How IoT in Supply Chain Management Drives Real Results

If you wonder how some companies keep their supply chains running smoothly—despite global disruptions—for a long time, the answer often comes down to three letters: IoT. The Internet of Things has quietly become the backbone of modern supply chains, offering real-time visibility, smarter asset management, and a level of operational efficiency that traditional methods simply can’t match. But adopting IoT in supply chain management isn’t as simple as plugging in a few sensors.
Successful integration demands strategic planning, a deep understanding of logistics complexities, and, often, the expertise of a development partner who knows how to connect the dots—literally and figuratively.
from 25 countries outsourced software development to Relevant
We provide companies with senior tech talent and product development expertise to build world-class software.
This guide explores how logistics software development services transform supply chain management with real-world examples, key benefits, challenges, and IoT opportunities. Relevant Software’s team shares insights to help you unlock IoT’s full potential and make smarter, data-driven decisions.
IoT in supply chain management
Supply chain management has evolved into a complex, global network where precision, speed, and visibility are non-negotiable. Traditional methods—reliant on manual tracking, siloed systems, and reactive decision-making—can no longer keep pace with growing customer demands, fluctuating markets, and frequent disruptions.
McKinsey’s fifth annual Global Supply Chain Leader Survey reveals that 90% of supply chain leaders have faced challenges in 2024, highlighting the ongoing vulnerabilities within global supply chains. This is where the Internet of Things (IoT) steps in, offering a transformative shift from fragmented operations to fully connected ecosystems.
What is IoT?
The Internet of Things (IoT) is a network of interconnected physical devices—each embedded with sensors, actuators, and communication technologies—that collect and transmit data over the Internet. In supply chain management, IoT transforms passive assets into active data points, creating a real-time feedback loop between the physical flow of goods and the digital systems managing operational technology.
You next read: What is IoT?
How is IoT used in supply chain?
With the rise of the Internet of Things (IoT), supply chains are evolving into something far more dynamic – intelligent, self-optimizing ecosystems. But how is IoT used in supply chains on a practical level? Let’s take a closer look.
- Data collection: IoT devices—such as sensors, RFID tags, and GPS trackers—gather granular data on asset location, environmental conditions, movement, and performance. This data includes temperature, humidity, shock levels, geographic coordinates, and even the operational status of machinery.
- Data transmission: Collected data is transmitted through communication protocols like Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, LTE/5G, or LPWAN (Low Power Wide Area Network) depending on range, power needs, and bandwidth requirements.
- Data processing and analysis: Once transmitted, data flows into cloud-based or edge-computing platforms, where it is aggregated and analyzed. Advanced analytics and AI algorithms process this information, identifying patterns, anomalies, and actionable insights.
- Real-time decision-making: Based on processed data, automated systems or human operators make decisions. This could range from rerouting shipments due to traffic delays to triggering maintenance on machinery showing signs of wear.
Examples of IoT devices in supply chain and logistics
The success of IoT in supply chain management relies on a network of smart devices that collect, transmit, and act on real-time data for supply management. Below are some of the most impactful IoT devices driving efficiency in supply chains and logistics.
- Environmental Sensors: These devices measure temperature, humidity, shock, and light exposure—critical in industries like food and pharmaceuticals where product integrity depends on maintaining specific environmental conditions.
- RFID Tags and Readers: RFID (Radio-Frequency Identification) tags use electromagnetic fields to identify and track tags attached to objects automatically. In warehouses and distribution centers, RFID streamlines inventory management, reducing human error and enhancing stock level accuracy.
- GPS Trackers: GPS devices provide real-time geolocation data for assets in transit. Integrated with telematics systems, they enable dynamic route optimization, estimated time of arrival (ETA) tracking, and proactive management of delays.
- Smart Cameras: Equipped with AI capabilities, these cameras do more than monitor spaces—they analyze activities. In warehouses, they help with quality control, security monitoring, and even tracking the movement of goods and personnel to optimize workflows.
