Exploring Healthcare RFID: Benefits, Applications, and Challenges

The healthcare industry is increasingly leaning toward the adoption of RFID technology, as evidenced by the latest market analysis, which predicts rapid growth to $20.28 Billion by 2031. One of the pivotal drivers propelling RFID’s proliferation in healthcare is its versatility and the plethora of usage – from ensuring the traceability of surgical instruments to monitoring the movements of patients and personnel. Consequently, healthcare RFID is rapidly becoming an integral component of the industry, ushering in a new era of efficiency and safety.
In this article, we will introduce you to the basics of RFID and its application, among the benefits and barriers to RFID technology in healthcare. Continue reading to get insights that cover it all.
from 25 countries outsourced software development to Relevant
We provide companies with senior tech talent and product development expertise to build world-class software.
RFID Technology in Healthcare: Brief Overview
Projected to reach a remarkable valuation of $20.28 billion by 2031, the worldwide medical RFID technology market is set for rapid expansion with a CAGR of 15,75%. This rise can be attributed to two crucial factors.
First is the unprecedented spike in hospital visits due to the COVID-19 pandemic and the increasing geriatric population worldwide. Second, the escalating demand for more streamlined and efficient hospital supply chain management. As the healthcare industry grapples with challenges like patient safety, cost management, and resource utilization, Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) technology is emerging as a transformative solution for all these cases.
This intelligent system offers unparalleled efficiency, accuracy, and safety, driving healthcare toward more streamlined operations and patient-centric practices. RFID is thus creating a paradigm shift in healthcare, moving it beyond the limitations of traditional methodologies such as barcoding and redefining how healthcare is delivered, setting a precedent for all future innovations.
What is RFID?
RFID represents a sophisticated innovation employing electromagnetic fields to identify and track labels affixed to items. These labels, or “tags,” are embedded with digital information that can be accessed from significant distances. This characteristic distinguishes RFID from barcode tags, requiring a direct line-of-sight for accurate reading.
RFID vs. Traditional Barcoding
While both RFID and barcoding serve the purpose of tracking and identifying objects, RFID offers distinct advantages that make it a superior choice in many applications.
One key advantage of RFID over traditional barcoding is the ability to read multiple tags simultaneously without line-of-sight. RFID uses radio waves to communicate between the tag and the reader, allowing quick and efficient data capture even in challenging environments. In contrast, barcoding requires direct visual contact with each barcode, which can be time-consuming and prone to errors when dealing with large quantities of items.
Another notable benefit of RFID is its ability to store and transmit more data than barcoding. RFID tags can hold a wealth of information, including unique identifiers, product details, and real-time sensor data. That enables enhanced inventory management, improved traceability, and increased operational efficiency.
RFID technology also offers superior durability and longevity compared to traditional barcodes. RFID tags are designed to withstand harsh conditions, such as temperature extremes, moisture, and physical stress, ensuring reliable performance throughout the lifecycle of the tagged items. In contrast, barcodes can easily damage or wear off, leading to scanning issues and compromised data accuracy.

How Medical RFID Tracking Works
Whether active or passive, RFID tags are attached to or embedded in hospital equipment or placed on tracking accessories worn by patients, visitors, and staff, relaying their position to RFID detectors. These detectors, located throughout the hospital, including corridors and wards, recognize the location of RFID tags and transmit this data to the cloud gateway through a secure firewall.
Once through the firewall, a streaming data processor funnels the raw information, including data about hospital assets, patients, and personnel, into a data reservoir. This reservoir acts as a primary repository, storing the information transmitted by RFID markers in its unaltered state. A big data repository then houses the filtered and processed data for subsequent analysis, focusing on areas such as hospital staff workflow efficiency and patient and asset movements.
The power of data analytics is harnessed to identify patterns and trends in the usage of hospital resources and the movement of tracked individuals, offering invaluable insights for enhancing asset availability, refining medical staff schedules, and improving patient safety.
