Internet of Things (IoT) Testing: Why Is It So Important?

The Internet of Things has become a top-trending technology — the supply and demand for IoT solutions are higher than ever. Still, that’s just the beginning.
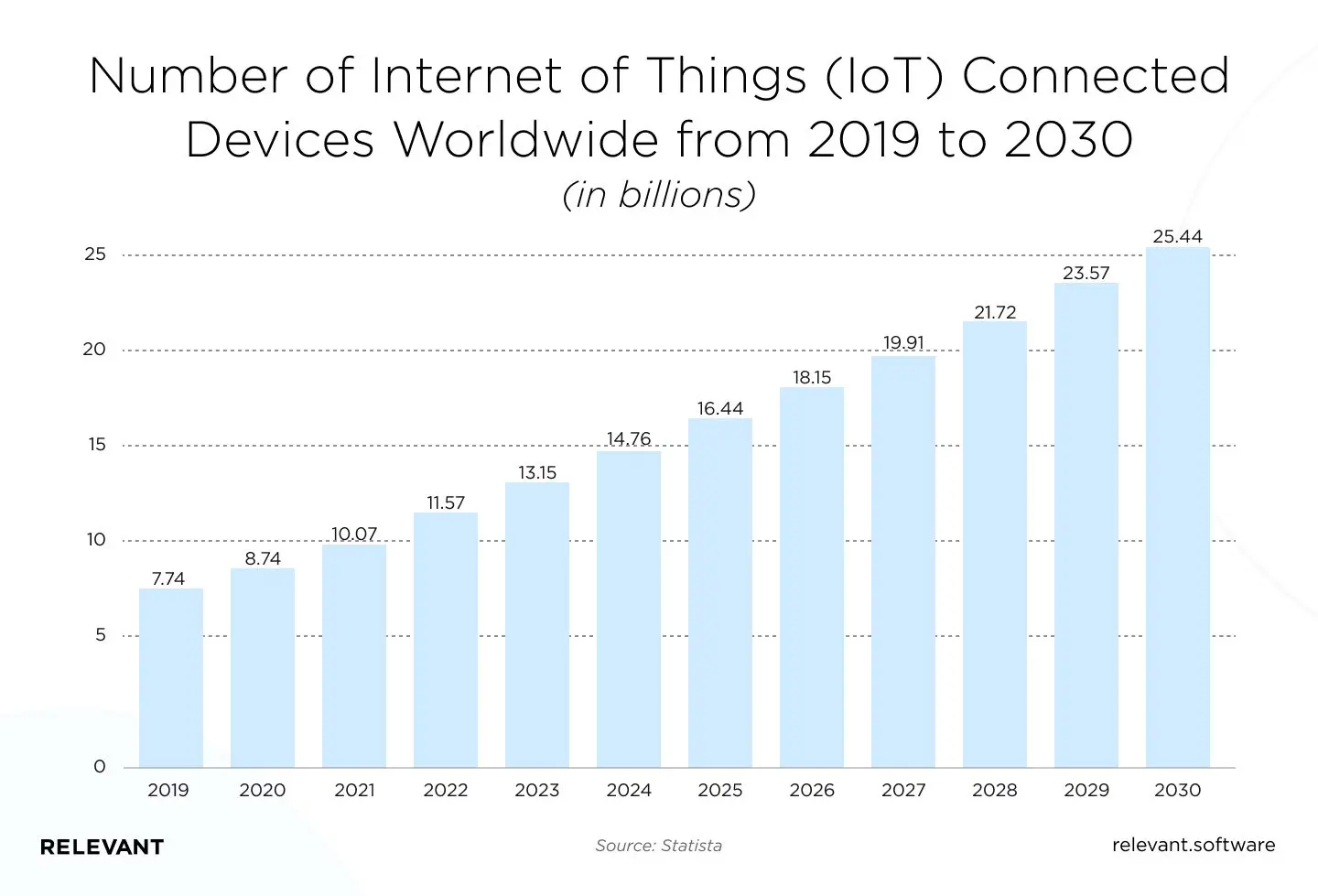
If in 2019, the number of connected IoT devices was over 7,74 billion, then by 2030, according to the most conservative estimates, there will be 25,44 billion. And that figure will grow even higher if we can address IoT solutions security and interoperability issues.
from 25 countries outsourced software development to Relevant
We provide companies with senior tech talent and product development expertise to build world-class software.
