Digital Twin in Healthcare: Revolutionizing Patient Care and Medical Research

By now, you’ve probably come across the digital twin concept. They serve as virtual representations of physical objects or systems, enabling simulations and performance analysis to derive valuable insights. But in the sphere of healthcare, digital twins hold even greater potential. They have the power to revolutionize how healthcare institutions operate and, most eminently, improve patient outcomes.
So what implications does digital twin technology hold for healthcare? Let’s examine the use cases, advantages, and challenges of digital twins in healthcare. By doing so, you’ll be better equipped to make the right choices and unlock the immense benefits that digital twins can bring to your organization and, most importantly, to the well-being of patients.
from 25 countries outsourced software development to Relevant
We provide companies with senior tech talent and product development expertise to build world-class software.
Modernizing Healthcare with Digital Twin Technology
Over the past decade, the healthcare industry has undergone a remarkable digital transformation, with the COVID-19 pandemic acting as a catalyst for the widespread adoption of digital technologies. This shift has impacted every aspect of healthcare and paved the way for exciting advancements.
One notable example of the digital revolution is the rise of digital twins. These virtual replicas of real-world objects are rapidly gaining traction in healthcare. Reports indicate that up to 66% of healthcare executives plan to invest in digital twin technologies within the next three years.
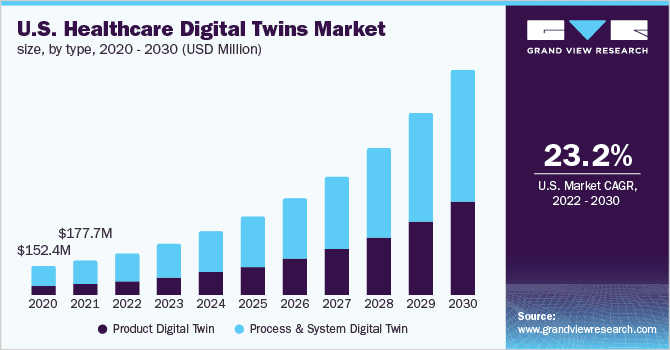
In contrast to traditional simulations, modern medical digital twins provide a unique approach by utilizing wearable device data, omics, and patient records to create valuable models. These connect the dots across various processes involving patients, doctors, healthcare organizations, and drug/device manufacturers. With advancements in real-time data feeds, machine learning, IoT, and AR/VR, digital twins have the potential to revolutionize patient diagnosis, treatment, and overall health improvement.
Digital Twin Healthcare: How It Works
Creating a digital twin requires accurate and structured data from various sources, including sensor-based systems like imaging scanners, lab tests, wearable monitoring devices, and clinical and scientific observations. This data is converted into a machine-readable format and used to build models ranging from predictive algorithms to comprehensive organ models with multiple simulation levels.
Continuous updates and feedback loops enhance the model over time, optimizing patient care and streamlining operations in the healthcare industry. Consequently, the digital twin can respond to changes, allowing for targeted improvements to be identified and achieved.
This data is then used to create a virtual copy of the patient, encompassing their anatomy, physiology, and health status. The digital twin can subsequently be employed to simulate different scenarios, such as the effects of various treatments or medications, and to offer real-time insights into the patient’s condition.
Digital Twin Model Components in the Healthcare Context
In the healthcare field, a digital twin system incorporates the typical hardware and software components found in other industries, along with specific elements that cater to healthcare requirements.
| Physical Entity | This is about the person or patient who serves as the groundwork for the Digital Twin representation. The physical entity represents the real-life individual and forms the basis for the digital representation. |
| Virtual Twin | The digital counterpart of the physical entity that captures relevant characteristics and attributes of the individual, enabling simulations and analysis to be performed in a virtual environment. |
| Digital Twin Data | Data aggregation, including historical and real-time patient data, analytical insights derived from a digital model, and the support of research, computational modeling, big data mining, and machine learning techniques. |
| Services | These services encompass real-time health monitoring, prompt diagnosis of medical conditions, personalized treatment strategies, and increased operational efficiency in healthcare institutions. |
| Data Connection | The procedure for transferring information between individuals and their digital equivalents involves the incorporation of data and services related to digital twins. |
Applications of Digital Twin in Healthcare
Although the notion of a fully developed digital twin has yet to be entirely achieved, we are progressively moving toward its actualization. Impressively, digital twins have made considerable advancements across multiple sectors in the healthcare field, such as:
Diagnosis and Treatment Decision Support
Digital twins enable the creation of virtual replicas of patients or specific medical conditions, allowing healthcare professionals to simulate different scenarios and evaluate the effectiveness of various treatment options. This technology paves the way for personalized and precise recommendations based on individual patient data and medical research. By leveraging digital twins, providers can significantly improve diagnostic accuracy, optimize treatment plans, and ultimately enhance patient outcomes.