A cornerstone of this system lies in the RFID tracking software’s business logic. It manages hospital asset requests, prioritizes events – for instance, if a patient exits the hospital premises without official discharge – and provides location data for patients, visitors, and staff members.
The staff application serves as a crucial tool for medical professionals and equipment technicians. It enables viewing the location of hospital assets, requesting their use, accessing patient location data, and receiving alerts about unusual patient or visitor behavior. Additionally, it allows supervisors to view the whereabouts of each unit’s staff and gather insights for workflow optimization.
Finally, the admin application allows for viewing and managing the list of monitored assets and tracked individuals, adding new assets and staff members, modifying essential data about tracked items and people, and authorizing access to the asset tracking system for medical and administrative personnel.
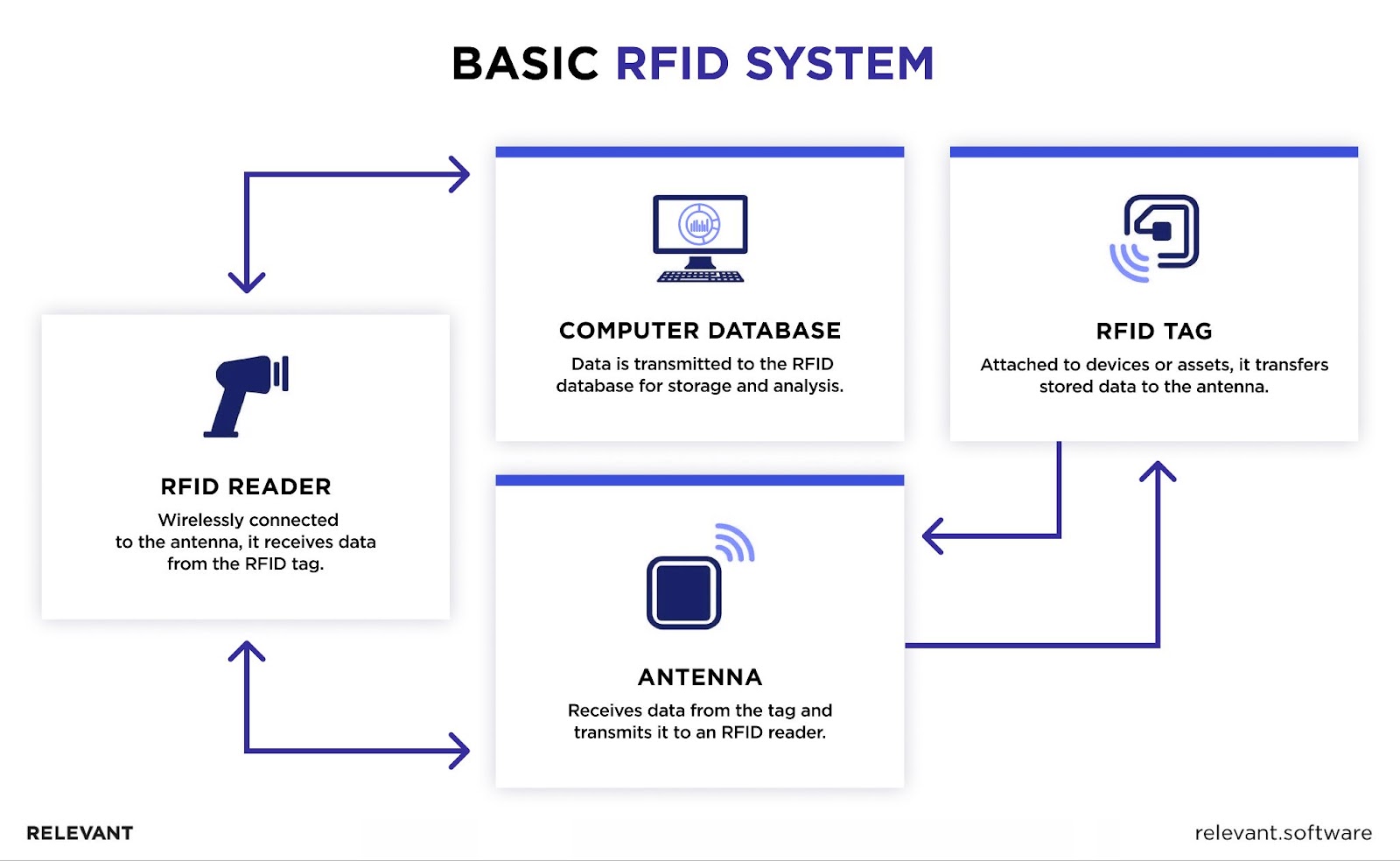
Benefits of RFID in Healthcare
RFID technology has catalyzed many advantages in the healthcare sector, fortifying operational efficiency and patient care standards. Let’s unpack five salient benefits reinforcing the necessity of embracing RFID in healthcare.