The more devices connect to the Internet of Things, the more important it is to keep the system effective and safe. However, traditional quality assurance services methods are no longer sufficient. Many devices require early testing, especially those undergoing continuous integration.
Since Relevant is an IoT expert and seasoned IoT software development company, we will explain the concept of IoT testing and why it is one of the most significant steps in an IoT project deployment.
What is IoT Testing?
The Internet of Things comprises three key components – devices, communications, and computing. Devices are things or physical objects connected to the Internet. The second component is communication, which is carried out via Wi-Fi or satellites and cellular services and is very important to keep the entire system working.
The third component is computation, which is done in a central location on the server and allows the system to run efficiently. An IoT application helps integrate all three elements for intelligent decision-making.
However, the heterogeneity of underlying devices and communication technologies and the need for interoperability at different levels – from communication and seamless integration of devices to the interaction of data generated by IoT resources- hinder the implementation of common IoT solutions globally.
Because the IoT is a network that communicates in real-time, performance and security issues in any part of it can negatively affect the performance of the rest of the network. One node compromised by a cyberattack can harm others. Therefore, you must detect all weak points before the product reaches consumers.
That’s what IoT testing is for – a series of QA tests designed to validate functionality, performance, and security, in which all devices take part, regardless of their shape, size and location.
Since the IoT is a fragmented system, there are certain difficulties associated with the testing process. These can be eliminated by setting up large test teams to examine all components for reliability across multiple platforms and devices.
What are the IoT testing types?
In theory, testing IoT solutions is similar to testing other software products; in reality, it has some distinctive peculiarities. Test types fall into two basic categories, which include separate subcategories.
Functional testing
As you might guess from the name, it involves checking how various functional aspects work. This group includes, for example:
- Unit testing. It tests each module or component of an application. The IoT development team usually performs this task.
- Integration testing. When all modules are integrated, it is essential to see how they work together.
- End-to-end testing. This type involves running tests for the entire software product.
- Smoke testing: This type of testing helps determine if the software is stable enough.
- Regression testing. Each added module leads to changes in the program. If it takes any updates to the firmware of the IoT device, they can also lead to changes in the system. It is crucial to ensure that all components are still working correctly after each update.
- Interface testing. Testers verify the GUI meets the specified requirements and specifications.
Non-functional testing
It focuses on aspects such as performance, reliability, security. In this category, we can define the following types:
- Performance testing. This process focuses on identifying software performance problems.
- Security testing. Because data security is vital to most IoT solutions, this type of testing is incredibly rigorous.
- Load testing. That allows you to determine how much load the software can withstand without degrading performance.
- Stress testing. These tests help you assess whether the system is performing as expected when there are insufficient resources.
- Compatibility testing. It will help you check if the application can work on different platforms / in different environments without errors and other problems. These tests are appropriate when the software is completely stable.
There are up to 40 types of testing in total. Let’s inspect the most used options for the Internet of Things in more detail.
Compatibility testing
Since IoT systems are built after multiple hardware and software configurations, the crucial phase of IoT testing should begin with running compatibility tests. This process typically involves testing various devices, browsers, operating systems, and communication modes to ensure maximum compatibility.
It determines whether a target product that implements a standard specification is compatible with other products that implement the exact specification. Each software component must recognize input from other programs, handle the workload associated with its role in the architecture, and provide accessible and valuable results.
Tip: Check the response time against a specific time and if the data sent is accurate.
