How AI Video Analytics Surveillance Software Transforms Security Operations and Beyond

The default surveillance setup still looks like this: lots of cameras, lots of screens, and a person expected to notice the right detail at the right second. That works until it doesn’t. CCTV gives you the truth, but usually on a delay, after the incident has already moved on and the team is stuck hunting through footage with a timeline and a headache.
That friction explains why AI video analytics surveillance software has moved from “interesting” to necessary across airports, logistics hubs, hospitals, campuses, utilities, retail chains, and smart buildings. The goal is simple: treat video as a live signal, not an archive, so teams can answer three questions fast: what happened, where it happened, and what should happen next.
If you evaluate custom computer vision or want to connect video analytics with wider automation, Relevant Software’s AI integration services outline the typical delivery path across cloud, edge, and hybrid environments. As an AI software development company, Relevant Software can also build the analytics layer itself when off-the-shelf tools cannot meet your accuracy, governance, or integration requirements.
from 25 countries outsourced software development to Relevant
We provide companies with senior tech talent and product development expertise to build world-class software.
What is AI video analytics surveillance software?
This section gets concrete fast because the phrase “video analytics” can describe anything from motion detection to a complete operational platform. In the context most teams care about, AI video monitoring is a system that analyzes video streams (live, recorded, or both), extracts structured signals from frames, and turns those signals into alerts, searchable evidence, and automated actions that support security operations.
The key output is not “AI.” The key output is decision support at scale:
- Real-time detection when response time changes outcomes
- Fast search when investigations burn hours and trust
- Consistent rules across cameras, sites, and operators
- Better evidence with timestamps, object trails, and export logs
How AI video analytics differs from traditional video surveillance
Traditional video surveillance works well for one job: recording footage for humans to review later. That is essential for investigations, insurance, and compliance. It breaks down when teams need the system to surface risk in real time and keep humans focused on the moments that matter.
A practical way to think about it is “now” versus “later.”
- Real-time analytics: models run on live streams and trigger an action when conditions match a rule. Example: a person crosses a restricted line after hours, a vehicle enters the wrong lane, smoke appears near a machine, or a crowd forms where it should not.
- Post-event analytics: works on recorded footage and turns it into something you can actually search. Instead of scrubbing timelines, the team can type a query like “red van near dock 7 between 01:00 and 03:00” and jump straight to the relevant clips.
Here is the operational difference in plain terms:
| Question your team asks | Traditional CCTV answers | AI-driven analytics answers |
| “Can we prove what happened?” | Yes, with review time | Yes, with faster evidence |
| “Can we react before damage grows?” | Only if someone sees it | Often, through alerting |
| Can we scale to 500+ cameras?” | With more people | With compute + governance |
| “Can we apply consistent rules?” | Operator-dependent | Rule and model-driven |
There is also a human factor that matters more than most vendor decks admit. Sustained screen monitoring does not scale well. Research in surveillance contexts has documented performance drop-offs during prolonged monitoring, including failures to detect objects after extended watch periods. That is not an insult to operators. It is a design constraint, like gravity.
That becomes the first practical litmus test for video analytics and AI. If your security posture depends on continuous attention across many feeds, you already run a system that fights human cognition every day.
Core technologies behind AI video surveillance (computer vision, ML, deep learning)
An AI video surveillance system works as a pipeline: it turns frames into detections, links them over time, then applies rules so the software can trigger useful alerts instead of noise.
Computer vision
What it does: Converts raw frames into visual facts such as objects, positions, and movement.
Where it helps most: Perimeter intrusion, zone entry, tailgating support, vehicle flow, safety visibility.
Typical capabilities:
- Object detection (people, vehicles, packages, smoke, PPE)
- Tracking across frames (direction, dwell time, speed)
- Segmentation for dense scenes (optional)
Common failure points: Glare, low light, motion blur, low bitrate compression, and camera vibration.
How teams reduce risk: Standardize camera settings, define zones early, start with high-signal events.
Machine learning
What it does: Converts visual facts into decisions by classifying events and applying logic that controls alert quality.
Where it helps most: Alert prioritization, false alarm reduction, consistent rules across sites and shifts.
Typical capabilities:
- Classification and attribute tagging (vehicle type, PPE present, crowd density)
- Temporal smoothing and filtering to remove single-frame noise
- Rules, thresholds, schedules, and escalation tiers for actionable alerts
Common failure points: Over-sensitive thresholds, poorly drawn zones, and rule conflicts across sites.
