods, ensuring they arrive safely and on time. This proactive approach, as always, helps businesses stay on schedule and keeps customers happy.
- Maintenance Made Easy: IoT enables predictive maintenance for fleet vehicles, making it easier than ever to keep them in top condition. Sensors detect potential issues early, before they turn into costly breakdowns. This keeps cars in top shape and extends their lifespan.
- Safety First: IoT enhances safety by monitoring driver behavior and vehicle conditions. Alerts for risky driving and real-time feedback promote safer driving habits, reducing accident risks. With IoT, you can have peace of mind knowing that both your drivers and vehicles are being monitored for safety.

IoT Software Development: Short Overview
What is IoT development in a practical sense? In our IoT overview, we detail the main pillars that make it all possible.
IoT Software Development Services
Custom software solutions are key to making the most of IoT. Generic software rarely meets the unique demands of different industries. Custom IoT software, however, is designed to fit each business’s specific requirements for smooth integration and peak performance.
For example, in healthcare, custom IoT software can track patient data in real-time, giving doctors immediate access to critical information. In agriculture, specialized software can monitor soil conditions and weather, helping farmers make informed decisions. These examples show why customized software is so crucial in leveraging IoT technology.
IoT App Development Essentials
So, we come to the most critical section, which explains what IoT development is and how to create effective IoT apps. In our IoT overview, we will outline key considerations and best practices to ensure apps function well and provide real value to users.
1. The app should address real users’ problems and offer practical solutions. Whether it’s monitoring health metrics, optimizing energy use in smart homes, or tracking inventory in a warehouse, the app must be designed with the end-user in mind.
2. In this process, security remains a top priority, given the sensitive nature of the data that IoT devices often handle. So, you must ensure robust security measures protect user data and build trust.
3. A successful IoT app must be user-friendly. Users should find the interface intuitive and straightforward to navigate and access the app’s features. That involves clear layouts, simple instructions, and responsive controls.
4. IoT apps must handle a growing number of devices and data streams. Designing for scalability from the start ensures the app can expand as needed. Compatibility with various devices and platforms is also crucial, allowing seamless integration into the user’s existing IoT ecosystem.
5. Proper data management matters. Your app needs to process, analyze, and display data clearly and concisely. Imagine being able to see all the essential data at a glance, presented in a way that makes sense.
To ensure complete success, follow these best practices from our experts:
- Conduct rigorous testing throughout development to identify and fix issues early.
- Provide regular updates after launch to keep the app functional and secure, and to adapt to new challenges and user feedback.
- Collaborate with experienced developers who understand IoT technology and possess industry knowledge.
- Use open-source tools and frameworks to accelerate development and reduce costs.
- Keep the app lightweight, using minimal power and bandwidth to boost performance.
Using Node.js for IoT Development
What is IoT capability with Node.js? Let’s take a look at why it is a top choice.
- Real-time Data Handling: Node.js excels at managing real-time data, which is crucial for IoT devices that need to communicate and exchange information constantly.
- Lightweight and Efficient: With a non-blocking, event-driven design, Node.js remains lightweight and efficient, making it suitable for high-performance applications with low resource demands.
- Extensive Community and Ecosystem: Node.js boasts a large community and a robust ecosystem of libraries and tools, enabling developers to use premade modules that speed up development.
- Cross-platform Compatibility: Because Node.js runs on multiple platforms, your IoT applications will run seamlessly across devices and operating systems.
- Effortless Integration with IoT Protocols: Node.js integrates seamlessly with a range of IoT protocols, including MQTT and CoAP, enabling smooth communication between devices.
- Scalability: Node.js’s architecture enables easy application scaling, which is essential for IoT projects that may grow in complexity and the number of connected devices over time.
- Efficient Data Processing: Node.js handles data processing efficiently, making it suitable for IoT applications that need to process large volumes of data quickly and reliably.
Strong Support for APIs: NodeJS IoT has excellent support for building and managing APIs, which are crucial for connecting IoT devices and enabling communication between them.
Azure IoT vs. AWS
Given the robust features of each platform, selecting between Azure IoT and AWS IoT can feel overwhelming. For instance, Azure IoT shines with its deep integration into Microsoft’s suite of products and offers a familiar environment for those already in the Microsoft ecosystem. On the other hand, AWS IoT provides unparalleled flexibility and a vast global infrastructure, making it a strong contender for businesses seeking highly customizable solutions.
Security features, analytics capabilities, user-friendliness, and cost structures differ between the two, each with its own set of benefits and trade-offs. Are you curious about which platform offers the best security measures or the most powerful analytics tools? Do you need a user-friendly interface or comprehensive documentation?
For a more detailed comparison that dives into these aspects and more, check out the complete analysis of Azure IoT vs AWS IoT.
Our IoT Case Studies
To back up our expertise with real examples, we will share two of our successful IoT case studies.
Case 1
Our client, a Canadian R&D company, developed a social robot designed to be a 24/7 companion. They came to us to revamp their web app, which was part of the robot’s content management system. The old platform was outdated and frustrating for users.
We overhauled the existing platform to manage the robot’s content and address flaws in the previous design. With improved UX and UI, the new front end is much more intuitive for users to navigate and manage the content.