Performance testing
The second phase of IoT software testing begins with validating the performance-related implementation. Some of the key factors that the performance testing process typically deals with include:
- Performance under maximum load or data.
- Testing system for several devices at the same time.
- Communication tests between devices.
- System usability such as RAM load, battery usage, power consumption.
- Testing the device under various network conditions and environmental factors.
It helps you test the speed of IoT applications in data-intensive environments. Testers can simulate heavy loads using cloud platforms and create custom scripts to test the program in challenging environments.
Tip: Performance testing in IoT should be done at the network and gateway level (protocols such as MQTT, HTTP, CoAP), system-level (processing, analytics, database), and application level.
Connection testing
The third testing stage ensures uninterrupted connectivity even when users cannot have a complete set of data. The stability of the IoT system depends on how well the devices and the hub are connected. After all, if it loses the connection for at least one second, it can cause data inaccuracy and system instability. Flawless connectivity, besides data recovery, is one of two critical features of connectivity testing.
Tip: Don’t forget to register all gadgets taking part in the IoT test with the network. Send periodic ping messages to make sure the error persists. The device must save the data to the database, which syncs with the hub to restore the connection (device shadow in AWS).
Usability testing
Because the user receives data on IoT devices in real-time, IoT software interfaces need to be manageable and informative. Usability testing ensures that the end-user gets intuitive and straightforward software that harmoniously represents all the graphical elements.
Tip: Ensure the IoT application has all its features, accords to the specifications, and checks user experience (UX).