Medical Device Design and Optimization
Digital Twin technology is highly valuable in the field of medical devices and equipment. Manufacturers can ensure product safety and effectiveness by utilizing digital twins for design, testing, and optimization. Virtual replicas allow organizations to simulate real-world scenarios, identify potential issues, and make necessary improvements before physical production, reducing costs, shortening development cycles, and enhancing overall device performance.
Additionally, digital twins provide predictive maintenance, as continuous monitoring of the virtual counterpart allows manufacturers to analyze real-time data and detect potential faults or malfunctions in advance. This proactive approach minimizes the risk of unexpected device failures, enhances patient safety, extends the lifespan of medical equipment, enables timely interventions, and reduces downtime, ensuring uninterrupted healthcare services.
Hospital and Facility Management
Digital twin technology can significantly enhance the operational efficiency of healthcare facilities, resulting in improved services while utilizing the same resources. For example, hospitals can optimize resource allocation and patient pathways to offer better experiences for patients. Moreover, energy planning and usage, resource logistics, administrative processes, and facility maintenance in hospitals can be strengthened with digital twin technology to promote a more sustainable future.
Remote Monitoring and Telemedicine
Digital twin technology revolutionizes patient monitoring using wearable devices like smartwatches and fitness trackers to collect real-time health data. This data, including vital signs, activity levels, and sleep patterns, is transmitted to a digital twin—an exact virtual replica of the patient. Instant analysis and interpretation by the digital twin provide valuable insights for healthcare professionals. In its turn, сontinuous monitoring enables personalized interventions, proactive detection of abnormalities, and remote patient monitoring, empowering healthcare providers to deliver optimized care and improve health outcomes.
In-depth Medical Research
Digital twin technology is also being used in medical research to simulate scenarios cost-effectively and safely before trying them in real-life conditions. This enables researchers to spot illness patterns, model the effects of therapies, and pinpoint the most promising areas for further study in living subjects. By comparing a large cohort of medical twins using digital twin technology, researchers can evaluate different treatment options for individuals with similar characteristics, helping to identify biological indicators for disorders.
Benefits of Digital Twin in Healthcare
In this section, we will explore the remarkable advantages digital twins bring to the table, showcasing their transformative impact on the healthcare landscape.
Enhanced Healthcare Access
As the IoT and digitalization continue to grow, more individuals gain equal access to vital digital information. Likewise, digital twinning in healthcare can enhance access to healthcare education, self-healthcare management resources, and various remote healthcare services, irrespective of geographical location constraints. The widespread availability of fitness and medical devices enables a larger population to engage in real-time health monitoring. This accessibility facilitates early warning signal detection and prompt diagnosis, alleviating the burden on already stretched healthcare resources.
Optimization and Risk Prediction
Through simulations in a virtual environment, the digital twin has the potential to mitigate risks and lower costs by optimizing bed scheduling and treatment solutions. Furthermore, by incorporating treatment methods and drug information into the model for verification, the digital twin can enhance treatment plans, leading to early disease diagnosis and prevention.
Monitoring and Precise Treatment
Wearable devices and mobile phones provide real-time health data, enabling digital twins to analyze abnormal conditions and deliver accurate treatments. By employing computer algorithm-based methods and principles in bioinformatics, Digital Twins can optimize treatment options, leading to improved patient survival rates and overall quality of life.
Digital Twin technology eliminates the limitations of traditional methods, empowering hospitals with advanced tools for informed decision-making. This integration of Digital Twins in healthcare grants patients greater autonomy and enhances the standard of care by enabling precise, personalized treatments.

Accelerated Innovation
In healthcare, the creation of digital replicas for vital organs or individual cells of specific patients paves the way for accelerated development and implementation of effective treatments. This personalized approach enables researchers to simulate diverse therapies and evaluate the potential responses based on patient characteristics.
The digitalization of genomic, organ, organ system-level, and surgical data empowers healthcare professionals to leverage modeling, simulation, validation, and outcome prediction, ultimately enhancing patient care and treatment efficacy.
Challenges of Implementing Digital Twin in Healthcare
Despite the numerous advantages offered by digital twin technology in healthcare, there exist significant challenges in its implementation. Among them:
Privacy and Security Concerns
One of the primary challenges associated with Digital Twins is ensuring the privacy and security of patient data. As Digital Twins heavily rely on collecting and analyzing sensitive medical information, protecting this data from unauthorized access and cyber threats is crucial. Healthcare organizations must develop robust data protection strategies and ensure that all stakeholders understand and comply with data privacy regulations.