How teams reduce risk: Pilot with a tight scope, measure false alarms per camera/day, tune by zone and time.
Deep learning
What it does: Powers detection and classification models that learn complex patterns beyond classic rule-based analytics.
Where it helps most: Crowded scenes, variable environments, complex object categories, and behaviors.
Typical capabilities:
- High-accuracy detectors and classifiers trained on large datasets
- Embeddings for similarity search and cross-camera matching (optional)
- Temporal models for activity recognition in specific scenarios (optional)
Common failure points: Domain shift when conditions change, bias from unrepresentative training data, and performance drops on poor footage.
How teams reduce risk: Validate on real site footage, keep a drift check cadence, and plan updates like software releases.
How AI video analytics works in surveillance systems
AI video analytics runs as a pipeline: ingest video, extract meaning, recognize events, then push outcomes into workflows security teams already use. The value comes from consistency and speed, not from “AI” as a label.
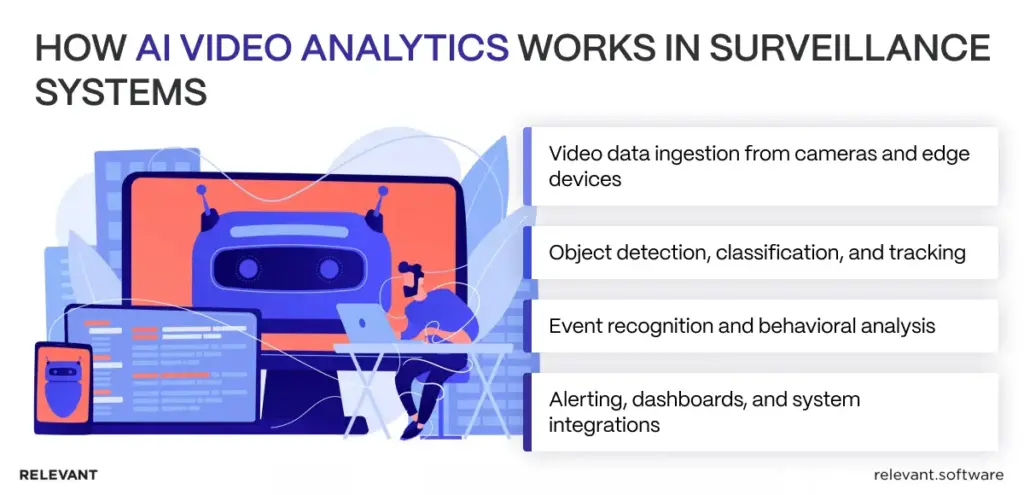
Video data ingestion from cameras and edge devices
The system pulls streams from cameras/VMS, normalizes formats and timestamps, and often uses edge boxes to buffer video and handle weak networks. Clean ingestion prevents delayed alerts and broken evidence trails.
Object detection, classification, and tracking
Models detect people, vehicles, and objects, classify them, and then track movement across frames. Tracking converts “something moved” into usable facts like direction, dwell time, and paths, which also enables fast search.
Event recognition and behavioral analysis
Rules sit on top of tracks and zones: line crossing, restricted entry, loitering, and wrong-way flow. Behavioral analysis can add anomaly detection, but it works best after basic events have stabilized and become low-noise.
Alerting, dashboards, and system integrations
Good alerts include a short clip, location, and reason, then route into incident tools or SOC workflows. Dashboards support live triage plus fast post-event search, while integrations keep the system usable in daily operations.
Key features of AI video analytics surveillance software
This feature set determines whether the platform helps security teams act faster or simply creates better-looking footage to review later. The strongest systems combine reliable detection with low-noise alert logic and fast forensic search, then connect those outputs to incident workflows.