Security testing
Because IoT software requires a lot of data for an application to function correctly, IoT security testing methodologies are essential to developing a robust IoT testing strategy. It includes three levels of testing.
- Network testing. It protects the IoT application from potential network layer attacks.
- System testing. It will ensure that user data is safe and well protected from leakage and hacking.
- Testing of IoT devices. This kind of test ensures that devices for an IoT application are protected from problems related to APIs, authentication, updates, configuration settings, etc.
Tip: Check for unauthorized access to the device, or make sure you can remotely delete data on jailbroken devices.
Beta testing
This type of user testing IoT requires testers to model realistic IoT test scenarios. That helps them prevent users from having problems with the final version of the IoT application and increases the chances of a successful release. It also helps business owners reduce bug fixing costs as glitches and usability issues are discovered during the beta phase.
By applying IoT testing, you can test IoT software at all stages of its development.
IoT Testing framework: What is it all about?
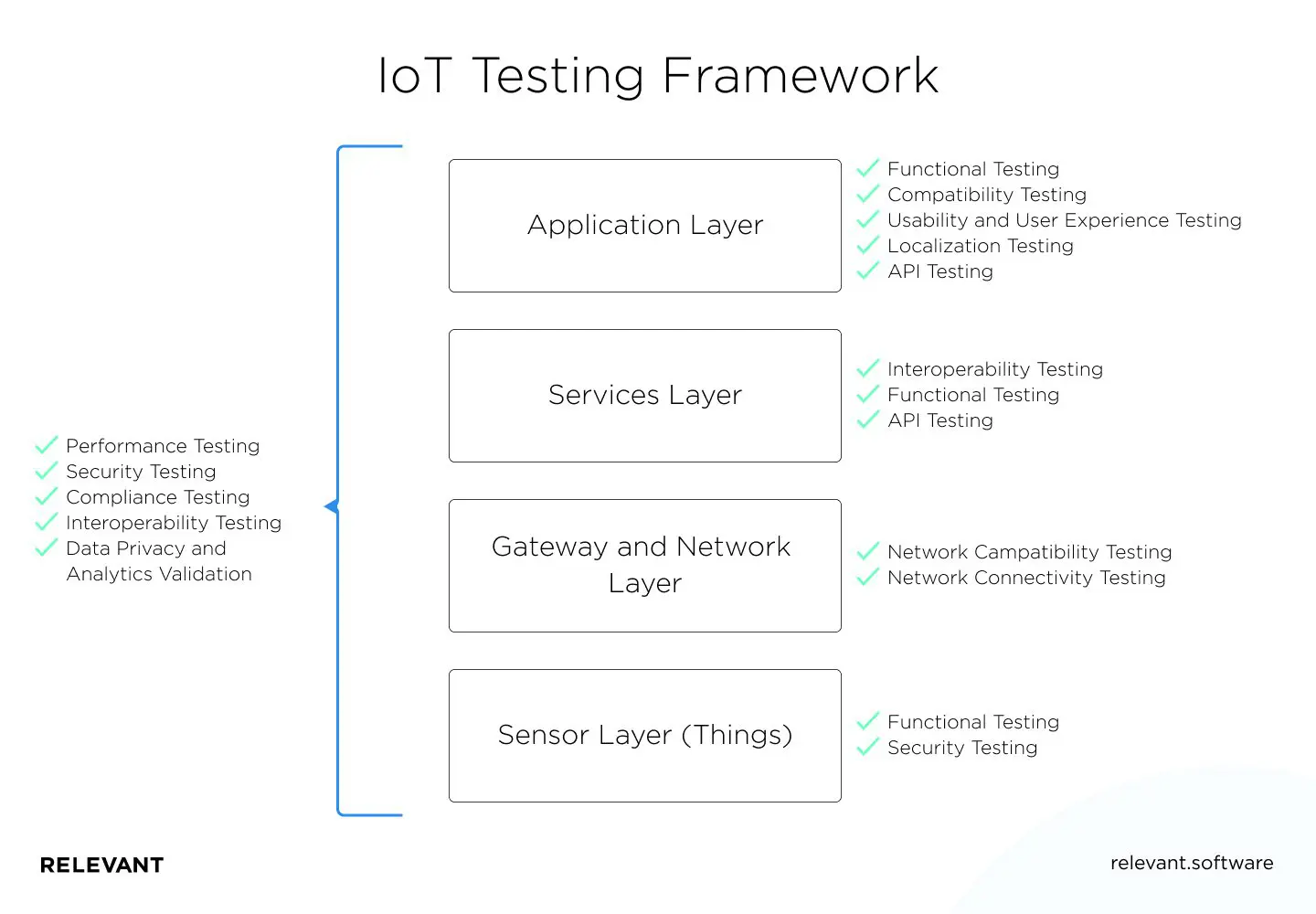
Testing for the Internet of Things requires a robust environment whose infrastructure depends on the devices involved in the IoT ecosystem. We can divide the IoT Testing Framework into the following levels:
- Application layer. Functional testing, compatibility testing, usability and user experience testing, API testing localization testing are performed at this level.
- Service level. At this level, compatibility testing, functional testing, and API testing are performed.
- Gateway and network layer. It relates to network compatibility and network connectivity testing.
- Sensory level. At this level, the tester will perform functional and security testing.
