In the not-so-distant past, managing chronic conditions meant frequent hospital visits. Routine checks were marked on calendars, and patients spent precious time in waiting rooms. Thanks to IoT healthcare devices, health monitoring is no longer confined to hospital settings, and routine follow-ups are being gradually replaced with telemedicine. Today, it’s a reality for millions of patients and medical practitioners.
Wearables that monitor everything from heart rhythms to oxygen levels and implants that keep a watchful eye on glucose or other critical biomarkers allow for proactive treatment. Adjustments to medications and lifestyle can be made before the patient even notices a symptom. In short, IoT software solutions bring a lot of positive changes to the sector and show no sign of slowing down. The global IoT medical devices market is on track to balloon from $41 billion in 2023 to $166 billion by 2028.
We provide companies with senior tech talent and product development expertise to build world-class software. Let's talk about how we can help you.
Contact usBelow, we’ll discuss the benefits of IoT devices in healthcare, review and understand the different types of connected medical equipment, and their role in improving patient care.
Table of Contents
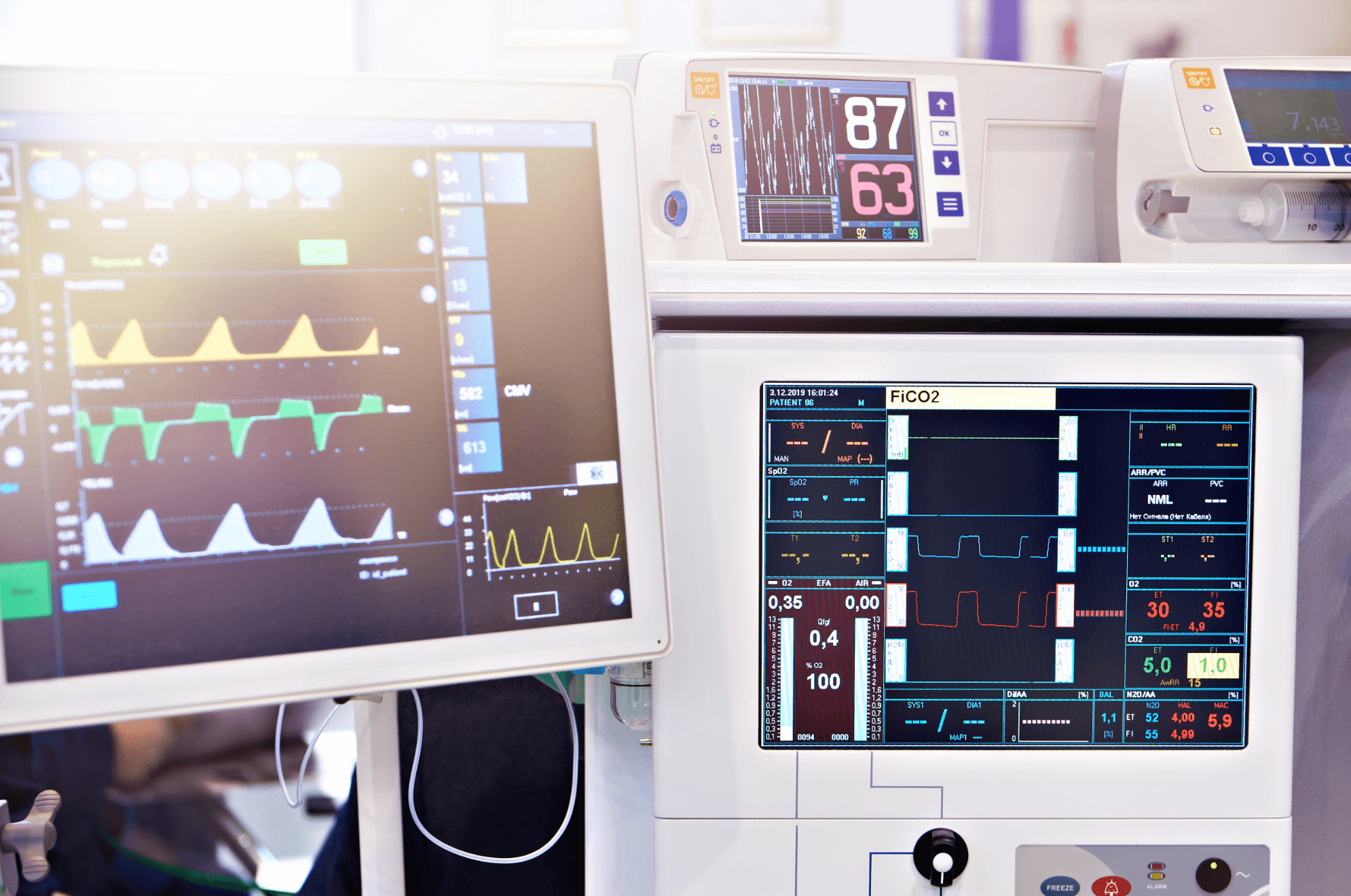
IoT healthcare devices, also known as IoMT solutions, are smart, interconnected tools equipped with built-in sensors and other technologies that gather health data and transmit it via cloud computing. They track information like heart rate, blood pressure, oxygen levels, and other vitals and can alert both patient and doctor to any changes that might require action. It’s a true leap in chronic disease management, which offers a level of monitoring that was previously impossible outside of the hospital.
Apart from tracking capabilities, smart IoT devices can deliver medications, assist with rehabilitation, help prevent health issues before they arise, and so much more. Their connectivity allows for integration into larger health systems so that information flows securely and flawlessly between patients, devices, and doctors. Together, all these devices, along with software, protocols, data flows, and interfaces, form an IoT architecture that offers a structured way of communication between all these components within an ecosystem.