| Feature | What it does | Best used for | Typical watch-outs |
| Object and person detection | Detects people/objects and attaches confidence + basic attributes | Baseline monitoring, safety, search | Low light, glare, and low bitrates can trigger false alarms. |
| Facial recognition and identity matching | Matches faces to approved identities/watchlists (policy-dependent) | Controlled entry points, high-risk areas | High privacy/compliance burden, needs strong lighting/angles |
| License plate recognition (ANPR/LPR) | Reads plates and links to time/camera events | Gates, lanes, logistics yards | Camera placement + shutter/IR quality decides accuracy |
| Intrusion detection and perimeter monitoring | Flags line crossing, zone entry, after-hours presence | Perimeters, restricted zones | Animals/weather artifacts require good suppression rules |
| Crowd monitoring and density analysis | Estimates occupancy/density by zone | Venues, campuses, public spaces | Occlusion and camera angle can distort counts |
| Anomaly and behavior detection | Flags deviations from standard patterns and risky behaviors | Stable environments with repeatable flow | Drift when layouts/seasons change, needs a feedback loop |
| Real-time alerts and incident reporting | Sends prioritized alerts with clips and incident context | Fast response, dispatch, SOC workflows | Alert fatigue if thresholds/zones are sloppy |
| Video search and forensic analysis | Searches by object, zone, time, direction; packages evidence | Investigations, audits, and insurance | Metadata consistency and access logs matter for custody |
AI video analytics use cases by industry
Industry examples keep AI video analytics grounded in operations. Each sector has its own version of “normal,” which is why the best programs start with a few high-impact events per site and build from there, instead of chasing an all-purpose model. The fastest results come when teams treat video analytics as part of a broader delivery approach, especially when using AI in software development to connect detection, incident workflows, and reporting into one coherent system.
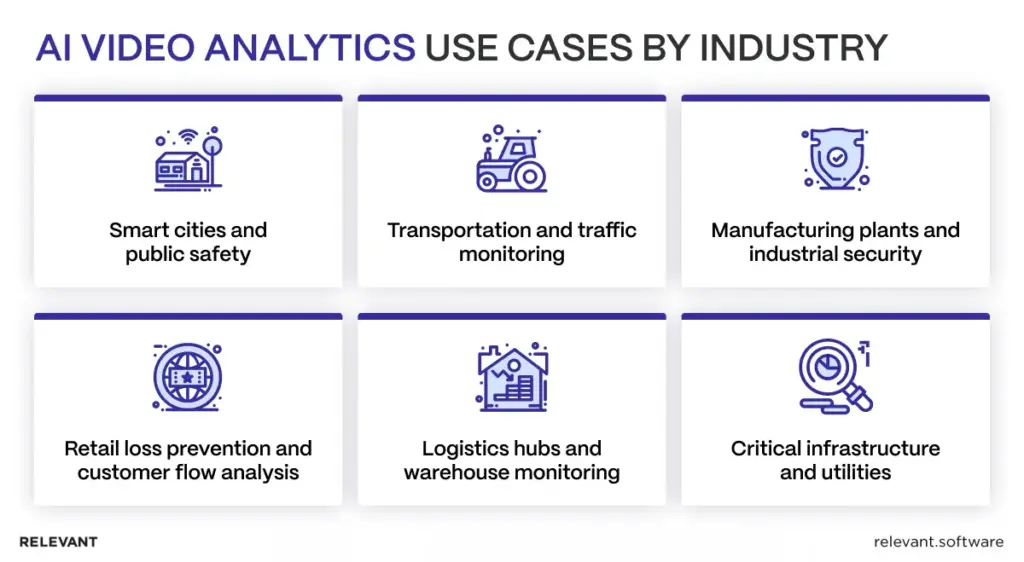
Smart cities and public safety
City teams use AI surveillance software to spot crowd build-up in public squares, detect after-hours movement around municipal buildings, and speed up investigations by searching for a person or vehicle across camera networks.
Transportation and traffic monitoring
Operators apply AI video surveillance to detect wrong-way vehicles in ramps or tunnels, measure congestion at checkpoints, and flag track or platform intrusions, then route alerts into traffic control or dispatch workflows.
Healthcare facilities and patient safety
Hospitals use AI video analytics software to monitor sensitive access points such as pharmacies and labs, reduce safety risks in corridors and public areas, and quickly reconstruct incidents with time- and zone-based search.
Manufacturing plants and industrial security
Plants rely on AI based video analytics to detect restricted-zone entry near machinery, support PPE compliance in defined areas, and monitor perimeter gates and yards where response time prevents downtime.
Retail loss prevention and customer flow analysis
Retail teams use AI security camera software to catch after-hours entry and the “hanging around too long” moments near high-risk shelves, then use flow patterns to adjust staffing and layout based on what shoppers actually do.
Logistics hubs and warehouse monitoring
Warehouses use AI video monitoring to track yard, dock, and forklift activity, then pull the right clip quickly when an “it was here a minute ago” inventory dispute arises.
Critical infrastructure and utilities
Utilities use AI security camera software to watch perimeters at substations and remote sites, spot unusual presence near high-value assets, and document incidents in a way that holds up in reviews. The result is a faster response with cleaner records for compliance and internal reporting.