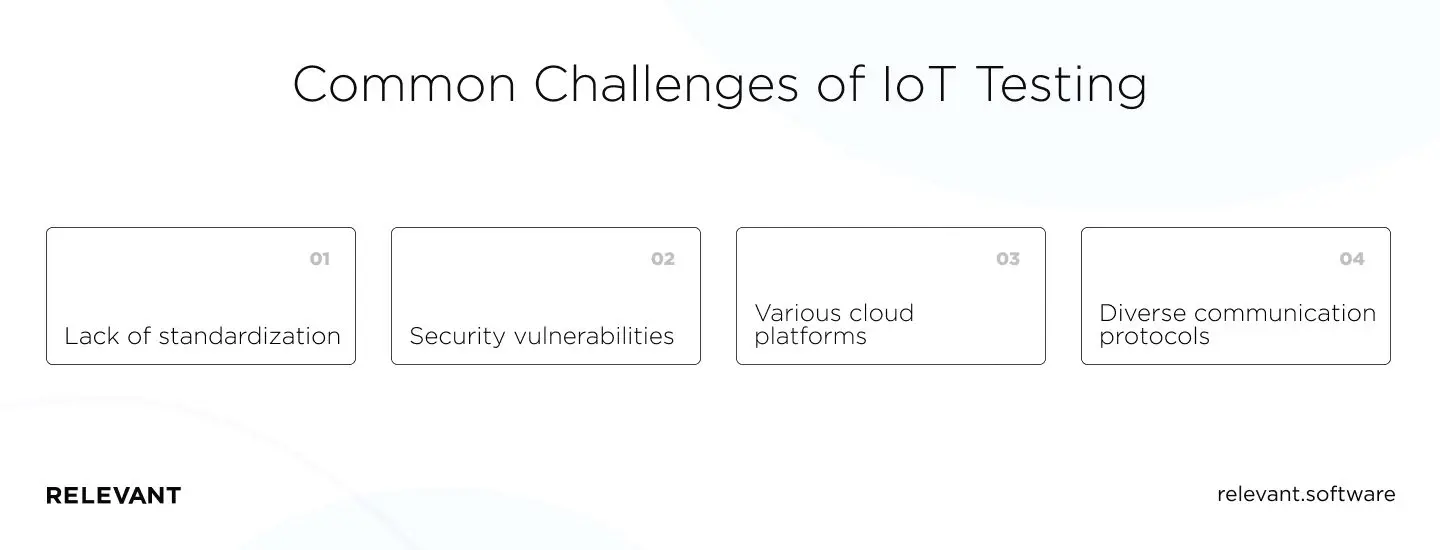
What are the common challenges of IoT testing, and how to address them?
The best IoT software testing strategies should foresee all the Internet of things testing challenges that can complicate the testing process for developers and QA engineers. Let’s look at the most important ones:
Lack of standardization
First, note the need to standardize the IoT environment at different levels, such as connectivity, communication protocols, platforms, and business models. But this is rarely the case.
Typically, each link in the IoT network has its hardware and software. That means that IoT testing services must include test cases for each type of hardware and software.
Tip: It is not entirely advisable to run all scripts at once. For effective testing, test cases of the most suitable combinations of integrations come to the market.
Security vulnerabilities
Because IoT devices that generate large amounts of data can be vulnerable to cybersecurity threats, they must systematically pass security testing in IoT. In this way, security loopholes can be identified and closed. For example, it is essential to use tools that validate password prompts and behavior on an IoT device upon initial user access.
Tip: Try to identify vulnerabilities in device architectures and firmware from the perspective of an attacker. For hints and tips, see our IoT penetration testing tutorial.
Various cloud platforms
IoT devices depend on their connectivity to various cloud platforms, such as Azure IoT, AWS IoT, and others, to keep their IoT devices running smoothly. To ensure the usability of such devices, we must test them on these cloud platforms. In the entire IoT ecosystem, devices generate many structured and unstructured data, and we should check them for accuracy and integrity to get the expected results.
Tip: Since it is difficult to test every IoT device running different OS versions properly, it becomes necessary to create solutions for testing IoT devices. In addition, we will update IoT device versions besides software and firmware updates. Hence, testing each device across different platforms (OS, browsers, and cloud) ensures that the components run smoothly and efficiently.
Diverse communication protocols
In an IoT environment, devices use various real-time communication protocols, such as XMPP, AMPQ, MQTT, and CoAP. These protocols help to establish a connection between devices and also between devices and the server.
In addition, different components in an IoT system can use other communication protocols to communicate. And until we test these components over communication protocols, latent failures will continue to cause functional or security problems.
Sensors present in devices can run out of memory when loading requests that exceed a threshold. So, instead of directing these requests directly to sensors, they use an IoT gateway to balance load requests between components. IoT testing helps verify the load balance between elements and extends their lifespan.
Tip: Every IoT device needs to be tested over communication protocols to ensure they work efficiently, reliably, and securely.