Improved Patient Safety
RFID technology in healthcare substantially contributes to patient safety. By tracking patients in real-time, hospitals can prevent mishaps such as patient misidentification or unauthorized movement, thereby reducing medical errors and improving overall patient safety. The technology also aids in the tracking of medical devices and instruments, helping prevent equipment from being misplaced or left within patients after surgical procedures.
Enhanced Inventory Management
RFID technology significantly mitigates stock deficiencies and excesses by providing live, moment-to-moment insight into inventory volumes. RFID tagging can identify expired or recalled pharmaceuticals and medical devices, enabling quick removal and preventing their use. This real-time and accurate asset tracking ultimately enhances patient care while driving efficiency in inventory management.
Reduced Operational Costs
RFID technology can lead to considerable cost savings. By reducing the time spent on manual inventory checks and equipment searching, healthcare professionals can focus more on patient care. It also mitigates the costs associated with lost or misplaced equipment. Furthermore, RFID aids in preventing overstocking and stockouts, leading to more efficient use of funds.
Patient Workflow Management
RFID can enhance patient workflow management. It provides precise data on the location of patients, staff, and resources, enabling a smoother patient flow and reducing bottlenecks. RFID technology for IoT-based personal healthcare in smart spaces can improve patient satisfaction, reduce wait times, and optimize resource allocation.
Greater Data Accuracy
RFID healthcare provides high data accuracy, which is critical in healthcare. Unlike manual or barcode-based systems, RFID does not rely on line-of-sight for data capture, reducing the chances of human error. This enhancement in precision undeniably paves the way for superior decision-making processes, fosters the formulation of more potent treatment blueprints, and culminates in optimizing patient outcomes.
Diverse Applications of RFID in Healthcare
RFID technology has a lot of applications in healthcare, from patient tracking to medication management. The flexibility and data accuracy of RFID makes it indispensable across various areas of healthcare operations.
Patient and Staff Tracking and Identification
Patient misidentification poses serious risks to patient safety within hospitals. RFID technology offers a robust solution through positive patient identification systems using smart wristbands with passive RFID tags. Hospitals can enhance safety procedures, prevent errors, and improve overall patient care by implementing such systems.
In addition to patient identification, RFID technology seamlessly integrates with existing healthcare information systems, minimizing errors in patient handling and enabling accurate retrieval of medical data. Furthermore, RFID’s applications extend to optimizing surgical procedures by ensuring the correct patient receives the intended treatment.
By enabling real-time patient tracking, RFID enhances visibility into the patient journey, reducing wait times, improving patient flow, and optimizing resource allocation. Moreover, RFID aids in monitoring elderly patients with chronic diseases at home and tracking the movement of visitors, staff, and patients, facilitating the identification and containment of infectious diseases.