Also, we integrated it with the Remote Device Management Platform for better synchronization, moved to a new database for improved performance and security, and added a 3D preview feature so content creators could see their work in action.
Case 2: Developing a Remote Sensor Platform for Global Leaders in Monitoring
Our client, a Norwegian company, developed a modern system that uses hardware sensor data and software algorithms to notify users of issues such as water leaks in industrial and residential areas. Their sensors track humidity and temperature, enabling real-time responses to prevent damage.
Although Sensor Innovation had a working product, it lacked an intuitive user interface and efficient operation functionality. Our goal was to revamp the UI and add new functionalities, including data display on a virtual building blueprint.
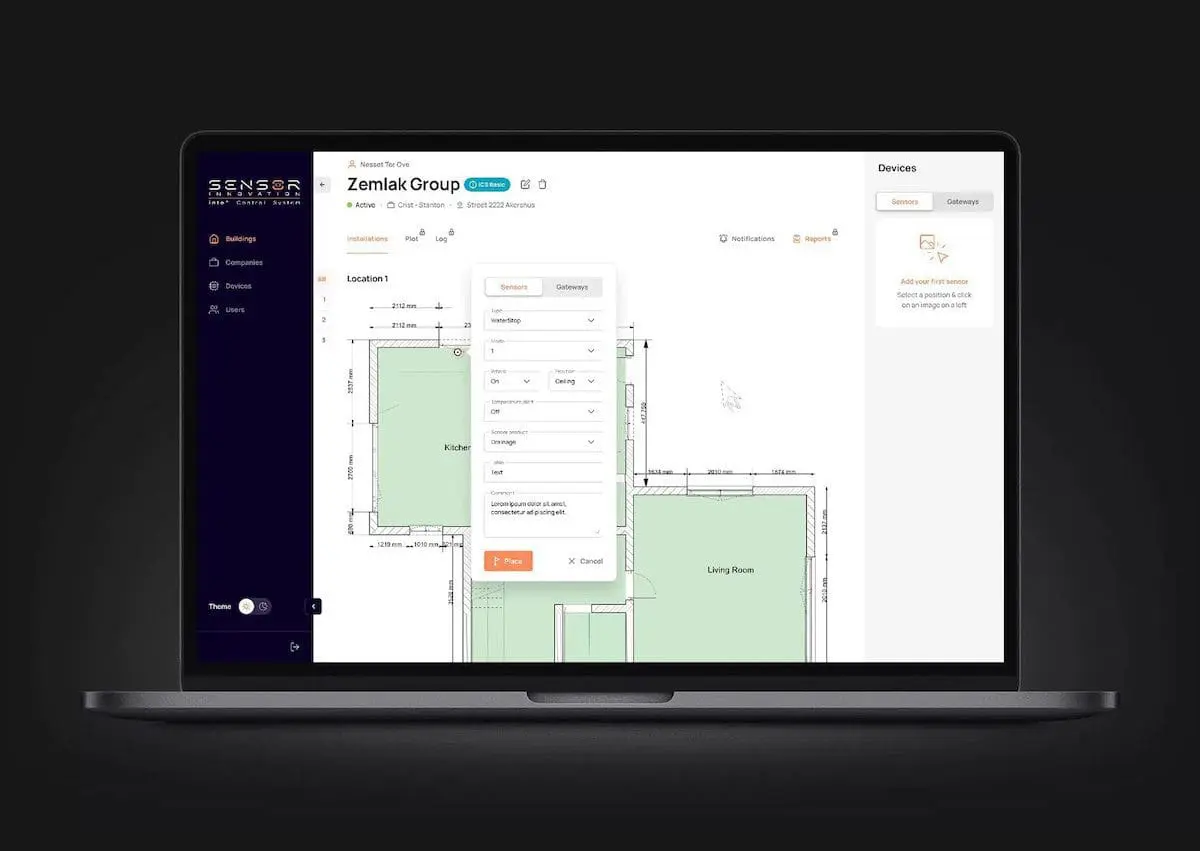
We assembled a multidisciplinary team to redesign the platform’s dashboard and make sensor management much more user-friendly. The upgraded platform now features a streamlined UI and improved performance. A weather timeline reduced false alarms, and virtual building maps optimized sensor coverage. We also optimized the site for mobile devices, ensuring it adapts to screen size changes and allows easy editing and the addition of new sensors.
What is IoT: Final Thoughts
The Internet of Things is a perspective thing. To give you a sense of its impact, IDC predicts that investments in the IoT ecosystem will surpass $1 trillion in 2026. And if that doesn’t impress you, Statista estimates the number of IoT devices will skyrocket to 29 billion by 2030. That’s enough for everyone on the planet to own about four connected gadgets!
We could assume Internet of Things technology is much more than a convenience; it truly transforms industries. Whether in healthcare or smart agriculture, these technologies offer significant value to businesses that want to improve efficiency and increase profitability.
But here’s the nuance: all these amazing advancements need top-notch Internet of Things software to work seamlessly. That’s where we come in with our 10+ years of software development expertise. From initial concept to deployment and support, our IoT experts are here to guide you every step of the way.
No matter if you aim to upgrade your smart home, optimize factory operations, or boost healthcare services, our IoT development services can help you reach your objectives. Contact us to start!


Hand-selected developers to fit your needs at scale! Let’s build a first-class custom product together.