The key benefits of IoT testing for your business
Now get a look at the primary advantages of testing for business users of IoT solutions:
- New business opportunities: Testing the Internet of Things software will speed up initiatives with less risk, driving innovation.
- Speed up time-to-market: IoT testing facilitates time-to-market by leveraging early automation.
- Improved interoperability: IoT QA testing ensures that end-users experience a quality user experience across multiple channels.
- Higher ROI. IoT Testing provides a comprehensive approach to validating the practical and non-functional requirements of IoT solutions. As a result, you will deliver safer solutions and, therefore, be more attractive to your customers.

How to test an IoT app: Example and tips
The main thing that differentiates IoT application testing from testing other types of software is that their relationship to external devices is fundamental. In this situation, the testing team must have specific knowledge of these devices and their capabilities.
Sometimes programmers have physical access to the required device, which facilitates the testing process. However, there are often situations when it is impossible to gain access to the device. As a result, testers have to use specialized software to simulate a specific environment and interaction.
What tools are used to test IoT apps?
The following are tools for performing a wide variety of IoT tests:
- Device/protocol simulators. Testers use them when there are many differences in device endpoints and their interfaces, and they allow you to simulate standard-compliant devices and then tweak them to display the actual states you want.
- API testing tools: Solutions are increasingly built using web services and REST APIs. Tools like Postman, Progress®, SoapUI check their connectivity, responsiveness, and performance.
- Recording and playback tools. Devices or applications, system, and user data/actions can be recorded and played back on simulators and applications to automate test execution.
- Data loggers from different devices. The recorded data automatically plays on other device endpoints, which helps test the compatibility of applications with varying sets of devices and communication layers.
- Mobile testing tools. These provide automated, functional mobile testing that replicates the end-user experience and ensures that the app performs as expected.
- Virtualization tools. Checking the behavior of an IoT app in real-time is difficult and time-consuming. And virtualization tools provide cost-effective and timely execution of compatibility tests without investing in various hardware, databases, platform services, etc.
- Automatic deployment tools. They are used to quickly deploy managed services, programmatically create virtual machines on-premises or in the cloud, and configure and deploy custom-built services and applications. Tools like Katello, Foreman, Ansible Tower® provide staging capabilities to run automated and IoT manual tests on time in continuous build, integration, and deployment environments.
- Security testing tools. These can be divided into threat modeling tools, static code analysis, and runtime threat creation tools. Tools such as OWASP ZAP, VGC, and Microsoft® Threat Modeling Tool identify threats, prioritize them, and provide remediation recommendations. Acunetix® and Netsparker® are two open-source security tools that can help detect vulnerabilities.
- Additional tools. Below are a few tools/equipment that you can use to test IoT solutions:
- Wireshark® and Tcpdump for monitoring network traffic,
- Fiddler for debugging HTTP traffic
- JTAG Dongle and digital storage oscilloscope for IoT testing equipment and tracking its parameters.

In addition, test cases and proprietary tools can improve the productivity, speed, and efficiency of QC execution.
Testing timeframes
Traditional testing methods, usually performed after product development, are time-consuming. In today’s fast-paced and highly competitive environment, this is unacceptable.
Early and frequent testing is the best way to detect and correct any potential problems early. That is especially important for IoT platforms, where continuous integration is the cornerstone of the technology. The idea is to include the stages of product testing in a schedule that runs in parallel with active development.