The wealth of data supplied by IoT applications, when analyzed and applied, gives insights capable of tremendously improving patient care. These IoT devices’ advantages in healthcare are extensive and touch on nearly every aspect of healthcare delivery. Here are just a few of them.
Remote patient care. Healthcare IoT devices reduce the need for frequent in-person doctor visits. If the patient’s health condition doesn’t require taking immediate action, a virtual consultation with a doctor may well replace an actual physical visit. Remote patient monitoring tools and smart IoT sensors can track a lot of essential health indicators and send this patient data directly to healthcare providers.
Improved treatment and diagnostics. Specialists can now treat their patients better and faster. Connected medical devices, wearables, and other IoT devices used in healthcare gather and process the most comprehensive and precise data about a patient’s health status. With this information at hand, doctors can easily detect the early signs of disease or abnormalities, make accurate diagnoses before serious symptoms present themselves, and adjust treatment plans.
Better drug and equipment management. Among other things, healthcare devices IoT can be used to simplify the management of drugs and medical equipment. Smart IoT-based systems help medical staff keep a close eye on when and how medicines are used, making it less likely for mistakes to happen. On top of that, hospitals can rely on IoT to provide the right conditions for drug storage. Similarly, personnel can easily find the necessary medical equipment, avoiding lost or under-utilized stuff. This saves a lot of time, which can be spent on patient care.
Automation of processes. When part of the routine work is replaced with automation tools, all other processes are also accelerated. With IoT tracking of medical supplies, hospitals will always have restocked items as needed without manual counts or orders. In the treatment rooms, IoT devices for healthcare can automate the update of electronic health records with real-time patient data and alert doctors to any concerning changes. Even medication dispensing can be automated where smart systems manage dosages and schedules and notify patients when it’s time to take medication.
Cost-efficiency. As we said above, IoT healthcare device solutions automate part of the processes, which reduces the need for manual work and hiring staff. For instance, patient monitoring equipment reduces the hours nurses spend on routine checks, allowing them to manage more patients. Meanwhile, constant remote monitoring minimizes in-person visits at all, which helps clinics decrease overhead costs for space and staffing. In addition, IoT technology systems can diagnose medical equipment on time to prevent major breakdowns or replacements that are far more costly.
The IoT healthcare device statistics are encouraging. Last year’s report by Juniper Research projected that smart hospitals will deploy over 7 billion IoMT devices by 2026. As you can understand, there is no lack of diversity and functionality, and the IoT healthcare devices list is quite long. All of them can be classified into different types, each serving different functions. Let’s examine their specific usage and IoMT device examples that fall under those categories.
Wearables have carved out a significant space for themselves in healthcare as a result of consumers’ increased interest in monitoring their health. If we compare the number of wearable devices shipped globally in 2014 – 28.8 million with 492 million in 2022, we have almost a 17-fold increase in just eight years.
So, these devices, usually worn on the body as accessories or implants, continuously track and analyze activity levels, vital statistics, and general health metrics. They serve two purposes: personal health tracking and out-of-hospital patient monitoring.
Implantable IoT devices healthcare professionals use to assist in the functioning of particular organs or tissues, observe physiological processes, or deliver medicines. They are placed inside the human body either temporarily or permanently, usually via surgical procedures.
Stationary medical devices traditionally used in hospitals and clinics are now also IoT-powered. They range from monitoring systems to sophisticated diagnostic machines and treatment equipment. They allow specialists to focus on treating the patient by delegating some of the tasks to connected medical devices.
Care is gradually moving from hospital settings to home environments, where people use different IoT-enabled medical equipment to manage their health from the comfort of their homes. These home-use devices are varied and can benefit not only patients with chronic conditions but also individuals to prevent diseases and make better lifestyle choices.
Remote patient monitoring (RPM) technology is one of the tools hospitals are increasingly turning to to improve outcomes and reduce costs of in-patient care. They use IoT-based applications in healthcare devices to monitor, report, and analyze patient health status outside of a traditional clinical setting.
RPM solutions become smarter and more affordable, and if you hire an experienced IoT developer, you can take advantage of this transformative tech. By the way, in our recent blog post, you can find all the benefits of remote patient monitoring solutions and how they help hospitals improve their bottom line.
The external environment of hospital areas can be smart, too. Powered by IoT technology, the systems controlling environmental parameters like air quality, temperature, and humidity can automatically adjust them for optimal conditions. It helps clinics maintain safety standards in critically vital areas like operating rooms and intensive care units and enhance patient well-being.
IoT applications in emergency response systems make them highly responsive and adaptable to critical situations due to real-time data collection and improved communication between systems. They alert staff, manage resources, and help coordinate care during life-threatening scenarios so that patients who require immediate attention get it in time. These smart-systems provide doctors and nurses with immediate updates so that they can react faster in emergency situations.
Moving to the digital landscape brings many benefits to the medical industry. But there are also some risks in IoT healthcare devices that hospitals should be aware of.
IoT devices in healthcare have reshaped every aspect of the industry, delivering truly positive results. Medical organizations around the globe are rapidly embracing IoT, recognizing the value and benefits it brings. Sure, there are challenges, but the positives are too compelling to ignore. Fewer hospital visits, more efficient care, and better decisions made faster, among others, encourage clinics to deploy IoT solutions actively.
As a healthcare software development company that specializes in IoMT development, we know medical solutions should be reliable, secure, and meet industry standards. With this in mind, we build high-quality IoT applications as per your requirements and integrate them smoothly into existing healthcare infrastructures without disrupting your business. Just contact us and let us know what you need.
What if your bank could complete in minutes what currently requires hours, without adding a…
Forecasting demand has never been more complex—or more critical. Traditional models, constrained by rigid statistical…
Did you know that hospitals generate around 50 petabytes of data each year, including clinical…