Medicine and Pharmaceutical Tracking
RFID technology enables real-time monitoring and tracking of medications throughout the supply chain, from production to distribution and administration. Each medication package has an RFID tag containing essential information such as the drug name, dosage, expiration date, and batch number. This helps healthcare practitioners to effortlessly ascertain the authenticity and integrity of medications, guaranteeing that patients are administered the appropriate medication precisely when needed.
With RFID-enabled medication tracking, healthcare facilities can streamline inventory management, prevent medication errors, and minimize the risk of counterfeit drugs entering the supply chain. By automating the process of medication tracking and reducing reliance on manual recordkeeping, RFID technology enhances operational efficiency and improves patient care outcomes.
Equipment and Medication Management
RFID technology enables real-time medical equipment tracking and monitoring, preventing misplacements and streamlining inventory management. Each piece of equipment is fitted with an RFID tag that contains vital information, such as equipment type, location, maintenance history, and calibration data. That empowers healthcare providers to easily locate and manage equipment, reducing the time and effort spent on manual tracking.
Similarly, RFID tags attached to medication packaging enhance medication management practices. These tags store crucial details, including medication name, dosage, expiration date, and lot number. With RFID-enabled medication management, healthcare professionals can swiftly access accurate information, verify medication authenticity, and prevent medication errors. RFID streamlines the process of locating and utilizing medical equipment, minimizes inventory discrepancies, and promotes adherence to medication protocols.

Temperature and Humidity Monitoring
Ensuring the optimal storage conditions for vital commodities such as food, vaccines, and medications is paramount to uphold their integrity and efficacy. Thus, a vigilant monitoring system for temperature and humidity within storage units becomes indispensable.
The integration of RFID technology automates compliance and safeguards perishable assets. Real-time temperature data is seamlessly transmitted from RFID-enabled tags to cloud-based software, establishing a robust and reliable monitoring network. If temperatures deviate from the recommended range, hospital staff receives instant text or email notifications, enabling them to take immediate corrective action.
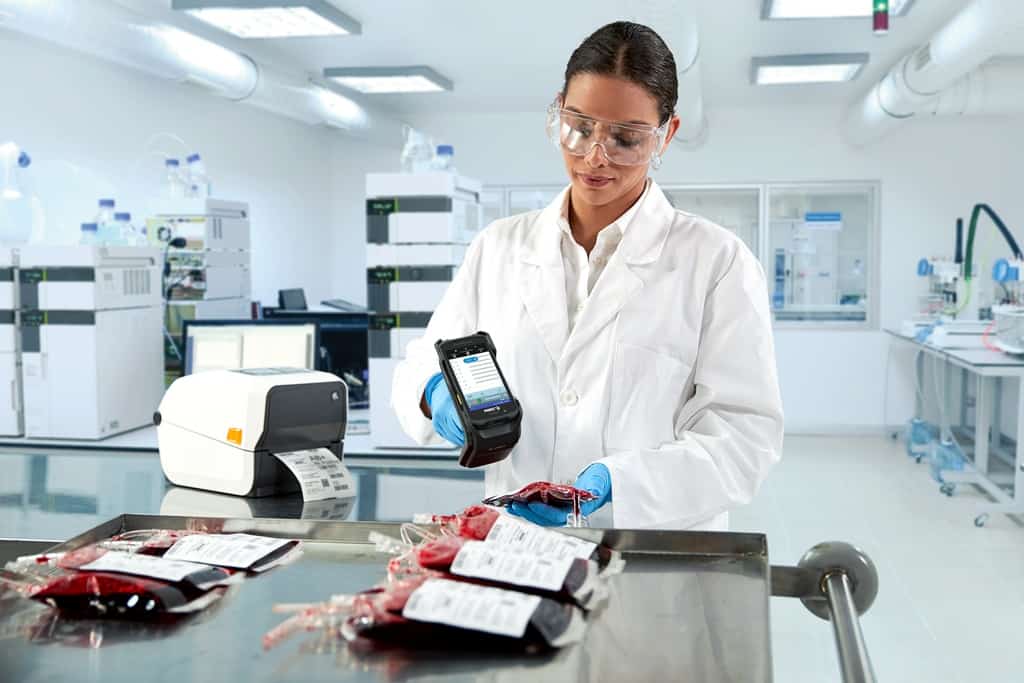
Blood Monitoring and Infection Control
RFID tags can be attached to blood bags or containers, enabling real-time tracking and monitoring throughout the blood supply chain. It ensures accurate inventory management, prevents errors in blood product administration, and enhances patient safety by reducing the risk of transfusion-related complications.