Benefits of AI video analytics for surveillance operations
Security leaders adopt intelligent video analytics solutions when they change daily operations, not when it looks impressive in a demo. The benefits of artificial intelligence below occur when alert logic remains low-noise, integrations connect to incident workflows, and teams measure outcomes such as response time, investigation effort, and governance quality.
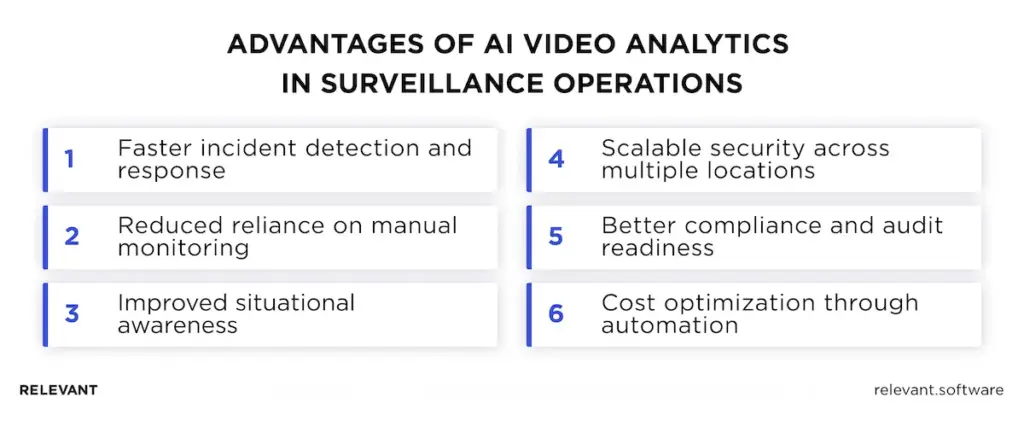
1. Faster incident detection and response
AI-powered video analytics software flags relevant events in real time, so operators can react faster with a clip, location, and trigger reason instead of hunting through feeds.
2. Reduced reliance on manual monitoring
Artificial intelligence for video surveillance shifts it from continuous watching to event verification, reducing fatigue-driven misses and time spent on routine screen monitoring.
3. Improved situational awareness
Tracking and event context help teams understand what changed, where it happened, and how it evolved, making decision-making during incidents calmer and more consistent.
4. Scalable security across multiple locations
Centralized policies, templates, and reporting make multi-site operations more consistent, so security outcomes depend less on local habits and staffing changes.
5. Better compliance and audit readiness
Structured logs, controlled exports, and enforceable retention rules improve chain of custody and simplify audit questions that often slow investigations.
6. Cost optimization through automation
Automation reduces hours spent on footage review and lowers avoidable dispatches, while faster investigations shrink the hidden operational costs of incidents.
Off-the-shelf vs custom AI video analytics software
Most teams begin with a vendor platform, and that often makes sense. Off-the-shelf analytics solutions deliver fast results when requirements remain standard, and site conditions match the vendor’s target environment, including camera placement and AI surveillance camera quality. In those cases, the “best video analytics software” is the one that fits your security operations without forcing significant process changes, especially for common scenarios such as intrusion detection, line crossing, crowd density, and basic forensic search.
Generic tools start to fail when locations vary, video quality shifts, or risk depends on context that the platform cannot see, such as schedules, access rules, and site-specific workflows across cloud based and on-prem setups. They can also fall short in more advanced capabilities such as facial recognition, nuanced threat detection, and reliable incident packaging, which limits situational awareness and increases alert noise during real security events.
Custom AI video analytics development becomes the smarter option when the goal is to streamline operations and standardize outcomes across sites, rather than only add features. It lets teams tune AI powered and AI driven detection and event logic to real environments, using machine learning that reflects your camera angles, lighting, vehicle types, and layouts. That approach supports artificial intelligence video surveillance programs where accuracy, governance, and evidence quality matter, including AI video analytics for commercial surveillance and platforms built by specialized video analytics companies.
How custom AI video analytics software is developed
Custom AI analytics video surveillance systems succeed when they follow a product process, not a research project. That keeps detection stable, alerts low-noise, and evidence defensible, with monitoring and governance built in from day one, which mirrors the step-by-step approach in the AI implementation roadmap.