Limited or fragmented data
Healthcare organizations often lack comprehensive data on their processes and patients, which is essential for digital twins’ accurate and unbiased functioning. Also, electronic health records and information are often scattered and hard to incorporate into operations. Unstructured data also demands manual efforts and lacks automation for processing. Furthermore, acquiring real physical monitoring stress data during human movement and merging different data types can be challenging, leading to restrictions in creating advanced digital twin models of the human body.
Integration with Existing Systems
Another challenge involves integrating Digital Twin technology with existing healthcare systems. Numerous hospitals and healthcare providers utilize disconnected systems that lack interoperability. Digital Twin technology must seamlessly integrate with these systems to provide a comprehensive view of patient health and streamline healthcare operations.
High Implementation Costs
The costs of implementing Digital Twin technology in healthcare can be substantial. Healthcare organizations must carefully consider the expenses associated with developing, implementing, and maintaining Digital Twin technology and determine whether the benefits justify the costs.
Regulatory and Ethical Considerations
Lastly, healthcare providers must address regulatory and ethical considerations when implementing Digital Twin technology. Compliance with regulations related to data privacy, patient consent, and ethical research practices is essential. Furthermore, providers must consider the potential ethical implications of using Digital Twin technology, such as ensuring that its use benefits patients without compromising their privacy or autonomy.
By addressing these challenges head-on, we can unlock the full potential of digital twin technology and revolutionize healthcare delivery.
Key Aspects for Healthcare Digital Twin Development
Various methods exist for building digital twins, including:
- A three-dimensional graphical representation;
- An Internet of Things (IoT) based framework;
- A combination of mathematical models;
- Visualization techniques including holography, augmented reality, and virtual reality.
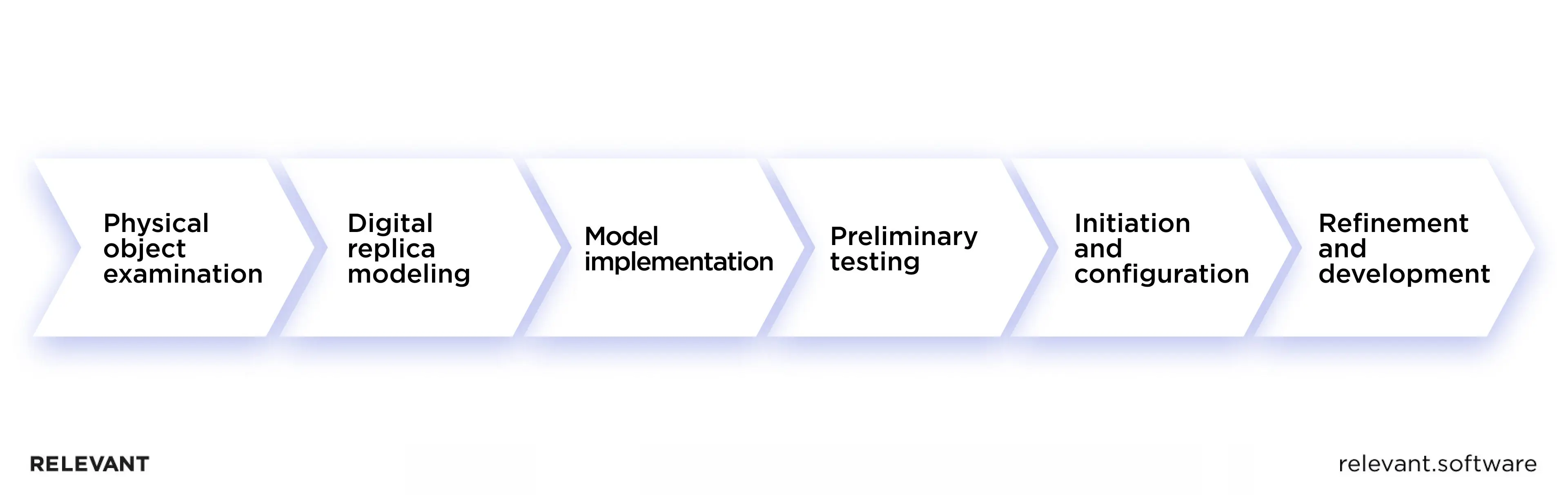
The following briefly outlines the stages involved in generating a digital twin.