- Actuators: These are the ‘action’ devices in IoT systems. When sensors detect a change (e.g., a temperature spike in a cold storage unit), actuators can trigger responses such as adjusting HVAC settings to maintain optimal conditions.
How these devices work together
Consider a cold chain logistics operation transporting perishable goods. Temperature sensors in refrigerated trucks monitor conditions in real time. If the temperature deviates from the preset threshold, the system immediately alerts fleet managers and activates actuators to recalibrate the cooling system.
Simultaneously, GPS trackers provide real-time location updates, allowing logistics teams to reroute the shipment if delays threaten product integrity. All this data streams into a centralized dashboard, offering full visibility and control over the shipment. This interconnected ecosystem turns IoT from a simple tracking tool into an intelligent supply chain management system—offering not just data but actionable insights that drive efficiency, reduce risks, and enhance operational agility.
Benefits of IoT in supply chains
Most businesses see IoT as a tool—a means to optimize, streamline, and save. But its true value lies in challenging the very foundations of supply chain management. It exposes inefficiencies no one thought to question, redefines what “efficiency” means, and forces a shift from reactive to predictive thinking.
The global Internet of Things (IoT) market is set to expand from $714.48 billion in 2024 to $4,062.34 billion by 2032, with a CAGR of 24.3%. This rapid growth highlights the importance of supply chain management software in helping businesses harness IoT’s full potential, streamline operations, and stay competitive in an increasingly connected world.
So, what are the benefits of Internet of Things supply chain solutions? Our experts have identified the main ones:
Real-time visibility & transparency
Global supply chains move enormous volumes every day, yet around 45% of companies still lack end-to-end visibility, according to McKinsey. IoT helps close this gap by providing real-time insight into asset location and condition through GPS trackers and RFID tags. In cold chain logistics, such as vaccine distribution, IoT sensors monitor temperature continuously and trigger alerts when thresholds are exceeded, preventing spoilage and supporting regulatory compliance.
Cost reduction & operational efficiency
Many view cost reduction as IoT’s headline benefit, but its true value runs deeper. IoT exposes the inefficiencies that traditional systems miss—subtle delays on production lines that ripple across operations or outdated warehouse layouts that quietly bleed time and money. It doesn’t just cut costs at the surface; it rewires processes at their core, creating efficiencies that compound over time.
Improved inventory management
Outdated, static tracking systems often cause inventory mismanagement. IoT transforms oversight into a dynamic, real-time process. RFID tags and smart shelves provide continuous stock updates, while predictive analytics forecast demand more accurately. This reduces overstock, prevents stockouts, and supports agile inventory strategies that align with shifting market demands.
Predictive maintenance & equipment monitoring
Downtime is the silent killer of supply chain efficiency. IoT sensors embedded in machinery detect micro-level anomalies—like subtle temperature shifts or unusual vibrations—that predict equipment failure long before it happens. GE Aviation uses IoT to monitor aircraft engines in real time, enabling predictive maintenance that reduces downtime and enhances safety.
Sustainability & waste reduction
As sustainability becomes a business imperative, IoT offers tangible pathways to greener operations. Route optimization reduces fuel consumption, while smart energy management systems in warehouses lower electricity usage, enhancing overall customer service. Cold chain logistics benefit immensely—temperature-controlled shipments equipped with IoT sensors minimize spoilage, directly reducing product waste and associated environmental impact.