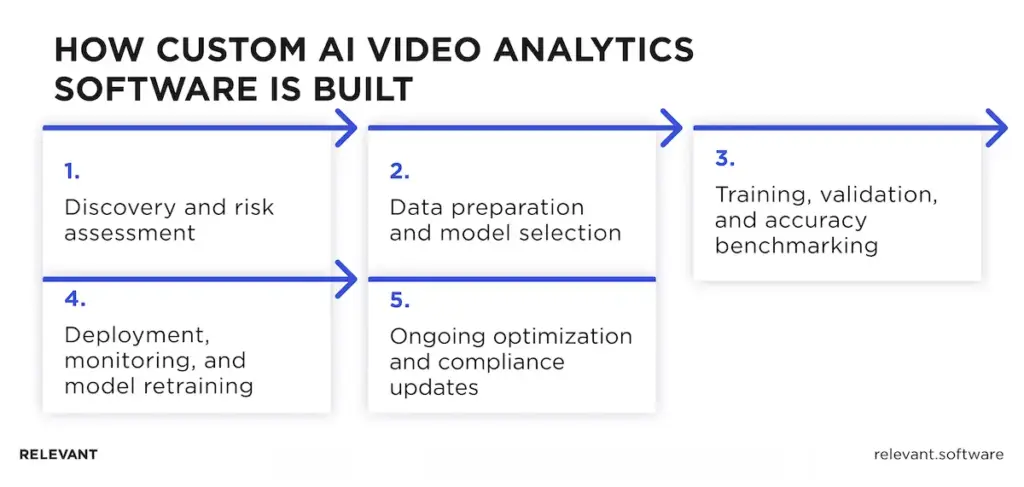
1. Discovery and risk assessment. Teams start by defining what “risk” means in your environment, then translate it into a short list of events with clear response actions. This is also where zones, camera coverage gaps, and success metrics get locked in, so the pilot does not drift into “let’s detect everything.”
2. Data preparation and model selection. Next comes the reality check: sampling footage from your cameras across lighting, seasons, and peak activity. The team labels key events, then selects models based on operational constraints such as edge latency, low-light performance, and false-alarm tolerance, not on impressive benchmark numbers.
3. Training, validation, and accuracy benchmarking. Training creates a model. Validation proves it works on your sites. Benchmarking sets acceptance thresholds by zone because a loading bay behaves differently from a lobby, even though procurement prefers a single, neat number.
4. Deployment, monitoring, and model retraining. Deployment includes version control, rollback, and integration into incident workflows, so alerts land where teams work. Monitoring tracks drift and alert quality, and retraining updates models when layouts, camera placement, or conditions shift enough to change outcomes.
5. Ongoing optimization and compliance updates. The long-term work is mostly unglamorous, which makes it all the more important: tuning thresholds, suppressing known noise patterns, reviewing operator feedback, and updating retention, access controls, and audit logs as policies evolve. This is the stage that separates “it worked in the pilot” from “it still works in six months.”
Future trends in AI video analytics for surveillance
Trends matter only when they map to operational advantage, so the focus here remains on what is likely to change how systems are built and governed.
Edge-first and low-latency analytics
Edge-first designs will expand as organizations demand faster response with lower bandwidth costs and tighter data locality. Expect better tooling for fleet-wide model updates, paired with stronger cybersecurity services to secure edge devices and release pipelines.
Multimodal AI combining video, audio, and sensors
Video alone often lacks context. Multimodal systems combine camera feeds with audio, access control, IoT sensors, and environmental signals, thereby improving confidence and reducing false alarms by enabling events to be verified across multiple inputs.
Predictive security and risk modeling
Analytics will move from detection toward forecasting, using historical incidents and site context to anticipate risk spikes and guide staffing. This works best with disciplined validation and machine learning consulting to keep predictions realistic.
Explainable AI and transparent decision logic
As adoption grows, teams will demand clearer reasons behind alerts and decisions, both for operator trust and for audits. Expect more emphasis on explainability, traceable decision logic, and evidence packaging that shows why a system escalated an event.
Conclusion
AI video analytics surveillance software delivers the most value when it makes security work feel calmer and more predictable. It helps teams spot incidents sooner, find the right footage faster, and apply the same rules across every site, even when people and shifts change. The most reliable path stays simple: start with a small set of high-impact events, tune alerts until they feel trustworthy, connect them to your incident process, and track a few quality metrics so performance stays steady over time.
If you would like support with the first steps, Relevant Software can help across the whole journey, including AI/ML development services for custom computer vision and model tuning, AI integration with VMS and security tooling, and secure deployment for regulated environments. Contact us to review your priorities and shape a rollout plan that fits your sites and your team.


Hand-selected developers to fit your needs at scale! Let’s build a first-class custom product together.