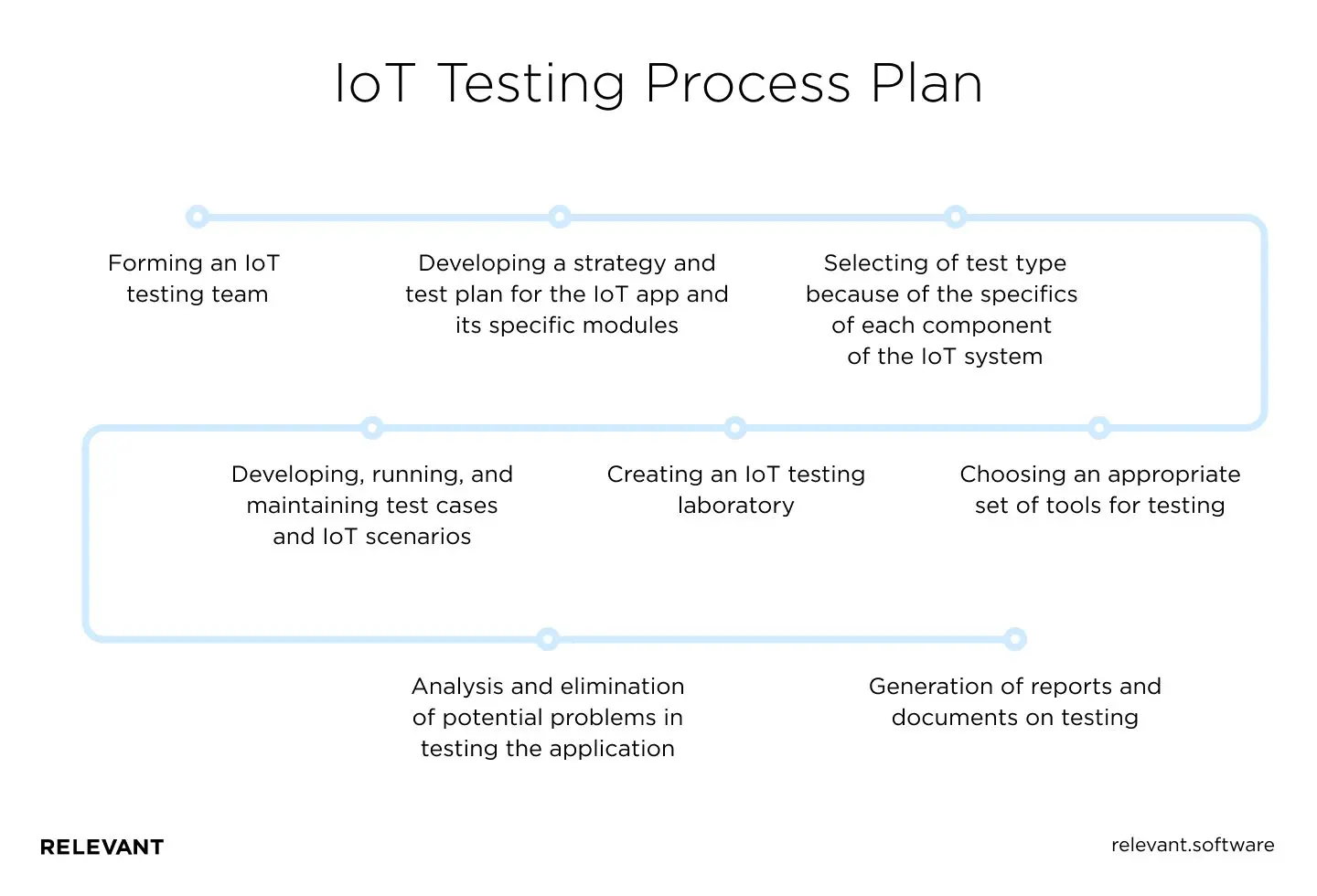
IoT Testing process plan
- Forming an IoT testing team;
- Developing a strategy and test plan for the IoT application and its specific modules;
- Selecting of test type because of the specifics of each component of the IoT system;
- Choosing an appropriate set of tools for testing;
- Creating an IoT testing laboratory;
- Developing, running, and maintaining test cases and IoT scenarios;
- Analysis and elimination of potential problems in testing the application;
- Generation of reports and documents on testing.
IoT system test protocol
The technical characteristics of IoT devices and problems with the devices and their firmware can interfere with the normal operation of the application. When we discover such issues during testing, we share our findings with clients and recommend changes.