- Physical object examination – Designing a comprehensive blueprint of the original item, which emulates all its features and behaviors across different situations. This step is optional and only necessary if a tangible prototype for the digital twin exists.
- Digital replica modeling – Employing mathematical approaches for computation and analysis to create an all-encompassing model.
- Model implementation – Combining mathematical models, data, and a user interface for digital twin management transforms it into a dynamic system.
- Preliminary testing of processes within the digital twin – Technical experts participate in this phase, gathering extensive data during tests to develop predictive algorithms for all potential conditions and scenarios.
- Initiation and configuration – Monitoring for any unforeseen failures or malfunctions not identified in previous stages.
- Refinement and development of the original object – Implementing adjustments to optimize effectiveness.
Final Words
As digital twin technology progresses, many organizations and industries are eager to digitize their processes using this cutting-edge approach. To make this leap, they’ll need a trustworthy technology partner to support their digital twin endeavors.
That’s where Relevant steps in. We provide the necessary expertise, healthcare software development solutions, and integration services to ensure a successful integration while safeguarding your data, simulations, and the real-world entities represented by the digital twin. If you’re considering the adoption of digital twin technology in your business, we are here to support you in confidently navigating this exciting journey.
Also, read more about HL7 and the benefits of exploring healthcare RFID.
FAQ
What is a digital twin in healthcare?
Digital twins in healthcare represent a “virtual doppelganger” of a patient’s physical, biological, and behavioral attributes, meticulously crafted through state-of-the-art data analytics and modeling. By mirroring real-time fluctuations in a patient’s health, digital twins assist healthcare providers in forecasting outcomes, fine-tuning treatments, and customized care plans, thus enhancing patient outcomes and curbing healthcare expenditures.How does digital twin technology work in healthcare?
Digital twin technology in healthcare functions by amassing and scrutinizing data from a myriad of sources, such as electronic health records, medical imaging, and wearable gadgets. This data is subsequently employed to generate a dynamic, digital portrayal of the patient, which can be perpetually updated as fresh information comes to light. Healthcare professionals can engage with the digital twin, experimenting with various treatment alternatives and observing patient reactions in a virtual setting, ultimately contributing to clinical decision-making and individualized care.What are the digital twin healthcare use cases?
Digital twin technology boasts a multitude of applications in healthcare, encompassing personalized medicine, remote patient monitoring, medical research, and clinical trials. By fashioning a virtual depiction of a patient’s health status, digital twins empower healthcare professionals to anticipate outcomes, hone treatments, and adapt care plans. Moreover, digital twins can be utilized to evaluate the efficacy of novel drugs and therapies, streamline clinical trials, and bolster population health management endeavors.What are the benefits of digital twins in healthcare?
The advantages of digital twin healthcare include improved patient outcomes, tailored care, diminished healthcare expenses, and augmented medical research. By emulating real-time variations in a patient’s health, digital twins enable healthcare professionals to make well-informed decisions, optimize treatments, and minimize risks. Additionally, digital twins can expedite drug development, refine clinical trial protocols, and buttress public health initiatives, ultimately paving the way for more effective and efficient healthcare systems.How does digital twin healthcare enhance medical research?
Digital twin healthcare bolsters medical research by offering a platform for the simulation and analysis of diverse treatment options, drug reactions, and disease progression scenarios. By generating a digital representation of a patient or a population, researchers can delve into the effects of different interventions, pinpoint patterns, and unearth insights that would otherwise be challenging or laborious to obtain through conventional methods. Consequently, this culminates in more informed decision-making, accelerated drug development, and an improved design of clinical trials.What is the use of digital twins in clinical trials?
In the context of clinical trials, digital twins are employed to optimize study protocols, reduce trial duration, and enhance patient safety. By simulating patient responses to different treatments in a virtual environment, researchers can identify potential risks and side effects, as well as adjust dosages and treatment plans accordingly. This not only ensures the safety of trial participants but also accelerates the process, allowing for the faster development and approval of new, life-saving treatments.What is a digital twin with an example?
Digital twin healthcare companies are advancing the use of this technology to meet industry demands, and significant progress has been made yet. Let’s take Dassault’s u0022Living Heart, u0022 a revolutionary virtual human heart model. This sophisticated software considers blood flow, mechanics, and electrical activity, transforming 2D scans into precise 3D models of individual hearts. Another example is French start-up Simu0026amp;Cure which supports brain treatment research and develops digital patient models for aneurysm treatment. These advancements empower doctors to detect latent illnesses, explore treatments, and enhance surgical preparation.

Hand-selected developers to fit your needs at scale! Let’s build a first-class custom product together.