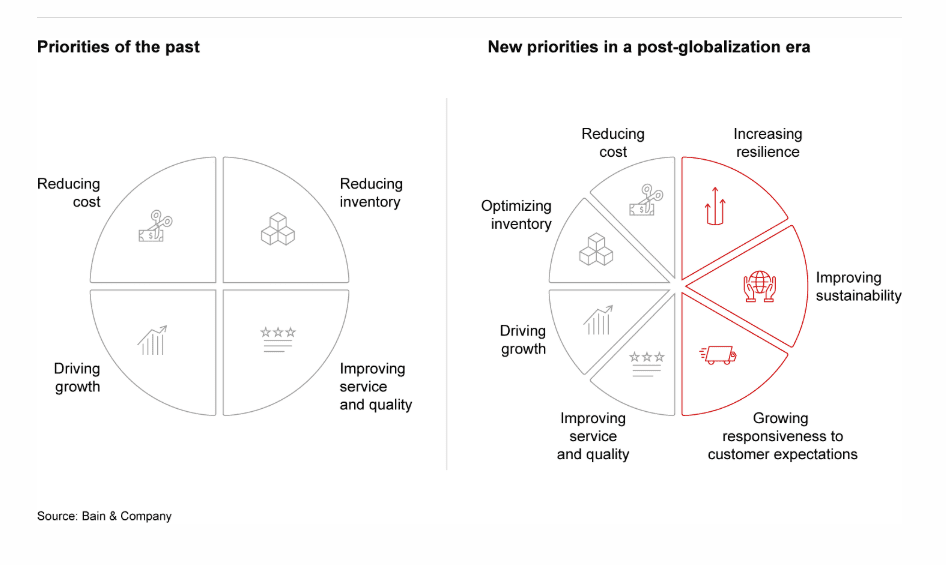
Source: Bain
Key applications of IoT in supply chain management
Companies that invest in supply chain software development services gain a significant edge in the supply chain industry, transforming their operations into more agile, efficient, and resilient ecosystems. By integrating the Internet of Things in supply chain management, businesses unlock real-time insights, optimize processes, and improve decision-making. Belo, Relevant Software experts have shared the core areas where IoT delivers the greatest impact.
Real-time asset tracking and monitoring
Live asset monitoring is now a necessity for global logistics. IoT-enabled devices—integrating GPS, RFID, and environmental sensors—offer uninterrupted visibility into the location, status, and condition of goods throughout transit.
Real IoT in supply chain example: Maersk uses IoT-enabled shipping containers to track cargo location and conditions throughout transit. These smart containers provide real-time updates on temperature, humidity, and handling, ensuring goods arrive safely and intact.
Smart warehousing and inventory management
IoT in inventory management has turned warehouses into intelligent, self-regulating ecosystems. Smart shelves equipped with RFID readers and weight sensors provide continuous stock updates, while automated guided vehicles (AGVs) and robotic pickers handle goods with speed and precision. But the real power comes when IoT data converges with AI-driven analytics. This fusion enables accurate demand forecasting, dynamic inventory optimization, and real-time stock replenishment.
Real IoT in supply chain example: Amazon uses IoT-powered Kiva robots in its fulfillment centers to transport inventory and optimize picking routes. This system speeds up order fulfillment, reduces human error, and improves warehouse efficiency.
Fleet and transportation management
Without IoT, fleet management often struggles with inefficiencies and unexpected delays. IoT provides real-time data on vehicle locations, fuel use, and driver habits, giving managers the tools to optimize routes, reduce idle time, and lower fuel costs. Predictive maintenance sensors track vehicle health, spotting issues before they trigger costly breakdowns—this results in smoother operations, quicker deliveries, and reduced expenses.
Real IoT in supply chain example: FedEx’s SenseAware platform, for example, provides live updates on high-value shipments, allowing for dynamic route optimization and improved delivery times.
Your next read: IoT in fleet management
Cold chain monitoring for perishable goods
Cold chains demand absolute precision, and IoT supply chain management delivers it. Temperature and humidity sensors embedded throughout the supply chain provide continuous oversight, ensuring that perishable goods—whether pharmaceuticals, food, or chemicals—remain within strict environmental thresholds. Real-time alerts flag even minor deviations, enabling corrective action before product integrity is compromised.
Real IoT in supply chain example: Hapag-Lloyd uses smart containers equipped with IoT sensors to monitor temperature and humidity during shipping. This system ensures food products, pharmaceuticals, and other sensitive cargo maintain quality standards throughout transit.
Predictive maintenance and equipment management
Unplanned downtime remains one of the most costly issues in potential supply chain disruptions. Smart supply chains mitigate this risk through predictive maintenance. Sensors monitor key metrics—vibration, temperature, pressure—across machinery and vehicles, detecting anomalies that signal wear or impending failure. These insights enable maintenance teams to act before breakdowns occur, reducing downtime and extending equipment life.