The client changes something in his device and sends us requirements for changing the software. These changes require repeating the regression testing step to ensure that the entire system functions as expected, even after upgrades.
Standard IoT testing involves the next stages:
Component check
We check such components:
- Network connectivity.
- Software applications.
- Built-in sensors.
- Hardware devices.
- Security systems.
- Server or cloud infrastructure.
Functionality check
The IoT system should only respond and function as required. In addition, each connected device must communicate adequately. To do this, we test:
- Exceptions and errors.
- Communication between devices.
- System response.
- Calculation results.
Conditions check
Testing carried under the maximum conditions. In addition, IoT testers have saved the responses of the IoT system in the following formats:
- Automated conditions.
- Manual conditions.
Performance check
We calculate the performance of an IoT system based on the following components:
- System health to failure occurs.
- Data transmission frequency.
- Device performance.
- Synchronization.
In the end, we provide comprehensive reports on identified vulnerabilities, tools and methods used to exploit system flaws, and recommendations for eliminating identified risks.
IoT software testing best practices
And now, we will give you some valuable tips for testing smart device applications to avoid common pitfalls regarding their performance.
Automate mature testing processes
Because of the increased speed of R&D and the need to go to market first, it makes sense to automate some repetitive processes. However, automation requires not only the right technologies and tools but also highly qualified specialists. The best way is to automate only mature processes, particularly those that will provide a high return on investment.
Use the possibilities of cloud services
By leveraging the power of cloud computing, you can simulate high loads on IoT applications and check how they react to large amounts of data. In addition, the method helps check the data amount sent by the IoT application to the hub, especially when the IoT devices are in a low power state. This point requires special attention from the QA side since it is an excellent indicator of the quality of IoT applications for users.
Ensure usability and safety
If the device has a built-in payment option, then it should be fast and secure. In the event of a loss of a wearable device, the user should lock the smart device through their mobile devices or IVR.
Conclusion
Testing IoT systems is not an easy task, and competence in this area matters. As an IoT software company, Relevant has this expertise and can test usability, security, performance, connectivity, and compatibility in:
- Mobile applications (supported on Amazon, iOS, Android, Windows platforms);
- Device firmware;
- Integration of equipment and mobile devices (BLE, Wi-Fi sync);
- API (sync and store data between cloud and mobile app or hardware device);
- Data security – authorization and authentication protocols (token-based, key-based, OAuth), role-based access (client, API), XSS / SQL injection (manual), cache storage security (keyboard, browser, app).
We are flexible in choosing and changing the types of software testing within the project. Our QA team can uncover the perfectly hidden problems of your product. So, if your IT team lacks the resources to test an existing IoT system, or you need to develop and test a new IoT solution, Relevant is here to help.
FAQ
What is IoT testing?
IoT Testing is a series of QA tests to ensure that an IoT device’s performance, functionality, and security comply with standards. IoT application testing ensures that each device is fully functioning, works efficiently, and delivers the expected results.Why is testing important in IoT?
Reliable IoT testing ensures system predictability and prevents unexpected failures. You can easily identify weak nodes in the network in advance and take measures to improve the system’s reliability.What are the IoT testing tools?
Testers use various tools to test IoT systems. They are divided into two categories: hardware and software IoT testing tools.IoT testing tools for hardware testing- JTAG Dongle- Digital Storage Oscilloscope- Software Defined RadioIoT testing tools for software testing- Wireshark- Tcpdump- ShodanHow to choose an IoT testing service provider?
When outsourcing software development, you need to study the portfolio, the case studies, the reviews, and the ratings of various IoT testing firms and only then proceed to the direct discussion of the desired services. IoT connected device testing services can be provided by:- Software testing companies have testing experience, but the Internet of Things isn’t their only specialty.- IoT consulting companies that offer end-to-end services (for example, IoT mobile apps development).

Hand-selected developers to fit your needs at scale! Let’s build a first-class custom product together.