Furthermore, RFID in hospitals aids in infection control efforts, identifying and locating individuals who may have come into contact with infectious diseases by tracking the movement of visitors, staff, and patients within healthcare facilities. That facilitates prompt interventions, such as isolating affected individuals and implementing appropriate preventive measures to contain the spread of infections.
During the SARS outbreak, Show Chan Hospital in Taiwan implemented the “Intelligent digital health network” project, utilizing active RFID tags to monitor patients’ body temperature and track potentially infectious individuals with fever. The successful application of RFID technology extended to a senior citizen home, where remote data link RFID features were employed to transmit movements and physiological data of disabled or bedridden patients. These real-world RFID examples in healthcare showcase its potential to enhance patient monitoring and improve care delivery in diverse settings.

Limitations of RFID in Healthcare
While the benefits of RFID technology are substantial, it’s also critical to consider its limitations within the healthcare setting.
Privacy and Security Concerns
In healthcare, data privacy, management, and security are paramount. However, regarding RFID technology, guaranteeing safety and confidentiality presents great difficulties in data exchange. Privacy concerns often stem from the potential counterfeiting of unencrypted sensitive data within RFID tags, unauthorized access to data, and interception during transmission. Furthermore, storing unencrypted patient data in RFID tags may raise legal concerns, as it could be perceived as a violation of government regulations such as the US Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA).
Additionally, as most RFID tags rely on wireless interfaces, RFID systems are susceptible to physical attacks such as timing attacks, fault integration, and power analysis attacks. Data transmission also raises concerns about eavesdropping, highlighting the need for standards that mandate the authentication of RFID tags or readers.
Healthcare organizations must establish comprehensive security protocols, implement robust encryption mechanisms, and develop stringent data governance frameworks to instill trust and confidence in the utilization of RFID technology.
Technological Limitations
RFID technology in healthcare faces some limitations that challenge its widespread adoption. One such limitation is electromagnetic interference (EMI) caused by RFID wireless transmissions, which can adversely affect the performance of electronic biomedical devices, jeopardizing patient safety. The proximity of RFID tags to medical equipment like external pacemakers or syringe pumps can trigger EMI, leading to equipment malfunctions and putting patients’ well-being at risk.
Furthermore, the accuracy and reliability of RFID systems pose another technological challenge. Unlike generally reliable barcodes, RFID tags may exhibit unexpected behavior in certain situations or with specific products. This variability raises concerns regarding the consistency and dependability of RFID technology.
These challenges encompass the development of robust and interoperable RFID systems and healthcare websites, ensuring seamless integration with existing healthcare infrastructure, and optimizing the performance of RFID devices and networks. Overcoming these obstacles requires a concerted effort to push the boundaries of technological innovation and unlock the full potential of RFID in healthcare.
Organizational and Financial Issues
Although the cost of RFID tag technology in the medical field has decreased over the past decade, it still represents a considerable expense. Presently, passive RFID tags cost approximately 10 cents. At the same time, active RFID tags can reach up to 20 dollars each, posing a substantial financial commitment for hospitals aiming to tag all their assets, staff, and patients.
Furthermore, besides the tags and readers, establishing the RFID infrastructure involves additional expenses such as middleware, databases, servers, and applications. It is important to consider costs related to training, business process redesign, organizational change, and ongoing maintenance of the RFID infrastructure.