Real IoT in supply chain example: Caterpillar, for instance, collaborates with Uptake to monitor its heavy equipment in real time, optimizing maintenance schedules and extending equipment life.
Automation and robotics in supply chain operations
Today’s supply chains thrive on automation, reducing human involvement. IoT-enabled robots in warehouses and factories don’t just follow static instructions—they adapt based on real-time data. Integrated with AI, these systems reroute workflows, optimize picking sequences, and make on-the-spot decisions. It’s about boosting productivity, cutting errors, and scaling operations efficiently.
Real IoT in supply chain example: Walmart uses Symbotic’s robotic systems in its distribution centers to automate product sorting, palletizing, and inventory handling. These robots, guided by IoT and AI, optimize warehouse workflows, improving speed and accuracy.
Challenges and risks of IoT in supply chain management
While IoT unlocks immense potential in supply chain management, it also introduces some complexities that require careful strategy, the right technology, and deep expertise. Below are the key challenges of IoT in supply chain—and how the Relevant Software product development team helps businesses overcome them.
Data security threats and privacy concerns
Every connected device in a supply chain represents a potential entry point for cyber threats. IoT networks, especially those spanning global operations, expose companies to risks such as unauthorized access, data breaches, and ransomware attacks.
How Relevant Software experts address this:
- End-to-end encryption to secure data in transit and at rest.
- Multi-factor authentication with role-specific access permissions.
- Encrypted protocols securing device-to-network data exchanges.
- Continuous threat detection paired with routine security assessments.
- Regular firmware updates to patch vulnerabilities and strengthen defenses.
High implementation costs
IoT deployments require significant investments in hardware, infrastructure, and integration, along with ongoing maintenance costs. Without a well-defined ROI strategy, these investments risk underperforming.
How Relevant Software experts maximize ROI:
- Phased IoT rollouts, starting with high-impact areas to generate early returns.
- Scalable, customizable solutions that grow alongside business needs.
- Strategic selection of cost-effective devices and platforms.
- Advanced analytics to measure ROI and optimize deployments.
- Continuous performance tracking to fine-tune operations and reduce costs.
Integration with legacy systems
According to the experience of Relevant Software’s clients, integrating modern IoT solutions with outdated, siloed legacy systems often leads to compatibility issues, data fragmentation, and increased complexity. Without seamless integration, businesses risk data inconsistencies and operational inefficiencies.
How Relevant Software experts ensure seamless integration:
- Development of custom middleware to bridge IoT devices with legacy systems.
- Use of standardized APIs for smooth data exchange.
- Modular integration strategies that avoid large-scale system overhauls.
- Data harmonization techniques to unify diverse data sources.
- Minimal-disruption deployment to maintain business continuity.
Data overload and complexity
IoT networks generate massive volumes of data—from location updates to equipment diagnostics. Without the right infrastructure, logistics companies risk data overload, leading to analysis paralysis and missed opportunities.
How Relevant Software experts simplify data management:
- Edge computing to process critical data directly at the source for faster insights.
- AI-powered analytics to detect patterns, anomalies, and key operational trends.
- Tailored dashboards to provide real-time supply chain visibility for informed decision-making.
- Instant alerts and automated reports to enhance efficiency across supply chain workflows.
Data ownership and control
In multi-vendor supply chains, data ownership can become unclear. Without explicit agreements, disputes over data rights may lead to compliance issues, security risks, and operational delays.
How Relevant Software experts solve it:
- Establishment of clear data governance frameworks, defining ownership and access rights
- Role-based access controls and permission hierarchies to safeguard sensitive data
- Blockchain-based audit trails for industries needing immutable, transparent data records (e.g., pharmaceuticals, food logistics)
Vendor lock-in risks
Many IoT solutions tie businesses to proprietary ecosystems, making it costly and difficult to switch vendors or scale operations flexibly.
How Relevant Software experts solve it:
- Development of vendor-agnostic IoT solutions compatible with diverse platforms
- Custom middleware that bridges IoT devices with existing and future systems
- Adoption of open standards and modular architectures, allowing businesses to evolve without expensive overhauls
Hidden operational costs
Businesses often underestimate the long-term expenses associated with IoT—such as data storage, bandwidth, and device maintenance—leading to eroded ROI over time.
How Relevant experts solve it:
- Scalable IoT architectures that optimize data transmission and reduce bandwidth costs
- Predictive maintenance protocols for IoT devices to extend hardware lifespan
- Real-time cost analytics dashboards that provide transparency into ongoing expenses
Ethical and Privacy Concerns
IoT devices collect vast amounts of sensitive data, from employee movements to vehicle locations, raising privacy concerns and increasing the risk of legal exposure.
How Relevant Experts solve it:
- Privacy-by-design principles, including data anonymization and encryption
- Full compliance with global privacy regulations (GDPR, CCPA)
- Built-in features like data masking, consent management, and audit logging
- Regular privacy impact assessments to align with evolving legal frameworks and protect brand integrity
Future Trends: AI-Driven IoT for Smarter Supply Chains
KPMG’s “Supply Chain Trends 2024 report emphasizes the critical role of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in modernizing supply chains. Generative AI in operations and IoT now redefine supply chain management, shifting operations from basic automation to intelligent, self-regulating ecosystems. AI-powered IoT solutions convert raw data into predictive insights, allowing supply chains to anticipate changes rather than react to them.
What is an example of IoT in the supply chain paired with AI?
- Predictive analytics: AI algorithms process data from IoT sensors to forecast demand shifts, inventory requirements, and potential disruptions. This foresight helps businesses adjust production schedules, reroute shipments, and optimize inventory before issues occur.
- Machine learning for process optimization: ML models use historical and real-time data to refine logistics strategies. They optimize delivery routes based on traffic patterns and adjust warehouse layouts to improve picking efficiency and reduce handling time.
- AI-enabled low-touch planning: Low-touch planning automates key supply chain tasks such as demand forecasting, inventory replenishment, and production scheduling. AI systems adapt plans in real time based on market changes and supply chain disruptions, reducing manual input and improving agility.
- Automated decision-making: AI-powered IoT platforms support real-time decisions without human intervention. Smart warehouses reroute autonomous robots, adjust temperature controls, or reallocate resources instantly based on live sensor data, boosting efficiency and accuracy.
- Enhanced risk management: AI identifies anomalies and predicts equipment failures or shipment risks by analyzing IoT data. This proactive approach reduces downtime, prevents spoilage, and minimizes costly disruptions.
- Sustainability optimization: AI leverages IoT data to optimize resource use, cutting energy consumption, waste, and emissions. Smart logistics networks adjust delivery routes to lower fuel usage and carbon footprints, contributing to greener supply chain operations.
As AI evolves, its synergy with IoT will create supply chains that stay connected and truly intelligent—capable of self-correction, adaptation to market shifts, and constant performance improvement.
Implement IoT in supply chain management with Relevant
Most companies adopt IoT with the expectation of improved tracking, cost reductions, and smoother operations. But here’s the paradox: when every competitor implements similar technology, those baseline improvements become the new status quo. Efficiency alone won’t create a lasting competitive edge.
The real differentiator lies in how businesses use IoT data to challenge assumptions and rethink strategies. It’s not just about knowing where a shipment is or when a machine might fail—it’s about using that insight to make smarter decisions that competitors haven’t even considered.
At Relevant Software, we don’t just offer IoT software development services—we solve real problems that supply chain leaders face every day. Our strength lies in understanding the complexity of modern logistics and designing systems that think ahead, adapt to disruptions, and unlock efficiencies that weren’t visible before.
If you’re ready to push past conventional solutions and build a smarter, more adaptive supply chain, we’re here to make it happen—not with off-the-shelf answers but with strategies built around your specific goals. Contact us!


Hand-selected developers to fit your needs at scale! Let’s build a first-class custom product together.