Healthcare institutions must navigate the challenges of change management, ensuring buy-in from stakeholders, training healthcare professionals, and optimizing processes to derive maximum benefits from RFID implementation. Additionally, there is a need for careful financial planning to address the initial investment costs, long-term sustainability, and return on investment (ROI) considerations associated with RFID technology in healthcare.
However, despite the initial investment required, the long-term benefits and return on investment (ROI) associated with RFID technology can outweigh the costs. Improved operational efficiency, enhanced patient care, and reduced errors and losses can contribute to significant cost savings and improved resource allocation in healthcare. Careful consideration of the total cost of ownership and the potential long-term advantages is crucial when evaluating the implementation of an RFID system in healthcare facilities.
Bottom Line
RFID technology stands as a critical pillar in the movement towards the “Internet of Things,” powering a host of groundbreaking advancements not only in healthcare but across a spectrum of industries. By leveraging radio frequency signals to store data and track locations, healthcare institutions can tap into real-time, data-driven insights concerning their supply chains, inventories, patient care protocols, and compliance mechanisms.
Such technology can substantially enhance the effectiveness of your organization’s operations, minimizing the necessity for manual intervention and subsequently reducing the probability of errors. With a transparent, data-driven system for managing assets and patient status, you gain a panoramic view of your operations, equipping you with the insights necessary to devise and implement new protocols and initiatives. The outcome is a tangible improvement in the quality of healthcare you deliver.
If your facility requires assistance integrating an RFID technology solution, do not hesitate to connect with Relevant. Your reliable partner in healthcare software development, we stand ready to elevate your operational efficiency and patient care standards.
Also, read more about HL7 standards.
FAQ
What is RFID in healthcare?
RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) technology uses wireless communication and electromagnetic fields to autonomously identify and track objects outfitted with RFID tags or labels. In the context of healthcare, RFID technology encompasses the tagging and tracking of medical assets, patient identification, inventory management, and workflow optimization.How can RFID technology improve patient safety in healthcare facilities?
RFID technology can significantly enhance patient safety by tracking patient movements in realtime and ensuring correct patient identification. That helps to prevent medical errors such as wrong patients, wrong procedures, and unauthorized activities. Furthermore, RFID can track medical supplies, controlling misplaced equipment or instruments left in patients after surgical procedures.What role does RFID play in managing healthcare inventory?
RFID technology unveils instantaneous insight into the stockpile volumes, thereby assisting in circumventing both over-accumulation and shortages of supplies. Moreover, it facilitates rapid detection of obsolete or revoked pharmaceuticals and medical equipment, ensuring timely extraction. At its core, it dramatically refines the inventory management process, culminating in augmented operational efficiency and heightened standards of patient care.Are there any privacy and security concerns related to the use of RFID in healthcare?
Yes, there are security concerns when using RFID technology through a potential risk of sensitive patient data being accessed by unauthorized individuals. Moreover, healthcare RFID must comply with strict regulatory standards like HIPAA, which adds another layer of complexity to its implementation.What are the initial costs and challenges in implementing RFID technology in healthcare?
Implementing RFID technology requires a significant initial investment in purchasing hardware, software, and system integration. Moreover, there can be resistance from staff members due to the change in traditional workflows, which might require training and time for them to adapt to the new system.How does RFID technology help in tracking medicines and verifying their authenticity?
RFID technology can track medicines from source to dispensation, ensuring their authenticity. It provides essential data about the drug’s origin, movement, and expiration and helps fight against counterfeit drugs.What technological limitations are associated with RFID in healthcare?
RFID technology may face issues like interference with other devices, impacting the accuracy and reliability of data collected. While strides are being made to overcome these challenges, they still pose a barrier to the seamless functioning of RFID systems in healthcare.

Hand-selected developers to fit your needs at scale! Let’s build a first-class custom product together.

